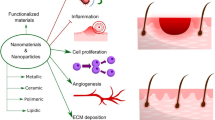
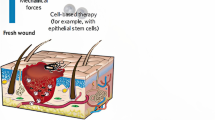
Abstract
The free radical nitric oxide (NO) is an important endogenous molecule that controls several biological processes, ranging from the promotion of vasodilatation to the acceleration of wound repair process and potent antimicrobial effects. NO is synthesized in human skin through the action of three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), with an important role in dermal vasodilatation, wound healing process, tissue repair, and skin defense against pathogens. During the past few years, interest has increased in the development of biologically friendly and versatile NO-releasing materials for biomedical applications, in particular, for topical/dermatological applications. Recently, the combination of NO donors/generations with nanomaterials has been emerging as a suitable strategy to carry and deliver therapeutic amounts of NO directly to the target site of application, including human skin, as discussed in this chapter. Thus, NO-releasing nanomaterials present great potential to treat skin diseases, highlighting skin infections caused by pathogens, because of the broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity of NO. In this sense, NO donors/generators have been incorporated in nanoparticles, leading to a sustained and localized delivery of NO. This chapter presents and discusses the recent advantages on the design and applications of NO-releasing nanomaterials for dermatological applications, mainly in promoting wound healing and in combating resistant pathogens.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AgNPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
- AuNPs:
-
Gold nanoparticles
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- GSNO:
-
S-Nitroso glutathione
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MSSA:
-
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
- nNOS:
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NO2−:
-
Nitrite
- NO3−:
-
Nitrate
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- O2:
-
Oxygen
- RONO2:
-
NO-releasing organic nitrates
- RSNO:
-
S-Nitroso molecules
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet radiation
- UVA:
-
Ultraviolet A radiation
References
Adler BL, Friedman AJ (2015) Nitric oxide therapy for dermatologic disease. Future Sci OA 1:FSO37
Aktan F (2004) iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci 75:639–653
Amadeu TP, Seabra AB, de Oliveira MG, Costa AMA (2007) S-Nitrosoglutathione containing hydrogel accelerates rat cutaneous wound repair. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 21:629–637
Barraud N, Kardak BG, Yepuri NR, Howlin RP, Webb JS, Faust SN, Kjelleberg S, Rice SA, Kelso MJ (2012) Cephalosporin-3′-diazeniumdiolates: targeted NO-donor prodrugs for dispersing bacterial biofilms. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:9057–9060
Basha M, Abou Samra MM, Awad GA, Mansy SS (2018) A potential antibacterial wound dressing of cefadroxil chitosan nanoparticles in situ gel: fabrication, in vitro optimization and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 544:129–140
Basnet P, Skalko-Basnet N (2013) Nanodelivery systems for improved topical antimicrobial therapy. Curr Pharm Des 19:7237–7243
Bozzuto G, Molinari A (2015) Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int J Nanomedicine 10:975–999
Brandwein M, Steinberg D, Meshner S (2016) Microbial biofilms and the human skin microbiome. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2:3
Cabrales P, Han G, Roche C, Nacharaju P, Friedman AJ, Friedman JM (2010) Sustained release nitric oxide from long-lived circulating nanoparticles. Free Radic Biol Med 49:530–538
Cals-Grierson MM, Ormerod AD (2004) Nitric oxide function in the skin. Biol Chem 10:179–193
Carpenter AW, Worley BV, Slomberg DL, Schoenfisch MH (2012) Dual action antimicrobials: nitric oxide release from quaternary ammonium-functionalized silica nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 13:3334–3342
Carter P, Narasimhan B, Wang Q (2019) Biocompatible nanoparticles and vesicular systems in transdermal drug delivery for various skin diseases. Int J Pharm 555:49–62
Chevalier Y, Bolzinger M (2015) Percutaneous penetration enhancers chemical methods in penetration enhancement, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin
Clebak K, Malone M (2018) Skin infections. Prim Care 45:433–454
Doyle MP, Hoekstra JW (1981) Oxidation of nitrogen oxides by bound dioxygen in hemoproteins. J Inorg Biochem 14:351–358
Duong HTT, Adnan NNM, Barraud N, Basuki JS, Kutty SK, Kenward J, Kumar N, Davis TP, Boyer C (2014) Functional gold nanoparticles for the storage and controlled release of nitric oxide: applications in biofilm dispersal and intracellular delivery. J Mater Chem B 2:5003–5011
Eileen O, Marika VD, Eoin S, Andrew H (2016) Novel targets in the glutamate and nitric oxide neurotransmitter systems for the treatment of depression. In: Systems neuroscience in depression. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 81–113
Engelman D, Fuller LC, Solomon AW (2016) Opportunities for integrated control of neglected tropical diseases that affect the skin. Trends Parasitol 32:843–854
Englander L, Friedman A (2010) Nitric oxide nanoparticle technology: a novel antimicrobial agent in the context of current treatment of skin and soft tissue infection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 3:45–50
Fang FC (1997) Mechanisms of nitric oxide-related antimicrobial activity. J Clin Invest 99:2818–2825
Fang CL, Aljuffali IA, Li YC, Fang JY (2014) Delivery and targeting of nanoparticles into hair follicles. Ther Deliv 5:991–1006
Feldmeier H, Heukelbach J (2009) Epidermal parasitic skin diseases: a neglected category of poverty-associated plagues. Bull World Health Organ 87:152–159
Friedman AJ, Han G, Navati MS, Chacko M, Gunther L, Alfieri A, Friedman JM (2008) Sustained release nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles: characterization of a novel delivery platform based on nitrite containing hydrogel/glass composites. Nitric Oxide 19:12–20
Georgii JL, Amadeu TP, Seabra AB, de Oliveira MG, Monte-Alto-Costa A (2011) Topical S-nitrosoglutathione-releasing hydrogel improves healing of rat ischaemic wounds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 5:612–619
Goyal R, Macri LK, Kaplan HM, Kohn J (2016) Nanoparticles and nanofibers for topical drug delivery. J Control Release 240:77–92
Grumezescu AM (2016) Nanobiomaterials in galenic formulations and cosmetics applications, 1st edn. William Andrew, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gutiérrez V, Seabra AB, Reguera RM et al (2016) New approaches from nanomedicine for treating leishmaniasis. Chem Soc Rev 45:152–168
Halpenny GM, Mascharak PK (2010) Emerging antimicrobial applications of nitric oxide (NO) and NO-releasing materials. Antiinfect Agents Med Chem 9:187–197
Hamblin MR, Avci P, Prow TW (2016) Nanoscience in dermatology, 1st edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Hasan S, Thomas N, Thierry B, Prestidge CA (2017) Biodegradable nitric oxide precursor-loaded micro- and nanoparticles for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Mater Chem B 5:1005–1014
Hetrick EM, Shin JH, Paul HS, Schoenfisch MH (2009) Anti-biofilm efficacy of nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 30:2782–2789
Heuer K, Hoffmanns MA, Demir E, Baldus S, Christine MV, Röhle M, Fuchs PC, Awakowicz P, Suschek CV, Opländer C (2015) The topical use of non-thermal dielectric barrier discharge (DBD): nitric oxide related effects on human skin. Nitric Oxide 44:52–60
Holliman G, Lowe D, Cohen H, Felton H, Felton S, Raj K (2017) Ultraviolet radiation-induced production of nitric oxide: a multi-cell and multi-donor analysis. Sci Rep 7:1–11
Huang Y, Yu F, Park YS, Wang J, Shin MC, Chung HS, Yang VC (2010) Co-administration of protein drugs with gold nanoparticles to enable percutaneous delivery. Biomaterials 31:9086–9091
Ignarro LJ (1999) Nitric oxide: a unique endogenous signaling molecule in vascular biology (Nobel lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed 38:1882–1892
Ignarro LJ (2000) Nitric oxide, biology and pathobiology, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Jankovic A, Ferreri C, Filipovic M, Ivanovic-Burmazovic I, Stancic A, Otasevic V, Korac A, Buzadzic B, Korac B (2016) Targeting the superoxide/nitric oxide ratio by L-arginine and SOD mimic in diabetic rat skin. Free Radic Res 50:S51–S63
Keefer LK (2011) Fifty years of diazeniumdiolate research: from laboratory curiosity to broad-spectrum biomedical advances. ACS Chem Biol 6:1147–1155
Kon K, Rai M (2016) Antibiotic resistance: mechanisms and new antimicrobial approaches, 1st edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Koshland DE Jr (1992) The molecule of the year. Science 258:186
Kraeling MEK, Top** VD, Keltner ZM, Belgrave KR, Bailey KD, Gao X, Yourick JJ (2018) In vitro percutaneous penetration of silver nanoparticles in pig and human skin. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 95:314–322
Kuhn A, Fehsel K, Lehmann P, Krutmann J, Ruzicka T, Kolb-Bachofen V (1998) Aberrant timing in epidermal expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase after UV irradiation in cutaneous lupus derythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 111:149–153
Lakshminarayanan R, Ye E, Young DJ, Li Z, Loh XJ (2018) Recent advances in the development of antimicrobial nanoparticles for combating resistant pathogens. Adv Healthc Mater 7:1–13
Landriscina A, Rosen J, Blecher-Paz K, Long L, Ghannoum MA, Nosanchuk JD, Friedman AJ (2015) Nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles as a treatment for cutaneous dermatophyte infections. Sci Lett J 4:193–198
Liu D, Fernandez BO, Hamilton A, Lang NN, Gallagher JMC, Newby DE, Feelisch M, Weller RB (2014) UVA irradiation of human skin vasodilates arterial vasculature and lowers blood pressure independently of nitric oxide synthase. J Invest Dermatol 134:1839–1846
López-Jaramillo P, Rincón MY, García RG, Silva SY, Smith E, Kamoeerapappun P, García C, Smith DJ, López M, Vélez ID (2010) A controlled, randomized-blinded clinical trial to assess the efficacy of a nitric oxide releasing patch in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis by Leishmania (V.) panamensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 83:97–101
Lyons CR (1995) The role of nitric oxide in inflammation. Adv Immunol 60:323–371
Macherla C, Sanchez DA, Ahmadi MS, Vellozzi EM, Friedman AJ, Nosanchuk JD, Martinez LR (2012) Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles for treatment of Candida albicans burn infections. Front Microbiol 3:1–9
Martinez LR, Han G, Chacko M, Mihu MR, Jacobson M, Gialanella P, Friedman AJ, Nosanchuk JD, Friedman JM (2009) Antimicrobial and healing efficacy of sustained release nitric oxide nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus skin infection. J Invest Dermatol 129:2463–2469
Mihu MR, Sandkovsky U, Han G, Friedman JM, Nosanchuk JD, Martinez LR (2010) Nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are therapeutic for Acinetobacter baumannii wound infections. Virulence 1:62–67
Mihu MR, Cabral V, Pattabhi R, Tar MT, Davies KP, Friedman AJ, Martinez LR, Nosanchuk JD (2017) Sustained nitric oxide-releasing nanoparticles interfere with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus adhesion and biofilm formation in a rat central venous catheter model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:1–11
Mollick MMR, Rana D, Dash SK, Chattopadhyay S, Bhowmick B, Maity D, Mondal D, Pattanayak S, Roy S, Chakraborty M, Chattopadhyay D (2015) Studies on green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) pulp extract having anticancer (in vitro) and antimicrobial applications. Arab J Chem 2015:1–13
Mordorski B, Costa-Orlandi CB, Baltazar LM, Carreño LJ, Landriscina A, Rosen J, Navati M, Mendes-Giannini MJS, Friedman JM, Nosanchuk JD, Friedman AJ (2017) Topical nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles are effective in a murine model of dermal Trichophyton rubrum dermatophytosis. Nanomedicine 13:2267–2270
Moreno E, Schwartz J, Fernández C et al (2014) Nanoparticles as multifunctional devices for the topical treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 11:579–597
Mowbray M, McLintock S, Weerakoon R, Lomatschinsky N, Jones S, Rossi AG, Weller RB (2009) Enzyme-independent NO stores in human skin: quantification and influence of UV radiation. J Invest Dermatol 129:834–842
Nguyen TK, Selvanayagam R, Ho KKK, Chen R, Kutty SK, Rice SA, Kumar N, Barraud N, Doung HTT, Boyer C (2016) Co-delivery of nitric oxide and antibiotic using polymeric nanoparticles. Chem Sci 7:1016–1027
Nusbaum AG, Kirsner RS, Charles CA (2012) Biofilms in dermatology. Skin Therapy Lett 17(7):1–5
Opländer C, Suschek CV (2013) The role of photolabile dermal nitric oxide derivates in ultraviolet radiation (UVR)-induced cell death. Int J Mol Sci 14:191–204
Opländer C, Deck A, Volkmar CM, Kirsch M, Liebmann J, Born M, van Abeelen F, van Faassen EE, Kröncke KD, Windolf J, Suschek CV (2013) Mechanism and biological relevance of blue-light (420–453 nm)-induced nonenzymatic nitric oxide generation from photolabile nitric oxide derivates in human skin in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med 65:1363–1377
Parani M, Lokhande G, Singh A, Gaharwar AK (2016) Engineered nanomaterials for infection control and healing acute and chronic wounds. Appl Mater Interfaces 8:10049–10069
Pelegrino MT, Weller RB, Chen X, Bernardes JS, Seabra AB (2017) Chitosan nanoparticles for nitric oxide delivery in human skin. Med Chem Commun 8:713–719
Pelegrino MT, de Araújo DR, Seabra AB (2018) S-Nitrosoglutathione-containing chitosan nanoparticles dispersed in Pluronic F-127 hydrogel: potential uses in topical applications. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 43:211–220
Percival SL, Emanuel C, Cutting KF, Williams DW (2012) Microbiology of the skin and the role of biofilms in infection. Int Wound J 9:14–32
Privett BJ, Nutz ST, Schoenfisch MH (2010) Efficacy of surface-generated nitric oxide against Candida albicans adhesion and biofilm formation. Biofouling 26:973–983
Quinn JF, Whittaker MR, Davis TP (2015) Delivering nitric oxide with nanoparticles. J Control Release 205:190–205
Sakdiset P, Okada A, Todo H, Sugibayashi K (2018) Selection of phospholipids to design liposome preparations with high skin penetration-enhancing effects. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 44:58–64
Schairer DO, Chouake JS, Nosanchuk JD, Friedman AJ (2012) The potential of nitric oxide releasing therapies as antimicrobial agents. Virulence 3:271–279
Seabra AB (2011) Nitric oxide-releasing nanomaterials and skin care. In: Beck R, Pohlmann A, Guterres S (eds) Nanocosmetics and nanomedicines, 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 253–268
Seabra AB (2017) Nitric oxide donors: novel biomedical applications and perspectives, 1st edn. Elsevier, New York
Seabra AB, Durán N (2017a) Nanoparticulated nitric oxide donors and their biomedical applications. Mini Rev Med Chem 17(3):216–223
Seabra AB, Durán N (2017b) Nitric oxide donors for treating neglected diseases. In: Nitric oxide donors: novel biomedical applications and perspectives, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 25–54
Seabra AB, Durán N (2018) Nitric oxide donors for prostate and bladder cancers: current state and challenges. Eur J Pharmacol 826:158–168
Seabra AB, Fitzpatrick A, Paul J, De Oliveira MG, Weller R (2004) Topically applied S-nitrosothiol-containing hydrogels as experimental and pharmacological nitric oxide donors in human skin. Br J Dermatol 151:977–983
Seabra AB, Justo GZ, Haddad PS (2015) State of the art, challenges and perspectives in the design of nitric oxide-releasing polymeric nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Biotechnol Adv 33:1370–1379
Seabra AB, Pelegrino MT, Haddad PS (2016) Can nitric oxide overcome bacterial resitance to antibiotics? In: Antibiotic resistance: mechanisms and new antimicrobial approaches, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 187–204
Slomberg DL, Lu Y, Broadnax AD, Hunter RA, Carpenter AW, Schoenfisch MH (2013) Role of size and shape on biofilm eradication for nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:9322–9329
Sonesson A, Przybyszewska K, Eriksson S, Mörgelin M, Kjellström K, Davies J, Potempa J, Schmidtchen A (2017) Identification of bacterial biofilm and the Staphylococcus aureus derived protease, staphopain, on the skin surface of patients with atopic dermatitis. Sci Rep 7:1–12
Stancic A, Jankovic A, Koracb A et al (2019) The role of nitric oxide in diabetic skin (patho)physiology. Mech Ageing Dev 172:21–29
Stuehr DJ, Haque MM (2018) Nitric oxide synthase enzymology in the twenty years after the Nobel prize. Br J Pharmacol 176(2):177–188
Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M, **a Y (2014) Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12320–12364
Wang PG, **an M, Tang X, Wu X, Wen Z, Cai T, Janczuk AJ (2002) Nitric oxide donors: chemical activities and biological applications. Chem Rev 102:1091–1134
Weller RB (2016) Sunlight has cardiovascular benefits independently of vitamin D. Blood Purif 41:130–134
Yang Y, Qi PK, Yang ZL, Huang N (2015) Nitric oxide based strategies for applications of biomedical devices. Biosurf Biotribol 1(3):177–201
Yarlagadda K, Hassani J, Foote IP, Markowitz J (2017) The role of nitric oxide in melanoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1868:500–509
Zhang Z, Tsai PC, Ramezanli T, Michniak-Kohn BB (2013) Polymeric nanoparticles-based topical delivery systems for the treatment of dermatological diseases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 5(3):205–218
Zou P, Yang X, Wang J, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang Y, Liu G (2016) Advances in characterisation and biological activities of chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides. Food Chem 190:1174–1181
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the support from CNPq (404815/2018-9) and FAPESP (2018/08194-2, 2018/02832-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pieretti, J.C., Seabra, A.B. (2020). Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanomaterials and Skin Infections. In: Rai, M. (eds) Nanotechnology in Skin, Soft Tissue, and Bone Infections. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35147-2_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35147-2_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-35146-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-35147-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)