Abstract
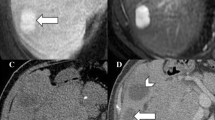
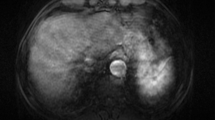
Chronic congestive hepatopathy predisposes to the development of benign regenerative nodules or focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) and malignant hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, characteristic parenchymal abnormalities within the congested liver at computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may result in an abnormal appearance of benign regenerative nodules or FNH. The American College of Radiology Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System criteria therefore no longer consider traditional enhancement characteristics applicable in patients with cardiac congestion and hepatic vascular disease. Imaging findings concerning for HCC in the congested liver include a heterogeneous or mosaic appearance of a mass, necrosis, internal lipid content, rapid growth, and venous tumor thrombus. Further evaluation of nodules with a hepatobiliary contrast agent or imaging follow-up is recommended to detect nodules with malignant potential in patients with congestive hepatopathy.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford RM, Book W, Spivey JR. Liver disease related to the heart. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2015;29(1):33–7.
Weisberg IS, Jacobson IM. Cardiovascular diseases and the liver. Clin Liver Dis. 2011;15(1):1–20.
Ahmed A. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Chronic Heart Failure Evaluation and Management guidelines: relevance to the geriatric practice. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(1):123–6.
Atz AM, et al. Survival data and predictors of functional outcome an average of 15 years after the Fontan procedure: the pediatric heart network Fontan cohort. Congenit Heart Dis. 2015;10(1):E30–42.
Gersony WM. Fontan operation after 3 decades: what we have learned. Circulation. 2008;117(1):13–5.
Pundi K, et al. Liver disease in patients after the Fontan operation. Am J Cardiol. 2016;117(3):456–60.
Asrani SK, Warnes CA, Kamath PS. Hepatocellular carcinoma after the Fontan procedure. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(18):1756–7.
Lautt WW. Hepatic circulation: physiology and pathophysiology. California, USA: San Rafael; 2009.
Lautt WW. Mechanism and role of intrinsic regulation of hepatic arterial blood flow: hepatic arterial buffer response. Am J Phys. 1985;249(5 Pt 1):G549–56.
Lautt WW. The hepatic artery: subservient to hepatic metabolism or guardian of normal hepatic clearance rates of humoral substances. Gen Pharmacol. 1977;8(2):73–8.
Eipel C, Abshagen K, Vollmar B. Regulation of hepatic blood flow: the hepatic arterial buffer response revisited. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(48):6046–57.
Lautt WW. Relationship between hepatic blood flow and overall metabolism: the hepatic arterial buffer response. Fed Proc. 1983;42(6):1662–6.
Giallourakis CC, Rosenberg PM, Friedman LS. The liver in heart failure. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6(4):947–67, viii-ix.
Asrani SK, et al. Congenital heart disease and the liver. Hepatology. 2012;56(3):1160–9.
Safran AP, Schaffner F. Chronic passive congestion of the liver in man. Electron microscopic study of cell atrophy and intralobular fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1967;50(3):447–63.
Myers RP, et al. Cardiac hepatopathy: clinical, hemodynamic, and histologic characteristics and correlations. Hepatology. 2003;37(2):393–400.
Wanless IR, Liu JJ, Butany J. Role of thrombosis in the pathogenesis of congestive hepatic fibrosis (cardiac cirrhosis). Hepatology. 1995;21(5):1232–7.
Simonetto DA, et al. Chronic passive venous congestion drives hepatic fibrogenesis via sinusoidal thrombosis and mechanical forces. Hepatology. 2015;61(2):648–59.
Driscoll DJ. Long-term results of the Fontan operation. Pediatr Cardiol. 2007;28(6):438–42.
Gewillig M, Goldberg DJ. Failure of the fontan circulation. Heart Fail Clin. 2014;10(1):105–16.
Dai DF, et al. Congestive hepatic fibrosis score: a novel histologic assessment of clinical severity. Mod Pathol. 2014;27(12):1552–8.
Arcidi JM Jr, Moore GW, Hutchins GM. Hepatic morphology in cardiac dysfunction: a clinicopathologic study of 1000 subjects at autopsy. Am J Pathol. 1981;104(2):159–66.
Sherlock S. The liver in heart failure; relation of anatomical, functional, and circulatory changes. Br Heart J. 1951;13(3):273–93.
Lefkowitch JH, Mendez L. Morphologic features of hepatic injury in cardiac disease and shock. J Hepatol. 1986;2(3):313–27.
Tanaka M, Wanless IR. Pathology of the liver in Budd-Chiari syndrome: portal vein thrombosis and the histogenesis of veno-centric cirrhosis, veno-portal cirrhosis, and large regenerative nodules. Hepatology. 1998;27(2):488–96.
Koehne de Gonzalez AK, Lefkowitch JH. Heart disease and the liver: pathologic evaluation. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2017;46(2):421–35.
Wells ML, et al. Benign nodules in post-Fontan livers can show imaging features considered diagnostic for hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42(11):2623–31.
Wells ML, et al. Imaging findings of congestive hepatopathy. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 2016;36(4):1024–37.
Gore RM, et al. Passive hepatic congestion: cross-sectional imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(1):71–5.
Yoneda N, et al. Benign hepatocellular nodules: hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging based on molecular background. Radiographics. 2016;36(7):2010–27.
Uchino K, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced liver injury mimicking metastatic tumor on images: a case report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013;43(10):1034–8.
Choi JH, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome mimicking metastatic colon cancer in the liver. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(4):2861–4.
Brancatelli G, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Radiology. 2001;219(1):61–8.
Choi BY, Nguyen MH. The diagnosis and management of benign hepatic tumors. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39(5):401–12.
Choi CS, Freeny PC. Triphasic helical CT of hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia: incidence of atypical findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170(2):391–5.
Zech CJ, et al. Diagnostic performance and description of morphological features of focal nodular hyperplasia in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver magnetic resonance imaging: results of a multicenter trial. Investig Radiol. 2008;43(7):504–11.
Grazioli L, et al. Hepatocellular adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging in differential diagnosis. Radiology. 2012;262(2):520–9.
Mohajer K, et al. Characterization of hepatic adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia with gadoxetic acid. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36(3):686–96.
Choi JY, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia or focal nodular hyperplasia-like lesions of the liver: a special emphasis on diagnosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(6):1004–9.
Radiology, A.C.o., American College of Radiology. Liver imaging reporting and data system in Version 2017.
Choi JY, Lee JM, Sirlin CB. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: part II. Extracellular agents, hepatobiliary agents, and ancillary imaging features. Radiology. 2014;273(1):30–50.
Hope TA, et al. Hepatobiliary agents and their role in LI-RADS. Abdom Imaging. 2015;40(3):613–25.
Suh YJ, et al. Differentiation of hepatic hyperintense lesions seen on gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(1):W44–52.
Elder RW, Parekh S, Book WM. More on hepatocellular carcinoma after the Fontan procedure. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(5):490.
Ewe SHT, Ju L. Hepatotocellular carcinoma—a rare complication post Fontan operation. Congenit Heart Dis. 2009;4(2):103–6.
Ghaferi AA, Hutchins GM. Progression of liver pathology in patients undergoing the Fontan procedure: chronic passive congestion, cardiac cirrhosis, hepatic adenoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129(6):1348–52.
Josephus Jitta D, et al. Three cases of hepatocellular carcinoma in Fontan patients: review of the literature and suggestions for hepatic screening. Int J Cardiol. 2016;206:21–6.
Rajoriya N, et al. A liver mass post-Fontan operation. QJM. 2014;107(7):571–2.
Rosenbaum J, et al. Cardiac cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in a 13-year-old treated with doxorubicin microbead transarterial chemoembolization. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012;48(3):E140–3.
Saliba T, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in two patients with cardiac cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22(7):889–91.
Yamada K, et al. Transarterial embolization for pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma with cardiac cirrhosis. Pediatr Int. 2015;57(4):766–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hilscher, M.B., Wells, M.L., Kamath, P.S. (2020). Liver Lesions in Congestive Hepatopathy. In: Roberts, L., Yang, J., Venkatesh, S. (eds) Evaluation and Management of Liver Masses. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46699-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46699-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-46698-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-46699-2
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)