Abstract
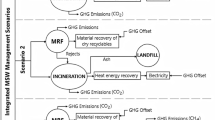
This study estimated the contribution of the polluter pays principle (PPP) on the reduction of environmental pollution and health risk for municipal solid waste (MSW). Data of MSW volume disposed (tonnes) in the landfill from 2011 to 2017 were obtained from the respective agency. The level of GHG emission (CH4, CO2), leachate production, heavy metals, on-methane organic compound (NMOC), and health risks were calculated using the mathematical equation for three PPPs implementation scenarios. The average volume of waste disposed in the landfill was 199,593.48 ± 16,094.14 tonnes/year. The volume has increased by 29.4%, from 14,912.80 ± 821.17 tonnes/month in 2011 to 19,300.47 ± 829.44 tonnes/month in 2017. Prediction on waste composition was made based on the average percentage provided by the National Solid Waste Management Department (NSWMD). Food waste dominates in household waste composition (57,472.94 ± 4634.30 tonnes/year) followed by institutional, commercial, and industrial waste composition (21935.32 ± 1768.75 tonnes/year). The emission of CH4 and CO2 in scenario 1 were 6058.96 tonnes/year and 151,473.88 tonnes/year, in scenario 2 were 5193.39 tonnes/year and 145,414.93 tonnes/year, and in scenario 3 were 4327.83 tonnes/year and 121,179.11 tonnes/year; respectively. The volume of leachate produced in scenario 1, scenario 2, and scenario 3 were 29,340.24 m3, 25,148.78 m3, and 20,957.32 m3, respectively. The total heavy metals production in leachate in scenario 1, scenario 2, and scenario 3 were 1.26 kg/year, 1.08 kg/year, and 0.901 kg/year, respectively. The total production of non-methane organic compounds (NMOCs) in scenario 1, scenario 2 and scenario 3 were 2.93E-01 m3, 2.52 E-01 m3, and 2.09E-01 m3, respectively. The implementation of PPP has the potential to reduce environmental pollution and health risk by reducing the total waste disposed in the landfill.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas MA, Wee ST (2014) Municipal solid waste management in Malaysia: an insight towards sustainability. In: 4th International conference on human habitat & environment. https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.1774.6246.
Abd Ghafar SW (2017) Food waste in Malaysia: trends, current practices and key challenges. FFTC Agricultural Policy Articles (Food security and safety). http://ap.fftc.agnet.org/ap_db.php?id=774&print=1
Abd Manaf L, Abu Samah MA, MohdZukki NI (2009) Municipal solid waste management in Malaysia: practices and challenges. Waste Manag 29:2902–2906
Abdul Jalil M (2010) Sustainable development in Malaysia: a case study on household waste management. J Sustain Dev 3(3):91–102
Abushammala MFM, Basri NEA, Kadhum AAH, Basri H, El-Shafie AH, Sharifah Mastura SA (2014) Evaluation of methane generation rate and potential from selected landfills in Malaysia. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1107/s13762-013-0197-0
Agamuthu P, Fauziah SH (2010) Heavy metal pollution in landfill environment, (June). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2010.5516886
Azmi MYJ, Junidah R, Siti Mariam A, Safiah MY, Fatimah S, Norimah AK, Poh BK, Kandiah M, Zalilah MS, Wan Abdul Manan W, Siti Haslinda MD, Tahir A (2009) Body Mass Index (BMI) of Adults: findings of the Malaysian Adult Nutrition Survey (MANS). Malays J Nutr 15(2):97–119, Epub 2009 Sep 15
Bashir MJK, Jun YZ, Yi LJ, Abushammala MFM, Abu Amr SS, Pratt LM (2020) Appraisal of student’s awareness and practices on waste management and recycling in the Malaysian University’s student hostel area. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-00988-6.
Boateng TK, Opoku F, Akoto O (2019) Heavy metal contamination assessment of groundwater quality: a case study of Oti landfill site, Kumasi. Appl Water Sci 9:33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0915-y
Chadar SN, Chadar K (2017) Solid waste pollution: a hazard to environment. Rec Adv Petrochem Sci 2(3):1–3
Chalvatzaki E, Lazaridis M (2010) Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from landfills: application to the akrotiri landfill site (Chania, Greece). Glob NEST J 12(1):108–116
Department of Statistics Malaysia (2019) Demographic Statistics First Quarter 2019, Malaysia. Retrieved from https://www.dosm.gov.my
EA-SWMC (2009) EU-Perak solid waste management planning seminar (P-SWMP). In: EU-Asia sustainable waste management Cycle. Impiana Casuarina Hotel, Ipoh
Emenike CU, Fauziah SH, Agamuthu P (2011) Characterization of active landfill leachate and associated impacts on edible fish (OrechromisMossambicus). Malays J Sci 30(2):99–104
Environmental Quality (Control of Pollution from Solid Waste Transfer Station and Landfill) Regulations (2009)
Fauziah SH, Agamuthu P (2012) Trends in sustainable landfilling in Malaysia, a develo** country. Waste Manag Res 30(7):656–663. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X12437564
Fauziah SH, Emenike CU, Agamuthu P (2013) Leachate risk and identification of accumulated heavy metals in Pangasius sutchi. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X13492840
Feuyit G, Nzali S, Lambi JN, Laminsi S (2019) Air quality and human health risk assessment in the residential areas at the proximity of the Nkolfoulou landfill in Yaoundé Metropolis, Cameroon. J Chem 2019, Article ID 3021894. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3021894
Habil I, Bilitewski B (2008) Pay-as-you-throw – a tool for urban waste management. Waste Manag 28(12):2759
Hoornweg D, Bhada-Tata P (2012) What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management. Urban development series;knowledge papers no. 15. World Bank, Washington, DC. © World Bank. http://www.openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/17388 License: CC BY 3.0 IGO
IPCC (2006) IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories § (2006). Retrieved from http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol5.html
Iqbal A, Tabinda AB, Yasar A (2019) Environmental risk assessment of a young landfill site and its vicinity for possible human exposure. Hum Ecol Risk Assess An Int J. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1706152
Ishigaki T, Hirata O, Oda T, Wangyao K, Chiemchaisri C, Towprayoon S, Lee D-H, Yamada M, Tomonori Ishigaki, Osamu Hirata, Takefumi Oda, Komsilp Wangyao, Chart Chiemchaisri, SirintornthepTowprayoon, Dong-Hoon Lee and Masato Yamada (2011) Greenhouse gas emission from solid waste disposal sites in asia. In: Kumar S (ed) Integrated waste management – volume II, ISBN: 978-953-307-447-4, InTech, Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/integrated-waste-management-volumeii/greenhouse-gas-emission-from-solid-waste-disposal-sites-in-asia
Johari A, Ahmed SS, Hashim H, Alkali H, Ramli M (2012) Economic and environmental benefits of landfill gas from municipal solid waste in Malaysia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:2907–2912
Klang Municipal Council (KMC) (2018) Waste management. Retrieved from http://www.mpklang.gov.my/en/citizens/services/waste-management
Latake PT, Pawar P, Ranveer AC (2015) The greenhouse effect and its impacts on environment. Int J Innov Res Creat Technol 1(3):333–337
Lee S, Paik HS (2011) Korean household waste management and recycling behaviour. Build Environ 46:1159–1166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2010.12.005
Luppi B, Parisi F, Rajagopalan S (2012) The rise and fall of the polluter-pays principle in develo** countries. Int Rev Law Econ 32(1):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irle.2011.10.002
Macklin Y, Kibble A, Pollitt F (2011) Impact on health of emissions from landfill sites: Advice from the Health Protection Agency. Health Protection Agency 2011. ISBN: 978-0-85951-704-1. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/334356/RCE-18_for_website_with_security.pdf
Masron T, Yaakob U, MohdAyob N, Mokhtar AS (2012) Population and spatial distribution of urbanisation in Peninsular Malaysia 1957–2000. Malays J Soc Space 8(2):20–29
Ministry of Housing and Local Government (KPKT) (2015) Solid waste management lab 2015. Retrieved from http://www.kpkt.gov.my/resources/index/user_1/Attachments/hebahan_slider/slaid_dapatan_makmal.pdf
Morling S (2010) Nitrogen removal and heavy metals in leachate treatment using SBR technology. J Hazard Mater 174:679–686
Morlok J, Schoenberger H, Styles D, Galvez-Martos J-L, Zeschmar-Lahl B (2017) The impact of pay-as-you-throw schemes on municipal solid waste management: the exemplar case of the county of Aschaffenburg, Germany. Resources 6(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/resources6010008
Muda MA (2016) Carbon and nitrogen flow in Jeram sanitary landfill Selangor, Malaysia. Material Flow Analysis (MFA) as an assessment tool. Lambert Academic Publishing
National Solid Waste Management Department (NSWMD) (2013) Survey on solid waste composition, characteristics & existing practice of solid waste recycling in Malaysia. Putrajaya. Retrieved from http://jpspn.kpkt.gov.my/resources/index/user_1/Sumber_Rujukan/kajian/Final_Report_REVz.pdf
Pazoki M, Delarestaghi RM, Rezvanian MR, Ghasemzade R, Dalaei P (2015) Gas production potential in the landfill of Tehran by landfill methane outreach program. Jundishapur J Health Sci 7(4). https://doi.org/10.17795/jjhs-29679
Prabpai S, Charerntanyarak L, Siri B, Moore MR, Noller BN (2009) Effects of residues from municipal solid waste landfill on corn yield and heavy metal content. Waste Manag 29:2316–2320
Shekdar AV (2009) Sustainable solid waste management: an integrated approach for Asian countries. Waste Manag 29:1438–1448
Skumatz LA (2008) Pay as you throw in the US: implementation, impacts, and experience. Waste Manag 28(12):2778–2785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.03.033
Skumatz LA, Freeman DJ (2006) Pay as you throw (PAYT) in the US: 2006 update and analyses. Prepared for US EPA and SERA, by Skumatz Economic Research Associates, Superior CO, December 2006. Retrieved from https://cswd.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/PAYTReportSera06.pdf
Srivastara S, Singhvi R (2015) Impact of solid waste on health and the environment. Int J Sci Res 4(9):1770–1773
US EPA (1997) Emission Factor Documentation for AP-42, Section 2-4, Municipal Solid Waste Landfills, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Research Triangle Park, NC. August.
US EPA (2005) Guidance for evaluating landfill gas emissions from closed or abandoned facilities. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development Washington, DC 20460
US EPA (2009) Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment). Office of Superfund Remediation and Technology Innovation Environmental Protection Agency Washington, D.C.
Vasanthi P, Kaliappan S, Srinivasaraghavan R (2008) Impact of poor solid waste management on ground water. Environ Monit Assess 143:227–238
WHO/IPCS (1994) Assessing Human Health Risks of Chemicals: Derivation of Guidance Values for Healthbased Exposure Limits. Environmental Health Criteria 170. Gene- va: WHO. http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc170.htm
WHO (1999) The World Health Report 1999. Basic Health Indicators, Annex Table 1. http://wwwnt.who.int/whosis/basic/basicqueryprocess.cfm
Yucekaya A (2014) Landfill gas to energy in Turkey: current and future. IBU J Sci Technol 2(1):55–64
Zhang DQ, Tan SK, Gersberg RM (2010) Municipal solid waste management in China: status, problems and challenges. J Environ Manag 91:1623–1633
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Klang Municipal Council (KMC) for providing the required data for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Irozi, M.F.I., Ismail, S.N.S., Praveena, S.M., Shamsuddin, A.S., Dom, N.C. (2022). The Contribution of Polluter Pays Principle (PPP) Approach on Environmental Pollution Reduction and Health Risk for Municipal Solid Waste (MSW). In: Samah, M.A.A., Kamarudin, M.K.A. (eds) Environmental Management and Sustainable Development. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93932-8_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93932-8_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93931-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93932-8
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)