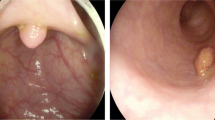
Abstract
In this chapter, all groups have used Residual Network (ResNet) (He et al. 2016) as part of different architectures with the purpose of solving the GIANA challenge. In some cases like RTC-ATC group ResNet-50 was used as a layer in Faster Convolutional Neural Network (FCNN) in order to build an automated recognition system to detect the presence of polyps in colonoscopy images.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anas, E. M. A., Nouranian, S., Mahdavi, S. S., Spadinger, I., Morris, W. J., Salcudean, S. E., Mousavi, P., & Abolmaesumi, P. (2017). Clinical target-volume delineation in prostate brachytherapy using residual neural networks. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 365–373). Springer.
Chaurasia, A., & Culurciello, E. (2017). Linknet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Felzenszwalb, P. F., Girshick, R. B., McAllester, D., & Ramanan, D. (2009). Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 32(9), 1627–1645.
Gal, Y., & Ghahramani, Z. (2016). Dropout as a Bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-16).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 1026–1034).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 770–778).
Hoang Ngan Le, T., Zheng, Y., Zhu, C., Luu, K., & Savvides, M. (2016). Multiple scale faster-rcnn approach to driver’s cell-phone usage and hands on steering wheel detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (pp. 46–53).
Hochreiter, S. (1998). The vanishing gradient problem during learning recurrent neural nets and problem solutions. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, 6(02), 107–116.
Hu, J., Shen, L., & Sun, G. (2018). Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 7132–7141).
Iglovikov, V., Rakhlin, A., Kalinin, A., & Shvets, A. (2017). Pediatric bone age assessment using deep convolutional neural networks. ar**v preprint ar**v:1712.05053.
Jiang, H., & Learned-Miller, E. (2017). Face detection with the faster r-cnn. In 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017) (pp. 650–657). IEEE.
Lin, T., Dollár, P., Girshick, R. B., He, K., Hariharan, B., & Belongie, S. J. (2016). Feature pyramid networks for object detection. CoRR, ar**v:abs/1612.03144.
Liu, Y., Minh Nguyen, D., Deligiannis, N., Ding, W., & Munteanu, A. (2017). Hourglass-shapenetwork based semantic segmentation for high resolution aerial imagery. Remote Sensing (vol. 9(6), p. 522).
Milletari, F., Navab, N., & Ahmadi, S.-A. (2016). V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV) (pp. 565–571). IEEE.
Mishkin, D., Sergievskiy, N., & Matas, J. (2017). Systematic evaluation of convolution neural network advances on the imagenet. Computer Vision and Image Understanding.
Rakhlin, A., Davydow, A., & Nikolenko, S. (2018, June). Land cover classification from satellite imagery with u-net and lovász-softmax loss. In The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, June 2018.
Rakhlin, A., Tiulpin, A., Shvets, A. A., Kalinin, A. A., Iglovikov, V. I., & Nikolenko, S. (2019). Breast tumor cellularity assessment using deep neural networks. In The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Oct 2019.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., & Sun, J. (2015). Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 91–99).
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., & Brox, T. (2015). U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 234–241). Springer.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15, 1929–1958.
Tompson, J., Goroshin, R., Jain, A., LeCun, Y., & Bregler, C. (2015). Efficient object localization using convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 648–656).
“What My Deep Model Doesn’t Know....” http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/yarin/blog_3d801aa532c1ce.html.
**e, S., Girshick, R., Dollár, P., Tu, Z., & He, K. (2017). Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 1492–1500).
Zhang, H., Cisse, M., Dauphin, Y. N., & Lopez-Paz, D. (2017). mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. ar**v preprint ar**v:1710.09412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Amaya-Rodriguez, I. et al. (2021). ResNet. In: Bernal, J., Histace, A. (eds) Computer-Aided Analysis of Gastrointestinal Videos. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64340-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64340-9_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-64339-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-64340-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)