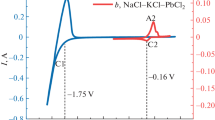
Abstract
In the NaCl–CaCl2 molten salt, a solid agglomerate of Fe2O3 particles is used as a raw material, and a graphite rod is used as an anode. At 800 °C, the composition and morphology of the product obtained by cyclic voltammetry and combined with constant cell pressure electrolysis at different times were analyzed by XRD and SEM to obtain the reduction mechanism of solid Fe2O3. (1) chemical formation of Ca2Fe2O5; (2) Ca2Fe2O5 was electrochemically reduced to metallic iron Ca2Fe2O5 → Fe3O4 → FeO → Fe, and finally electrolyzed for 5 h at a battery voltage of 2.5 V to prepare metal iron with an oxygen content of 1.29%. The electrolysis efficiency was 97.6%. The electrolysis product iron appears as interconnected micron-sized network particles. These studies provide theoretical support for the direct electroreduction of Fe2O3 particles to prepare metallic iron.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allanore A, Lavelaine H, Valentin G, Birat JP, Lapicque F (2007) Electrodeposition of metal iron from dissolved species in alkaline media. J Electrochem Soc 154:187–193
Allanore A, Lavelaine H, Valentin G et al (2010) Observation and modeling of the reduction of hematite particles to metal in alkaline solution by electrolysis. Electrochimica Acta 12:4007–4013
Zou XL, Gu SL, Lu XG et al (2015) Electroreduction of Iron(III) oxide pellets to iron in alkaline media: a typical shrinking-core reaction process. Metall Mater Trans B 3:1262–1274
Tang D, Yin H, **ao W et al (2013) Reduction mechanism and carbon content investigation for electrolytic production of iron from solid Fe2O3 in molten K2CO3–Na2CO3 using an inert anode. J Electroanalyt Chem 689:109–116
Li GM, Wang DH, Chen Z (2009) Direct reduction of solid Fe2O3 in molten CaCl2 by potentially green process. J Mater Sci Technol 25:767–771
Panigrahi M, Shibata E, Iizuka A, Nakamura T (2013) Production of Fe–Ti alloy from mixed ilmenite and titanium dioxide by direct electrochemical reduction in molten calcium chloride. Electrochim Acta 93(4):143–151
Wang YQ, Lin RS, Ye GA et al (2015) Progress of Ag/AgCl reference electrode in high-temperature chloride molten salt. Modern Chem Ind 35:21–25
Chen G, Gordo Z, Fray DJ (2004) Direct electrolytic preparation of chromium powder. Metall Mater Trans B 35:23–233
Vishnu DM, Sanil N, Shakila L et al (2013) A study of the reaction pathways during electrochemical reduction of dense Nb2O5 pellets in molten CaCl2 medium. Electrochim Acta 100:51–62
Hyslop DJ, Abdelkader AM, Cox A (2010) Electrochemical synthesis of a biomedically important Co–Cr alloy. Acta Mater 58:3124–3130
**ao W, ** X, Deng Y et al (2006) Electrochemically driven three-phase interlines into insulator compounds: electro reduction of solid SiO2 in molten CaCl2. ChemPhysChem 7(8):1750–1758
Song QS, Xu Q, Kang X et al (2010) Mechanistic insight of electrochemical reduction of Ta2O5 to tantalum in a eutectic CaCl2–NaCl molten salt. J Alloy Compd 490(1–2):241–246
Vishnu DS, Sanil N, Shakila L et al (2013) A study of the reaction pathways during electrochemical reduction of dense Nb2O5 pellets in molten CaCl2 medium. Electrochim Acta 100(7):51–62
Acknowledgements
The study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 51874141, 51674120) and the Hebei Province Graduate Innovation Program (Project No. 2017050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jia, L., Li, H., Cai, Z., Liang, J. (2020). Electrochemical Behavior of Fe2O3 in Electro-Deoxygenation in NaCl–CaCl2 Molten Salt System. In: TMS 2020 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36296-6_119
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36296-6_119
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-36295-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-36296-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)