Abstract
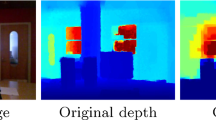
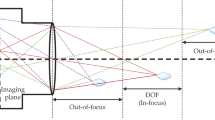
Defocus Blur Detection (DBD) aims to separate in-focus and out-of-focus regions from a single image pixel-wisely. This task has been paid much attention since bokeh effects are widely used in digital cameras and smartphone photography. However, identifying obscure homogeneous regions and borderline transitions in partially defocus images is still challenging. To solve these problems, we introduce depth information into DBD for the first time. When the camera parameters are fixed, we argue that the accuracy of DBD is highly related to scene depth. Hence, we consider the depth information as the approximate soft label of DBD and propose a joint learning framework inspired by knowledge distillation. In detail, we learn the defocus blur from ground truth and the depth distilled from a well-trained depth estimation network at the same time. Thus, the sharp region will provide a strong prior for depth estimation while the blur detection also gains benefits from the distilled depth. Besides, we propose a novel decoder in the fully convolutional network (FCN) as our network structure. In each level of the decoder, we design the Selective Reception Field Block (SRFB) for merging multi-scale features efficiently and reuse the side outputs as Supervision-guided Attention Block (SAB). Unlike previous methods, the proposed decoder builds reception field pyramids and emphasizes salient regions simply and efficiently. Experiments show that our approach outperforms 11 other state-of-the-art methods on two popular datasets. Our method also runs at over 30 fps on a single GPU, which is 2x faster than previous works. The code is available at: https://github.com/vinthony/depth-distillation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
We simplify this model by ignoring the influence of camera parameters since we can only obtain a 2D RGB image in the dataset.
References
Bae, S., Durand, F.: Defocus magnification. Comput. Graph. Forum 26, 571–579 (2007). Wiley Online Library
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFS. IEEE TPAMI 40(4), 834–848 (2017)
Chen, W., Fu, Z., Yang, D., Deng, J.: Single-image depth perception in the wild. In: NeurIPS, pp. 730–738 (2016)
Cun, X., Xu, F., Pun, C.M., Gao, H.: Depth-assisted full resolution network for single image-based view synthesis. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 39(2), 52–64 (2018)
Eigen, D., Puhrsch, C., Fergus, R.: Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. In: NeurIPS, pp. 2366–2374 (2014)
Godard, C., Mac Aodha, O., Brostow, G.J.: Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In: CVPR, pp. 270–279 (2017)
Godard, C., Mac Aodha, O., Firman, M., Brostow, G.J.: Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3828–3838 (2019)
Golestaneh, S.A., Karam, L.J.: Spatially-varying blur detection based on multiscale fused and sorted transform coefficients of gradient magnitudes. In: CVPR, March 2017
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., Dean, J.: Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. ar**v preprint ar**v:1503.02531 (2015)
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.H.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: CVPR, pp. 3203–3212 (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: CVPR, pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
Hu, X., Fu, C.W., Zhu, L., Heng, P.A.: Depth-attentional features for single-image rain removal. In: CVPR, pp. 8022–8031 (2019)
Hu, X., Zhu, L., Fu, C.W., Qin, J., Heng, P.A.: Direction-aware spatial context features for shadow detection. In: CVPR, pp. 7454–7462 (2018)
Jiang, P., Ling, H., Yu, J., Peng, J.: Salient region detection by UFO: uniqueness, focusness and objectness. In: CVPR, pp. 1976–1983 (2013)
Karaali, A., Jung, C.R.: Image retargeting based on spatially varying defocus blur map. In: ICIP, pp. 2693–2697. IEEE (2016)
Karaali, A., Jung, C.R.: Edge-based defocus blur estimation with adaptive scale selection. IEEE TIP 27(3), 1126–1137 (2017)
Krähenbühl, P., Koltun, V.: Efficient inference in fully connected CRFS with gaussian edge potentials. In: NeurIPS, pp. 109–117 (2011)
Lee, J., Lee, S., Cho, S., Lee, S.: Deep defocus map estimation using domain adaptation. In: CVPR, pp. 12222–12230 (2019)
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., Yang, J.: Selective kernel networks. In: CVPR, pp. 510–519 (2019)
Li, Z., et al.: Learning the depths of moving people by watching frozen people. In: CVPR, pp. 4521–4530 (2019)
Lin, T.Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: CVPR, pp. 2117–2125 (2017)
Liu, S., Huang, D., et al.: Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In: ECCV, pp. 385–400 (2018)
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., Darrell, T.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: CVPR, June 2015
Lopez-Paz, D., Bottou, L., Schölkopf, B., Vapnik, V.: Unifying distillation and privileged information. ar**v preprint ar**v:1511.03643 (2015)
Marc, L., Andrew, A., Nora, W.: Depth of field. http://graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs178/applets/dof.html
Odena, A., Dumoulin, V., Olah, C.: Distill 1(10), e3 (2016)
Park, J., Tai, Y.W., Cho, D., Kweon, I.S.: A unified approach of multi-scale deep and hand-crafted features for defocus estimation. In: CVPR cs.CV (2017)
Peng, H., Li, B., **ong, W., Hu, W., Ji, R.: RGBD salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8691, pp. 92–109. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_7
Qi, C.R., Liu, W., Wu, C., Su, H., Guibas, L.J.: Frustum pointnets for 3d object detection from RGB-D data. In: CVPR, pp. 918–927 (2018)
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, C., Gao, C., Dehghan, M., Jagersand, M.: Basnet: boundary-aware salient object detection. In: CVPR, June 2019
Qu, Y., Chen, Y., Huang, J., **e, Y.: Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In: CVPR, pp. 8160–8168 (2019)
Shi, J., Li, X., Jia, J.: Discriminative blur detection features. In: CVPR (2014)
Shi, J., Xu, L., Jia, J.: Just noticeable defocus blur detection and estimation. In: CVPR, pp. 657–665 (2015)
Tang, C., Zhu, X., Liu, X., Wang, L., Zomaya, A.: Defusionnet: defocus blur detection via recurrently fusing and refining multi-scale deep features. In: CVPR, pp. 2700–2709 (2019)
Wikipedia contributors: Depth of field – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (2019). Accessed 17 Oct 2019
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.Y., So Kweon, I.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: ECCV, pp. 3–19 (2018)
Wu, Z., Su, L., Huang, Q.: Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: CVPR, pp. 3907–3916 (2019)
**e, S., Girshick, R.B., Dollár, P., Tu, Z., He, K.: Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: CVPR (2017)
Xu, G., Quan, Y., Ji, H.: Estimating defocus blur via rank of local patches. In: CVPR, pp. 5371–5379 (2017)
Yi, X., Eramian, M.: LBP-based segmentation of defocus blur. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(4), 1626–1638 (2016)
Zhang, H., Patel, V.M.: Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: CVPR (2018)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: CVPR, pp. 2881–2890 (2017)
Zhao, W., Zhao, F., Wang, D., Lu, H.: Defocus blur detection via multi-stream bottom-top-bottom fully convolutional network. In: CVPR, pp. 3080–3088 (2018)
Zhao, W., Zhao, F., Wang, D., Lu, H.: Defocus blur detection via multi-stream bottom-top-bottom network. IEEE TPAMI 42, 1884–1897 (2019)
Zhao, W., Zheng, B., Lin, Q., Lu, H.: Enhancing diversity of defocus blur detectors via cross-ensemble network. In: CVPR, June 2019
Zheng, Q., Qiao, X., Cao, Y., Lau, R.W.: Distraction-aware shadow detection. In: CVPR, June 2019
Zhu, L., et al.: Bidirectional feature pyramid network with recurrent attention residual modules for shadow detection. In: ECCV (2018)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thanks Nan Chen for her helpful discussion. This work was partly supported by the University of Macau under Grants: MYRG2018-00035-FST and MYRG2019-00086-FST, and the Science and Technology Development Fund, Macau SAR (File no. 0034/2019/AMJ, 0019/2019/A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cun, X., Pun, CM. (2020). Defocus Blur Detection via Depth Distillation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, JM. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2020. ECCV 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12358. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58601-0_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58601-0_44
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-58600-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-58601-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)