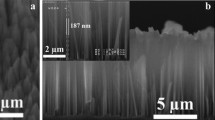
Abstract
One-dimensional (1D) nanostructures, including nanorods, nanowiskers, nanowires, nanotubes and nanobelts, have been receiving a great deal of research attention from industry and academia in recent years. Due to their special and outstanding many characteristics, such as effective light–trap** ability, bandgap tunability, efficient charge carrier collection, high carrier mobility, large surface-to-volume ratio and excellent thermal conductivity, such nanostructures play a very important role in the manufacture of high-performance devices with novel functionalities. To date, a number of materials, such as TiO2 (titanium-oxide), ZnO2 (zinc-oxide), Si (silicon), C (carbon), Ga2O3 (gallium oxide) and SnO2 (tin-oxide), have been employed in the production of one-dimensional 1D structures for the fabrication of high-performance electronic and opto-electronic devices. Among them, silicon (Si) is particularly attractive material for a wide range of opto-electronic device application owing to its highly developed technology and outstanding features such as high thermal conductivity, facile do** control, hardness and excellent optical and electrical properties. In this chapter, although we discuss the recent advances in optoelectronic applications of 1D Si nano-/microstructures, it focuses mainly on our own recent studies based on the synthesis of ordered and disordered Si-nanowires/micropillars and their applications in photodetection and harvesting solar energy. In particular, a special focus will be given on the fabrication of Si nano-/microstructures based solar cells with transferred 1D nano-/microstructures from Si-wafer to glass substrates via using a fracture-transfer printing technique, which have demonstrated the possibility of the fabrication of low-cost, transparent, flexible and high-efficient next generation 1D Si nano-/microstructures based next generation opto-electronic devices.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Zhai, L. Li, Y. Ma, M. Liao, X. Wang, X. Fang, J. Yao, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, One-dimensional inorganic nanostructures: synthesis, field-emission and photodetection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40(5), 2986–3004 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00126K
X. Xu, X. Fang, T. Zhai, H. Zeng, B. Liu, X. Hu, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Tube-in-Tube TiO2 nanotubes with porous walls: fabrication, formation mechanism, and photocatalytic properties. Small 7(4), 445–449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201001849
C. Bartolo-Perez, W. Qarony, S. Ghandiparsi, A.S. Mayet, A. Ahamed, H. Cansizoglu, Y. Gao, E. Ponizovskaya Devine, T. Yamada, A.F. Elrefaie, S.-Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, Maximizing absorption in photon-trap** ultrafast silicon photodetectors. Adv. Photon. Res. 2(6), 2000190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adpr.202000190
Y. Gao, H. Cansizoglu, K.G. Polat, S. Ghandiparsi, A. Kaya, H. Mamtaz, A. Mayet, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, T. Yamada, E.P. Devine, A. Elrefaie, S.-Y. Wang, M. Islam, Photon-trap** microstructures enable high-speed high-efficiency silicon photodiodes. Nat. Photonics 11, 301–308 (2017)
S. Ghandiparsi, A.F. Elrefaie, A.S. Mayet, T. Landolsi, C. Bartolo-Perez, H. Cansizoglu, Y. Gao, H.H. Mamtaz, H.R. Golgir, E.P. Devine, T. Yamada, S.Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, High-speed high-efficiency photon-trap** broadband silicon pin photodiodes for short-reach optical interconnects in data centers. J. Lightwave Technol. 37(23), 5748–5755 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2019.2937906
A.S. Mayet, H. Cansizoglu, Y. Gao, S. Ghandiparsi, A. Kaya, C. Bartolo-Perez, B. AlHalaili, T. Yamada, E. Ponizovskaya Devine, A.F. Elrefaie, S.-Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, Surface passivation of silicon photonic devices with high surface-to-volume-ratio nanostructures. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 35(5), 1059–1065 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.35.001059
M. Liu, Y. Lu, Z.B. **e, G.M. Chow, Enhancing near-infrared solar cell response using upconverting transparentceramics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95(2), 800–803 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.09.018
Y. Luo, Y. Huang, G. Zang, X. Ren, X. Duan, S. Cai, Q. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Wang, Zero bias PIN photodetector based on gradient band distribution and do** gradient profile. Infrared Phys. Technol. 67, 391–396 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infrared.2014.09.008
O. Guller, E. Peksu, H. Karaagac, Synthesis of TiO2 nanorods for Schottky-Type UV-photodetectors and third-generation solar cells. physica status solidi (a) 215(4), 1700404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201700404
T. Gao, Q.H. Li, T.H. Wang, CdS nanobelts as photoconductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(17):173105 (2005).https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1915514
J.S. Jie, W.J. Zhang, Y. Jiang, X.M. Meng, Y.Q. Li, S.T. Lee, Photoconductive characteristics of single-crystal CdS nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 6(9), 1887–1892 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl060867g
H. Kind, H. Yan, B. Messer, M. Law, P. Yang, Nanowire ultraviolet photodetectors and optical switches. Adv. Mater. 14(2), 158–160 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(20020116)14:2%3c158::AID-ADMA158%3e3.0.CO;2-W
X. Liu, C. Li, S. Han, J. Han, C. Zhou, Synthesis and electronic transport studies of CdO nanoneedles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1950–1952 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1562331
M. Salvato, M. Scagliotti, M. De Crescenzi, M. Boscardin, C. Attanasio, G. Avallone, C. Cirillo, P. Prosposito, F. De Matteis, R. Messi, P. Castrucci, Time response in carbon nanotube/Si based photodetectors. Sens. Actuators, A 292, 71–76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.04.004
G. Shen, D. Chen, One-dimensional nanostructures for photodetectors. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 4, 20–31 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2174/187221010790712101
H. Wu, Y. Sun, D. Lin, R. Zhang, C. Zhang, W. Pan, GaN nanofibers based on electrospinning: facile synthesis, controlled assembly, precise do**, and application as high performance UV photodetector. Adv. Mater. 21(2), 227–231 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200800529
Y. Cui, Z. Zhong, D. Wang, W.U. Wang, C.M. Lieber, High performance silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett. 3(2), 149–152 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl025875l
K. Das, S. Mukherjee, S. Manna, S. Ray, A. Raychaudhuri, Single Si nanowire (diameter ≤ 100nm) based polarization sensitive near-infrared photodetector with ultra-high responsivity. Nanoscale 6 (2014).https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR03170A
H. Karaagac, M.S. Islam, Enhanced field ionization enabled by metal induced surface states on semiconductor nanotips. Adv. Func. Mater. 24(15), 2224–2232 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201303308
E. Peksu, O. Guller, M. Parlak, M.S. Islam, H. Karaagac, Towards the fabrication of third generation solar cells on amorphous, flexible and transparent substrates with well-ordered and disordered Si-nanowires/pillars. Physica E: Low-Dimen. Syst. Nanostructures 124, 114382 (2020).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2020.114382
E. Peksu, H. Karaagac, A third generation solar cell based on wet-chemically etched Si nanowires and sol-gel derived Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 774, 1117–1122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.012
Z. Zhang, R. Zou, L. Yu, J. Hu, One-dimensional silicon-based semiconductor nanomaterials: synthesis, structures, properties and applications. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Material Sciences 36, 148–173 (2011)
M.D. Henry, S. Walavalkar, A. Homyk, A. Scherer, Alumina etch masks for fabrication of high-aspect-ratio silicon micropillars and nanopillars. Nanotechnology 20(25), 255305 (2009).https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/25/255305
H.P. Yoon, Y.A. Yuwen, C.E. Kendrick, G.D. Barber, N.J. Podraza, J.M. Redwing, T.E. Mallouk, C.R. Wronski, T.S. Mayer, Enhanced conversion efficiencies for pillar array solar cells fabricated from crystalline silicon with short minority carrier diffusion lengths. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96(21), 213503 (2010).https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3432449
J. Kim, H. Han, Y.H. Kim, S.-H. Choi, J.-C. Kim, W. Lee, Au–Ag Bilayered metal mesh as a Si etching catalyst for controlled fabrication of Si nanowires. ACS Nano 5(4), 3222–3229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2003458
K. Peng, M. Zhang, A. Lu, N.-B. Wong, R. Zhang, S.-T. Lee, Ordered silicon nanowire arrays via nanosphere lithography and metal-induced etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(16), 163123 (2007).https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2724897
H.J. In, C.R. Field, P.E. Pehrsson, Periodically porous top electrodes on vertical nanowire arrays for highly sensitive gas detection. Nanotechnology 22(35), 355501 (2011).https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/35/355501
X.D. Bai, Z. Xu, S. Liu, E.G. Wang, Aligned 1D silicon nanostructure arrays by plasma etching. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 6(7), 804–808 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stam.2005.05.015
C.-H. Hsu, H.-C. Lo, C.-F. Chen, C.T. Wu, J.-S. Hwang, D. Das, J. Tsai, L.-C. Chen, K.-H. Chen, Generally applicable self-masked dry etching technique for nanotip array fabrication. Nano Lett. 4(3), 471–475 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl049925t
Y. Hung, S. Lee, B.J. Thibeault, L.A. Coldren, Fabrication of highly ordered silicon nanowire arrays with controllable sidewall profiles for achieving low-surface reflection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 17(4), 869–877 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2010.2068540
D. Baklykov, M. Andronic, O. Sorokina, S. Avdeev, K. Buzaverov, I. Ryzhikov, I. Rodionov, Self-controlled cleaving method for silicon DRIE process cross-section characterization. Micromachines 12(5) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050534
E. Baquedano, R.V. Martinez, J.M. Llorens, P.A. Postigo, Fabrication of silicon nanobelts and nanopillars by soft lithography for hydrophobic and hydrophilic photonic surfaces. Nanomaterials (Basel) 7(5), 109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7050109
H. Berthet, J. Jundt, J. Durivault, B. Mercier, D. Angelescu, Time-of-flight thermal flowrate sensor for lab-on-chip applications. Lab. Chip 11(2), 215–223 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0LC00229A
B. Saadany, M. Malak, M. Kubota, F. Marty, Y. Mita, D. Khalil, T. Bourouina, Free-space tunable and drop optical filters using vertical bragg mirrors on silicon. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 12(6), 1480–1488 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2006.884082
M. Sasaki, Silicon etching for multiple-height microstructures, in J. Yan (ed.) Micro and Nano Fabrication Technology. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 1–22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6588-0_29-1
R. Abdolvand, F. Ayazi, An advanced reactive ion etching process for very high aspect-ratio sub-micron wide trenches in silicon. Sens. Actuators, A 144(1), 109–116 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2007.12.026
W.J. Park, J.H. Kim, S.M. Cho, S.G. Yoon, S.J. Suh, D.H. Yoon, High aspect ratio via etching conditions for deep trench of silicon. Surf. Coat. Technol. 171(1), 290–295 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00288-3
A. Cutarelli, S. Ghio, J. Zasso, A. Speccher, G. Scarduelli, M. Roccuzzo, M. Crivellari, N. Maria Pugno, S. Casarosa, M. Boscardin, L. Conti, Vertically-aligned functionalized silicon micropillars for 3D culture of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cortical progenitors. Cells 9(1), 88 (2020)
D. Mikulik, A.C. Meng, R. Berrazouane, J. Stückelberger, P. Romero-Gomez, K. Tang, F.-J. Haug, Fontcuberta i Morral A, McIntyre PC, Surface defect passivation of silicon micropillars. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 5(20), 1800865 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201800865
V.K. Singh, J. Nagaraju, S. Avasthi, Radial junction silicon solar cells with micro-pillar array and planar electrode interface for improved photon management and carrier extraction. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19(3), 341–346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2018.12.016
R. Chaudhary, Comparison between silicon nanopillars prepared by Bosch process and metal assisted chemical etching. Protocols Reports Paper 52, 1–8 (2018)
A. Oates, F.J. Cabrera-España, A. Agrawal, H.S. Reehal, Fabrication and characterisation of Si micropillar PV structures. Mater. Res. Innov. 18(7), 500–504 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1179/1433075X14Y.0000000244
M.Y. Efremov, E.A. Olson, M. Zhang, L.H. Allen, Glass transition of thin films of poly (2-vinyl pyridine) and poly (methyl methacrylate): nanocalorimetry measurements. Thermochim. Acta 403, 37–41 (2003)
V.J. Logeeswaran, J. Oh, A.P. Nayak, A.M. Katzenmeyer, K.H. Gilchrist, S. Grego, N.P. Kobayashi, S.Y. Wang, A.A. Talin, N.K. Dhar, M.S. Islam, A Perspective on nanowire photodetectors: current status, future challenges, and opportunities. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 17(4), 1002–1032 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2010.2093508
R. Elbersen, W. Vijselaar, R.M. Tiggelaar, H. Gardeniers, J. Huskens, Fabrication and do** methods for silicon nano- and micropillar arrays for solar-cell applications: a review. Adv. Mater. 27(43), 6781–6796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502632
H. Han, Z. Huang, W. Lee, Metal-assisted chemical etching of silicon and nanotechnology applications. Nano Today 9(3), 271–304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2014.04.013
K.E. Bean, Anisotropic etching of silicon. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 25(10), 1185–1193 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1109/T-ED.1978.19250
X. Li, Metal assisted chemical etching for high aspect ratio nanostructures: a review of characteristics and applications in photovoltaics. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 16(2), 71–81 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2011.11.002
R. Bhujel, U. Rizal, A. Agarwal, B.S. Swain, B.P. Swain, Synthesis and characterization of silicon nanowires by electroless etching. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27(6), 2655–2660 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3179-z
S.-S. Yoon, D.-Y. Khang, Stretchable, Bifacial Si-organic hybrid solar cells by vertical array of SI micropillars embedded into elastomeric substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11(3), 3290–3298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b17826
H. Lin, F. Wu, P. Gao, W. Shen, Shape-controlled silicon microwire arrays from Au–Ag-catalyzed metal-assisted chemical etching for radial junction solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2(8), 5871–5876 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b01006
Y. Qian, D.J. Magginetti, S. Jeon, Y. Yoon, T.L. Olsen, M. Wang, J.M. Gerton, H.P. Yoon, Heterogeneous optoelectronic characteristics of Si micropillar arrays fabricated by metal-assisted chemical etching. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 16349 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73445-x
G. Baytemir, F. Es, R. Turan, Comparison of influence of gold contamination on the performances of planar and three dimensional c-Si solar cells. Renew. Energy 142, 393–399 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.04.081
G. Baytemir, E.H. Ciftpinar, R. Turan, Enhanced metal assisted etching method for high aspect ratio microstructures: applications in silicon micropillar array solar cells. Sol. Energy 194, 148–155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.10.033
H, Karaagac, A hybrid solar cell based on silicon nanowire and organic thin film. physica status solidi (a) 211(11):2503–2508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201431320
H. Karaagac, M. Parlak, M.S. Islam, Synthesis of Si nanowires by electroless etching technique and their integration into I–III–VI2 thin films for solar cells. MRS Proc. 1408, 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.40
H. Karaagac, M. Parlak, E. Yengel, M.S. Islam, Heterojunction solar cells with integrated Si and ZnO nanowires and a chalcopyrite thin film. Mater. Chem. Phys. 140(1), 382–390 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.03.053
Y. Li, Q. Chen, D. He, J. Li, Radial junction Si micro/nano-wire array photovoltaics: Recent progress from theoretical investigation to experimental realization. Nano Energy 7, 10–24 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.04.015
B. Pal, K.J. Sarkar, P. Banerji, Fabrication and studies on Si/InP core-shell nanowire based solar cell using etched Si nanowire arrays. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 204, 110217 (2020).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2019.110217
K. Lee, I. Hwang, N. Kim, D. Choi, H.-D. Um, S. Kim, K. Seo, 17.6%-Efficient radial junction solar cells using silicon nano/micro hybrid structures. Nanoscale 8(30), 14473–14479 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR04611H
A. Smyrnakis, P. Dimitrakis, P. Normand, E. Gogolides, Fabrication of axial p-n junction silicon nanopillar devices and application in photovoltaics. Microelectron. Eng. 174, 74–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2017.02.011
I. Leontis, M.A. Botzakaki, S.N. Georga, A.G. Nassiopoulou, Study of Si nanowires produced by metal-assisted chemical etching as a light-trap** material in n-type c-Si solar cells. ACS Omega 3(9), 10898–10906 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01049
M. Seo, S. Yoon, H. Cho, S. Lee, K. Kim, B.D. Kong, M. Meyyappan, C. Baek, Solar cell using hourglass-shaped silicon nanowires for increased light-trap** path. IEEE J. Photovoltaics 10(2), 475–479 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOTOV.2020.2964329
P. Yadav, M. Patel, H. Kim, Y. Cho, H. Kim, J. Kim, J. Yi, D.-W. Kim, Routes for realizing high-performing Si solar cells by using periodic structures. Mater. Res. Bull. 94, 92–99 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.05.027
H.-P. Wang, D. Periyanagounder, A.-C. Li, J.-H. He, Fabrication of silicon hierarchical structures for solar cell applications. IEEE Access, 1–1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2885169
H.-S. Kim, D.B. Patel, H. Kim, M. Patel, K.R. Chauhan, W. Park, J. Kim, Electrical and optical properties of Si microwire solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 164, 7–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.01.046
L. Karmakar, D. Das, Single-step fabrication of single-junction c–Si nano-structured solar cells by optimization of plasma etching parameters. J. Alloys Compounds 847, 155352 (2020).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155352
M.D. Kumar, H. Kim, J. Kim, Periodically patterned Si pyramids for realizing high efficient solar cells by wet etching process. Sol. Energy 117, 180–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.04.034
M.Y. Yeh, P.H. Lei, S.H. Lin, C.D. Yang, Copper-Zinc-Tin-Sulphur thin film using spin-coating technology. Materials 9(7), 526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070526
L. Vj, A.M. Katzenmeyer, M.S. Islam, Harvesting and transferring vertical pillar arrays of single-crystal semiconductor devices to arbitrary substrates. IEEE T Electron Dev 57(8), 1856–1864 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2010.2051195
E. Peksu, M. Terlemezoglu, M. Parlak, H. Karaagac, Characterization of one-step deposited Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films derived from a single crystalline powder. Renew. Energy 143, 1133–1142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.05.076
E.C. Garnett, P. Yang, Silicon nanowire radial p−n junction solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(29), 9224–9225 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8032907
L. Tsakalakos, J. Balch, J. Fronheiser, B.A. Korevaar, O. Sulima, J. Rand, Silicon nanowire solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(23), 233117 (2007).https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2821113
F. Jiang, H. Shen, W. Wang, L. Zhang, Preparation and properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber and Cu2ZnSnS4/amorphous silicon thin-film solar cell. Appl. Phys. Express 4, 4101 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1143/APEX.4.074101
N. Song, M. Young, F. Liu, P. Erslev, S. Wilson, S.P. Harvey, G. Teeter, Y. Huang, X. Hao, M.A. Green, Epitaxial Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film on Si (111) 4° substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106(25), 252102 (2015).https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4922992
L. Vj, J. Oh, A.P. Nayak, A.M. Katzenmeyer, K.H. Gilchrist, S. Grego, N.P. Kobayashi, S.Y. Wang, A.A. Talin, N.K. Dhar, M.S. Islam, A perspective on nanowire photodetectors: current status, future challenges, and opportunities. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 17(4), 1002–1032 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2010.2093508
V.J. Logeeswaran, A. Sarkar, M.S. Islam, N.P. Kobayashi, J. Straznicky, X. Li, W. Wu, S. Mathai, M.R.T. Tan, S.-Y. Wang, R.S. Williams, A 14-ps full width at half maximum high-speed photoconductor fabricated with intersecting InP nanowires on an amorphous surface. Appl. Phys. A 91(1), 1–5 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4394-x
K. Zang, X. Jiang, Y. Huo, X. Ding, M. Morea, X. Chen, C.-Y. Lu, J. Ma, M. Zhou, Z. **. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 628 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00733-y
H. Cansizoglu, C. Bartolo-Perez, Y. Gao, E. Ponizovskaya Devine, S. Ghandiparsi, K.G. Polat, H.H. Mamtaz, T. Yamada, A.F. Elrefaie, S.-Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, Surface-illuminated photon-trap** high-speed Ge-on-Si photodiodes with improved efficiency up to 1700 nm. Photon Res. 6(7), 734–742 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/PRJ.6.000734
C. Bartolo-Perez, S. Chandiparsi, A.S. Mayet, H. Cansizoglu, Y. Gao, W. Qarony, A. AhAmed, S.-Y. Wang, S.R. Cherry, M. Saif Islam, G. Ariño-Estrada, Avalanche photodetectors with photon trap** structures for biomedical imaging applications. Opt. Express 29(12), 19024–19033 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.421857
H. Cansizoglu, A.S. Mayet, S. Ghandiparsi, Y. Gao, C. Bartolo-Perez, H.H. Mamtaz, E.P. Devine, T. Yamada, A.F. Elrefaie, S.Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, Dramatically enhanced efficiency in ultra-fast silicon MSM photodiodes via light trap** structures. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 31(20), 1619–1622 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2019.2939541
S. Ghandiparsi, A.F. Elrefaie, H. Cansizoglu, Y. Gao, C. Bartolo-Perez, H.H. Mamtaz, A. Mayet, T. Yamada, E.P. Devine, S.-Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, High-speed high-efficiency broadband silicon photodiodes for short-reach optical interconnects in data centers, in Optical Fiber Communication Conference, San Diego, California, 2018/03/11 2018. OSA Technical Digest (online). Optical Society of America, p W1I.7. https://doi.org/10.1364/OFC.2018.W1I.7
H. Cansizoglu, E.P. Devine, Y. Gao, S. Ghandiparsi, T. Yamada, A.F. Elrefaie, S. Wang, M.S. Islam, A New Paradigm in high-speed and high-efficiency silicon photodiodes for communication—part i: enhancing photon-material interactions via low-dimensional structures. IEEE T Electron Dev. 65(2), 372–381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2017.2779145
H. Cansizoglu, A.F. Elrefaie, C. Bartolo-Perez, T. Yamada, Y. Gao, A.S. Mayet, M.F. Cansizoglu, E.P. Devine, S.Y. Wang, M.S. Islam, A New paradigm in high-speed and high-efficiency silicon photodiodes for communication—part II: device and vlsi integration challenges for low-dimensional structures. IEEE T Electron Dev. 65(2), 382–391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2017.2779500
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Karaağaç, H., Peksu, E., Alhalaili, B., Islam, M.S. (2022). One-Dimensional Silicon Nano-/microstructures Based Opto-Electronic Devices. In: Ünlü, H., Horing, N.J.M. (eds) Progress in Nanoscale and Low-Dimensional Materials and Devices. Topics in Applied Physics, vol 144. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93460-6_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93460-6_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-93459-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-93460-6
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)