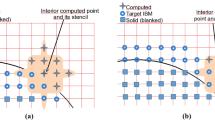
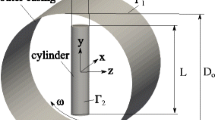
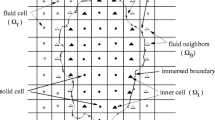
Abstract
In this article, we present an immersed boundary method (IBM) for the simulation of compressible flows encountered in aerodynamics. The immersed boundary methods allow the mesh not to conform to obstacles, whose influence is taken into account by modifying the governing equations locally (either by a source term within the equation or by imposing the flow variables or fluxes locally, similarly to a boundary condition).
A main feature of the approach we propose is that it relies on structured Cartesian grids in combination with a dedicated HPC Cartesian solver, taking advantage of not only their low memory and CPU time requirements but also the automation of the mesh generation and adaptation. Turbulent flow simulations are performed with Reynolds-Averaged Navier–Stokes equations or with Large-Eddy Simulation approach, in combination with a wall function at high Reynolds number, in order to mitigate the cell count resulting from the isotropic nature of Cartesian cells.
The objective of this paper is to demonstrate the capability of the present immersed boundary method on Cartesian adaptive grids to capture compressible flow features. Results obtained are in good agreement with classical body-fitted approaches but with a significant reduction of the time of the whole process, that is, a day for RANS simulations, including the mesh generation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoit, C., Péron, S., Landier, S.: Cassiopee: a CFD pre- and post-processing tool. Aerospace Sci. Technol. 45, 272–283 (2015)
Berger, M.J., Aftosmis, M.J.: Progress towards a Cartesian cut-cell method for viscous compressible flow. In: 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, pp. 2012–1301 (2012)
Berger, M.J., Aftosmis, M.J.: An ODE-based wall model for turbulent flow simulations. AIAA J., 1–15 (2017)
Beyer, R.P., LeVeque, R.J.: Analysis of a one-dimensional model for the immersed boundary method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(2), 332–364 (1992)
Boris, J.P., Grinstein, F.F., Oran, E.S., Kolbe, R.L.: New insights into large eddy simulation. Fluid Dyn. Res. 10(4-6), 199–228 (1992)
Brehm, C., Barad, M.F., Kiris, C.C.: Open rotor computational aeroacoustic analysis with an immersed boundary method. In: 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, p. 0815 (2016)
Capizzano, F.: Turbulent wall model for immersed boundary methods. AIAA J. 49(11), 2367–2381 (2011)
Chen, Z.L., Hickel, S., Devesa, A., Berland, J., Adams, N.A.: Wall modeling for implicit large-eddy simulation and immersed-interface methods. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 28(1), 1–21 (2014)
Coakley, T.J.: Implicit upwind methods for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations. AIAA J. 23(3), 374–380 (1985)
Coirier, W.J., Powell, K.G.: Solution-adaptive Cartesian cell approach for viscous and inviscid flows. AIAA J. 34(5), 938–945 (1996)
Dandois, J., Mary, I., Brion, V.: Large-eddy simulation of laminar transonic buffet. J. Fluid Mech. 850, 156–178 (2018)
Daude, F., Mary, I., Comte, P.: Self-adaptive Newton-based iteration strategy for the les of turbulent multi-scale flows. Comput. Fluid. 100, 278–290 (2014)
Edwards, J.R., Liou, M.-S.: Low-diffusion flux-splitting methods for flows at all speeds. AIAA J. 36(9), 1610–1617 (1998)
Fadlun, E.A., Verzicco, R., Orlandi, P., Mohd-Yusof, J.: Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 161(1), 35–60 (2000)
Garnier, E., Mossi, M., Sagaut, P., Comte, P., Deville, M.: On the use of shock-capturing schemes for large-eddy simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 153(2), 273–311 (1999)
Jameson, A., Yoon, S.: Lower-upper implicit schemes with multiple grids for the Euler equations. AIAA J. 25(7), 929–935 (1987)
Laurent, C., Mary, I., Gleize, V., Lerat, A., Arnal, D.: DNS database of a transitional separation bubble on a flat plate and application to RANS modeling validation. Comput. Fluids 61, 21–30 (2012)
Le Garrec, T., Mincu, D.C., Terracol, M., Casalino, D., Ribeiro, A.: Aeroacoustic prediction of the LEISA2 high-lift airfoil: Lattice Boltzmann method vs. Navier-Stokes Finite Volume method and experiments. In: Turbulence and Interactions Conference (2015)
Le Gouez, J.M.: A finite volume method for high Mach number flows on high-order grids. In: 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) (2018)
Mary, I.: Flexible Aerodynamic Solver Technology in an HPC environment. Maison de la Simulation Seminars (2016). http://www.maisondelasimulation.fr/seminar/data/201611_slides_1.ppt
Mary, I., Sagaut, P.: Large Eddy simulation of flow around an airfoil near stall. AIAA J. 40(6), 1139–1145 (2002)
Meakin, R.L.: Object X-Rays for cutting holes in composite overset structured grids. In: 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, pp. 2001–2537 (2001)
Mittal, R., Iaccarino, G.: Immersed boundary methods. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 37, 239–261 (2005)
Mittal, R., Dong, H., Bozkurttas, M., Najjar, F.M., Vargas, A., von Loebbecke, A.: A versatile sharp interface immersed boundary method for incompressible flows with complex boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 227(10), 4825–4852 (2008)
Mochel, L., Weiss, P.-E., Deck, S.: Zonal immersed boundary conditions: application to a high-Reynolds-number afterbody flow. AIAA J. 52(12), 2782–2794 (2014)
Musker, A.J.: Explicit expression for the smooth wall velocity distribution in a turbulent boundary layer. AIAA J. 17(6), 655–657 (1979)
Nakahashi, K.: Immersed boundary method for compressible Euler equations in the Building-Cube Method. AIAA Paper, pp. 2011–3386 (2011)
Péron, S., Benoit, C.: Automatic off-body overset adaptive Cartesian mesh method based on an octree approach. J. Comput. Phys. 232(1), 153–173 (2013)
Péron, S., Benoit, C., Renaud, T., Mary, I.: An immersed boundary method on Cartesian adaptive grids for the simulation of compressible flows around arbitrary geometries. Eng. Comput. 1–19 (2020)
Peskin, C.S.: Flow patterns around heart valves: a numerical method. J. Comput. Phys. 10(2), 252–271 (1972)
Peskin, C.S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 11, 479–517 (2002)
Poinot, M.: Five good reasons to use the hierarchical data format. Comput. Sci. Eng. 12(5), 84–90 (2010)
Renaud, T., Benoit, C., Péron, S., Mary, I., Alferez, N.: Validation of an immersed boundary method for compressible flows. In: AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum. AIAA Paper, pp. 2019–2179 (2019)
Roe, P.L.: Approximate Riemann solvers, parameter vectors, and difference schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 43(2), 357–372 (1981)
Rumsey, C.L., Wedan, B., Hauser, T., Poinot, M.: Recent updates to the CFD general notation system (CGNS). In: 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, vol. 10, pp. 6–2012 (2012)
Sethian, J.A.: Fast marching methods. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 199–235 (1999)
Spalart, P.R., Allmaras, S.R.: A one-equation turbulence model for aerodynamic flows. AIAA J. 94 (1992)
Terracol, M., Manoha, E.: Wall-resolved large eddy simulation of a high-lift airfoil: detailed flow analysis and noise generation study. In: 20th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. AIAA Paper, pp. 2014-3050 (2014)
Tseng, Y.-H., Ferziger, J.H.: A ghost-cell immersed boundary method for flow in complex geometry. J. Comput. Phys. 192(2), 593–623 (2003)
Vreman, A.W.: Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation of the Compressible Turbulent Mixing Layer. Universiteit Twente, Enschede (1995)
Zhu, W.J., Behrens, T., Shen, W.Z., Sørensen, J.N.: Hybrid immersed boundary method for airfoils with a trailing-edge flap. AIAA J. 51(1), 30–41 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Péron, S., Renaud, T., Benoit, C., Mary, I. (2021). An Immersed Boundary Method on Cartesian Adaptive Grids for the Simulation of Compressible Flows. In: Deiterding, R., Domingues, M.O., Schneider, K. (eds) Cartesian CFD Methods for Complex Applications. SEMA SIMAI Springer Series(), vol 3. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61761-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-61761-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-61760-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-61761-5
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)