Abstract
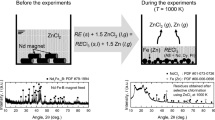
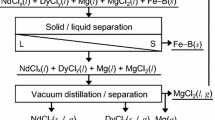
The selective recovery of rare earth elements from Nd-Fe-B magnets through a novel selective chlorination process using zinc chloride was investigated. A Nd-Fe-B magnet powder and zinc chloride mixture in an alumina crucible was positioned in a gas-tight quartz tube. This quartz tube was placed in an electric furnace preheated to 1000 K for 1.5 h for the reactions. After the experiments, a mixture of metallic iron and neodymium chloride was produced owing to the selective chlorination of rare earth elements in the magnet powder. In addition, the chlorination efficiencies of neodymium, dysprosium, and praseodymium were 96.5%, 57.2%, and 97.6%, respectively, under certain conditions. Therefore, it was demonstrated that the novel selective chlorination using zinc chloride developed in this study is feasible for the efficient recycling of Nd-Fe-B magnets.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haider SK, Lee J-Y, Kim D, Kang YS (2020) Eco-friendly facile three-step recycling method of (Nd-RE)2Fe14B magnet sludge and enhancement of (BH)max by ball milling in ethanol. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 8:8156–8163
Takeda O, Okabe TH (2014) Current status on resource and recycling technology for rare earths. Metall Mater Trans E 1:160–173
Akahori T, Miyamoto Y, Saeki T, Okamoto M, Okabe TH (2017) Optimum conditions for extracting rare earth metals from waste magnets by using molten magnesium. J Alloys Compd 703:337–343
Okabe TH, Takeda O, Fukuda K, Umetsu Y (2003) Direct extraction and recovery of neodymium metal from magnet scrap. Mater Trans 44:798–801
Takeda O, Okabe TH, Umetsu Y (2006) Recovery of neodymium from a mixture of magnet scrap and other scrap. J Alloys Compd 408–412:387–390
Kobayashi S, Kobayashi K, Nohira T, Hagiwara R, Oishi T, Konishi H (2011) Electrochemical formation of Nd-Ni alloys in molten LiF-CaF2-NdF3. J Electrochem Soc 158:E142–E146
Saito T, Sato H, Ozawa S, Yu J, Motegi T (2003) The extraction of Nd from waste Nd-Fe-B alloys by the glass slag method. J Alloys Compd 353:189–193
Shirayama S, Okabe TH (2018) Selective extraction and recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap by utilizing molten MgCl2. Metall Mater Trans B 49:1067–1077
Uda T (2002) Recovery of rare earths from magnet sludge by FeCl2. Mater Trans 43:55–62
Hua Z, Wang J, Wang L, Zhao Z, Li X, **ao Y, Yang Y (2014) Selective extraction of rare earth elements from NdFeB scrap by molten chlorides. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 2:2536–2543
Lim K-H, Choi C, Moon G, Lee T-H, Kang J (2021) Selective Chlorination of Rare Earth Elements from a Nd-Fe-B Magnet Using Zinc Chloride. J Sustain Metall 7:794–805
Barin I (1995) Thermochemical data of pure substances. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim
Hatada N (2014) Chesta: Software for Creating Chemical Potential Diagram, version 3.2.6.9, http://www.aqua.mtl.kyoto-u.ac.jp/wordpress/chestaEng.html
Windholz M, Budavari S, Blumetti RF, Otterbein E.S (1983) The Merch Index – An encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals, 3rd ed. Rahway N.J. USA, pp. 9932
Jacob KT, Dixit A, Rajput A (2016) Stability field diagrams for Ln-O-Cl systems. Bull Mater Sci 39:603–611
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, the Korean Ministry of Industry (Project No. 20000970, 21-9805)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lim, KH., Choi, C., Moon, G., Lee, TH., Kang, J. (2022). Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Nd-Fe-B Magnet Through Selective Chlorination Using Zinc Chloride. In: Lazou, A., Daehn, K., Fleuriault, C., Gökelma, M., Olivetti, E., Meskers, C. (eds) REWAS 2022: Develo** Tomorrow’s Technical Cycles (Volume I). The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92563-5_77
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92563-5_77
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-92562-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-92563-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)