Abstract
Mobile applications make it easier than ever to edit images and share these images on the Internet. Even if this image manipulation is not a criminal offense in most cases, retouched images can have a number of negative effects.
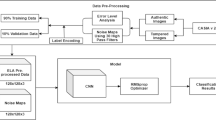
The goal of this work is to provide a solution for an automatic recognition of image retouching. For this, we adapt a well known convolutional neural network (CNN) from [5] to the domain of RGB images and create a data set to train it. Specifically, we process 1 000 images with nine different filters using Snapseed, an image editing app. Then, we use these 10 000 images in two different experiments to train the adapted CNN. The first experiment compares each single filter with the original images, while the second experiment tries to distinguish all ten classes at once.
Overall, the first experiment achieves an accuracy of over 99% for most classes, and the second experiments a total accuracy of roughly 88%. Finally, we analyze, why some of the classes have lower accuracies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Agung, N.F.A., Darma, G.: Opportunities and challenges of Instagram algorithm in improving competitive advantage. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 4(1), 743–747 (2019)
Amerini, I., Ballan, L., Caldelli, R., Del Bimbo, A., Del Tongo, L., Serra, G.: Copy-move forgery detection and localization by means of robust clustering with J-Linkage. Signal Process. Image Commun. 28(6), 659–669 (2013)
Amerini, I., Ballan, L., Caldelli, R., Del Bimbo, A., Serra, G.: A SIFT-based forensic method for copy-move attack detection and transformation recovery. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 6(3), 1099–1110 (2011)
Amerini, I., Uricchio, T., Ballan, L., Caldelli, R.: Localization of JPEG double compression through multi-domain convolutional neural networks. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1865–1871. IEEE (2017)
Bayar, B., Stamm, M.C.: A deep learning approach to universal image manipulation detection using a new convolutional layer. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, pp. 5–10 (2016)
Bayar, B., Stamm, M.C.: Design principles of convolutional neural networks for multimedia forensics. Electron. Imaging 2017(7), 77–86 (2017)
Bayar, B., Stamm, M.C.: Constrained convolutional neural networks: a new approach towards general purpose image manipulation detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 13(11), 2691–2706 (2018)
Böhme, R., Freiling, F.C., Gloe, T., Kirchner, M.: Multimedia forensics is not computer forensics. In: Geradts, Z.J.M.H., Franke, K.Y., Veenman, C.J. (eds.) IWCF 2009. LNCS, vol. 5718, pp. 90–103. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-03521-0_9
Chen, J., Kang, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Z.J.: Median filtering forensics based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(11), 1849–1853 (2015)
Cox, I., Miller, M., Bloom, J., Fridrich, J., Kalker, T.: Digital Watermarking and Steganography. Morgan kaufmann (2007)
Cozzolino, D., Poggi, G., Verdoliva, L.: Splicebuster: A new blind image splicing detector. In: 2015 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2015)
Cozzolino, D., Verdoliva, L.: Camera-based image forgery localization using convolutional neural networks. In: 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 1372–1376. IEEE (2018)
Dang-Nguyen, D.T., Pasquini, C., Conotter, V., Boato, G.: RAISE: a raw images dataset for digital image forensics. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference, pp. 219–224 (2015)
Ferrara, P., Bianchi, T., De Rosa, A., Piva, A.: Image forgery localization via fine-grained analysis of CFA artifacts. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(5), 1566–1577 (2012)
Kirchner, M., Böhme, R.: Hiding traces of resampling in digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 3(4), 582–592 (2008)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 60(6), 84–90 (2017)
Lukáš, J., Fridrich, J., Goljan, M.: Detecting digital image forgeries using sensor pattern noise. In: Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents VIII, vol. 6072, p. 60720Y. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2006)
Lup, K., Trub, L., Rosenthal, L.: Instagram# Instasad?: exploring associations among Instagram use, depressive symptoms, negative social comparison, and strangers followed. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 18(5), 247–252 (2015)
Marra, F., Gragnaniello, D., Verdoliva, L., Poggi, G.: A full-image full-resolution end-to-end-trainable CNN framework for image forgery detection. IEEE Access 8, 133488–133502 (2020)
Meena, K.B., Tyagi, V.: Image forgery detection: survey and future directions. In: Shukla, R.K., Agrawal, J., Sharma, S., Singh Tomer, G. (eds.) Data, Engineering and Applications, pp. 163–194. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6351-1_14
Pasquini, C., Amerini, I., Boato, G.: Media forensics on social media platforms: a survey. EURASIP J. Inf. Secur. 2021(1), 1–19 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13635-021-00117-2
Pasquini, C., Boato, G., Pérez-González, F.: Statistical detection of JPEG traces in digital images in uncompressed formats. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 12(12), 2890–2905 (2017)
Piva, A.: An overview on image forensics. International Scholarly Research Notices 2013 (2013)
Shashidhar, T., Ramesh, K.: Reviewing the effectivity factor in existing techniques of image forensics. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 7(6), 3558–3569 (2017)
Swaminathan, A., Wu, M., Liu, K.R.: Digital image forensics via intrinsic fingerprints. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 3(1), 101–117 (2008)
Lahousen, T., Linder, D., Gieler, T., Gieler, U.: Der Hautarzt 68(12), 973–979 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00105-017-4064-7
Verdoliva, L.: Media forensics and DeepFakes: an overview. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 14(5), 910–932 (2020)
Van der Walt, S., et al.: scikit-image: image processing in Python. PeerJ 2, e453 (2014)
Yang, P., Baracchi, D., Ni, R., Zhao, Y., Argenti, F., Piva, A.: A survey of deep learning-based source image forensics. J. Imaging 6(3), 9 (2020)
Yerushalmy, I., Hel-Or, H.: Digital image forgery detection based on lens and sensor aberration. Int. J. Comput. Vision 92(1), 71–91 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The second authors is supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) under grant no. I 4057-N31 (“Game Over Eva(sion)”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Aumayr, D., Schöttle, P. (2022). U Can’t (re)Touch This – A Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Image Retouching. In: Sclaroff, S., Distante, C., Leo, M., Farinella, G.M., Tombari, F. (eds) Image Analysis and Processing – ICIAP 2022. ICIAP 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13232. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06430-2_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06430-2_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-06429-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-06430-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)