Abstract
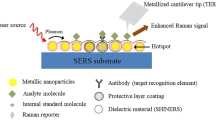
Recent advancements in nanotechnology largely enabled fabrication of plasmonic nanostructures of desired structural features and substantially improved the sensitivity and selectivity of the conventional optical sensing techniques. The plasmonic nanostructure mitigates the limitation of weak scattering cross-section in Raman spectroscopy via electromagnetic as well as chemical enhancement mechanism. The plasmonic nanostructure combined with the Raman spectroscopy technique, popularly known surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy, has been now established as an effective tool for molecular finger printing of analyte molecule and find applications diverse areas, ranging from biosensors to art. This chapter explains the mechanism behind the surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy with an emphasis on the factors contributing towards the enhancement in the Raman signal. Further, an account of the difference between conventional and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy is presented. The role of hot spots and the rationale behind the choice of metal nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates is described. In addition, various approaches adopted for the fabrication of substrates in 1D, 2D, and 3D is explained in detail. A detailed account of a few emerging areas wherein this technique finds applications is also given in the chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, F., Guo, Y., Hou, S., Quan, Q.: Photonic-plasmonic hybrid single-molecule nanosensor measures the effect of fluorescent labels on DNA-protein dynamics. Sci. Adv. 3(5), e1602991 (2017)
Mejía-Salazar, J., Oliveira Jr, O.N.: Plasmonic biosensing: focus review. Chem. Rev. 118(20), 10617–10625 (2018)
Taylor, A.B., Zijlstra, P.: Single-molecule plasmon sensing: current status and future prospects. ACS Sens. 2(8), 1103–1122 (2017)
Willner, M.R., Vikesland, P.J.: Nanomaterial enabled sensors for environmental contaminants. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16(1), 95 (2018)
Ye, D., Zuo, X., Fan, C.: DNA nanotechnology-enabled interfacial engineering for biosensor development. Ann. Rev. Anal. Chem. 11, 171–195 (2018)
Yunus, I.S., Harwin, Kurniawan, A., Adityawarman, D., Indarto, A.: Nanotechnologies in water and air pollution treatment. Environ. Technol. Rev. 1(1), 136–148 (2012)
Butler, H.J., Ashton, L., Bird, B., Cinque, G., Curtis, K., Dorney, J., Esmonde-White, K., Fullwood, N.J., Gardner, B., Martin-Hirsch, P.L.: Using Raman spectroscopy to characterize biological materials. Nat. Protocols 11(4), 664 (2016)
Czamara, K., Majzner, K., Pacia, M. Z., Kochan, K., Kaczor, A., Baranska, M.: Raman spectroscopy of lipids: a review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 46(1), 4–20 (2015)
Demirel, G., Usta, H., Yilmaz, M., Celik, M., Alidagi, H.A., Buyukserin, F.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): an adventure from plasmonic metals to organic semiconductors as SERS platforms. J. Mater. Chem. C 6(20), 5314–5335 (2018)
Fleischmann, M., Hendra, P.J., McQuillan, A.J.: Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 26(2), 163–166 (1974)
Jeanmaire, D.L., Van Duyne, R.P.: Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 84(1), 1–20 (1977)
Otto, A.: The ‘chemical’(electronic) contribution to surface‐enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. Int. J. Orig. Work Aspects Raman Spectrosc. Includ. Higher Order Process. Brill. Rayleigh Scatt. 36(6–7), 497–509 (2005)
Yamamoto, Y.S., Ishikawa, M., Ozaki, Y., Itoh, T.: Fundamental studies on enhancement and blinking mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and basic applications of SERS biological sensing. Front. Phys. 9(1), 31–46 (2014)
Stiles, P.L., Dieringer, J.A., Shah, N.C., Van Duyne, R.P.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1, 601–626 (2008)
Fan, M., Andrade, G.F., Brolo, A.G.: A review on the fabrication of substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and their applications in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chimica Acta 693(1–2), 7–25 (2011)
Ngo, H.T., Wang, H.-N., Fales, A.M., Vo-Dinh, T.: Plasmonic SERS biosensing nanochips for DNA detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408(7), 1773–1781 (2016)
Tsoutsi, D., Sanles-Sobrido, M., Cabot, A., Gil, P.-R.: Common aspects influencing the translocation of SERS to biomedicine. Current Med. Chem. 25(35), 4638–4652 (2018)
Torres-Nunez, A., Faulds, K., Graham, D., Alvarez-Puebla, R., Guerrini, L.: Silver colloids as plasmonic substrates for direct label-free surface-enhanced Raman scattering analysis of DNA. Analyst 141(17), 5170–5180 (2016)
Garcia-Rico, E., Alvarez-Puebla, R.A., Guerrini, L.: Direct surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectroscopy of nucleic acids: from fundamental studies to real-life applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47(13), 4909–4923 (2018)
Campion, A., Kambhampati, P.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 27(4), 241–250 (1998)
Ding, S.-Y., You, E.-M., Tian, Z.-Q., Moskovits, M.: Electromagnetic theories of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(13), 4042–4076 (2017)
Le Ru, E., Etchegoin, P.: Principles of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: and related plasmonic effects. Elsevier (2008)
Chalmers, J.M., Edwards, H.G., Hargreaves, M.D.: Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy in Forensic Science. Wiley (2012)
Zong, C., Xu, M., Xu, L.-J., Wei, T., Ma, X., Zheng, X.-S., Hu, R., Ren, B.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: reliability and challenges. Chem. Rev. 118(10), 4946–4980 (2018)
Persson, B.N.J., Zhao, K., Zhang, Z.: Chemical contribution to surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(20), 207401 (2006)
Valley, N., Greeneltch, N., Van Duyne, R.P., Schatz, G.C.: A look at the origin and magnitude of the chemical contribution to the enhancement mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4(16), 2599–2604 (2013)
Zayak, A., Hu, Y., Choo, H., Bokor, J., Cabrini, S., Schuck, P., Neaton, J.: Chemical Raman enhancement of organic adsorbates on metal surfaces. Physical Rev. Lett. 106(8), 083003 (2011)
Moskovits, M.: Surface‐enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a brief retrospective. J. Raman Spectrosc. Int. J. Orig. Work Aspects Raman Spectrosc. Includ. Higher Order Process. Brill. Rayleigh Scatt. 36(6–7), 485–496 (2005)
Lee, H.K., Lee, Y.H., Koh, C.S.L., Phan-Quang, G.C., Han, X., Lay, C.L., Sim, H.Y.F., Kao, Y.-C., An, Q., Ling, X.Y.: Designing surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platforms beyond hotspot engineering: emerging opportunities in analyte manipulations and hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48(3), 731–756 (2019)
Pilot, R., Signorini, R., Fabris, L.: Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy: principles, substrates, and applications. In: Metal Nanoparticles and Clusters, pp. 89–164. Springer (2018)
Ye, J., Wen, F., Sobhani, H., Lassiter, J.B., Van Dorpe, P., Nordlander, P., Halas, N.J.: Plasmonic nanoclusters: near field properties of the Fano resonance interrogated with SERS. Nano Lett. 12(3), 1660–1667 (2012)
Postaci, S., Yildiz, B.C., Bek, A., Tasgin, M.E.: Silent enhancement of SERS signal without increasing hot spot intensities. Nanophotonics 7(10), 1687–1695 (2018)
Kleinman, S.L., Frontiera, R.R., Henry, A.-I., Dieringer, J.A., Van Duyne, R.P.: Creating, characterizing, and controlling chemistry with SERS hot spots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15(1), 21–36 (2013)
Petryayeva, E., Krull, U.J.: Localized surface plasmon resonance: nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing—a review. Anal. Chimica Acta 706(1), 8–24 (2011)
Liu, H., Yang, Z., Meng, L., Sun, Y., Wang, J., Yang, L., Liu, J., Tian, Z.: Three-dimensional and time-ordered surface-enhanced Raman scattering hotspot matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(14), 5332–5341 (2014)
Sun, Y., Han, Z., Liu, H., He, S., Yang, L., Liu, J.: Three-dimensional hotspots in evaporating nanoparticle sols for ultrahigh Raman scattering: solid–liquid interface effects. Nanoscale 7(15), 6619–6626 (2015)
Wang, H., Fang, J., Xu, J., Wang, F., Sun, B., He, S., Sun, G., Liu, H.: A hanging plasmonic droplet: three-dimensional SERS hotspots for a highly sensitive multiplex detection of amino acids. Analyst 140(9), 2973–2978 (2015)
Le Ru, E.C., Etchegoin, P.G.: Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 63, 65–87 (2012)
West, P.R., Ishii, S., Naik, G.V., Emani, N.K., Shalaev, V.M., Boltasseva, A.: Searching for better plasmonic materials. Laser Photonics Rev. 4(6), 795-808 (2010)
Cottancin, E., Celep, G., Lermé, J., Pellarin, M., Huntzinger, J., Vialle, J., Broyer, M.: Optical properties of noble metal clusters as a function of the size: comparison between experiments and a semi-quantal theory. Theor. Chem. Acc. 116(4–5), 514-523 (2006)
Cialla, D., Pollok, S., Steinbrücker, C., Weber, K., Popp, J.: SERS-based detection of biomolecules. Nanophotonics 3(6), 383–411 (2014)
Karthick Kannan, P., Shankar, P., Blackman, C., Chung, C.H.: Recent advances in 2D inorganic nanomaterials for SERS sensing. Adv. Mater. 1803432 (2019)
Jayram, N.D., Aishwarya, D., Sonia, S., Mangalaraj, D., Kumar, P.S., Rao, G.M.: Analysis on superhydrophobic silver decorated copper Oxide nanostructured thin films for SERS studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 477, 209–219 (2016)
Cong, S., Yuan, Y., Chen, Z., Hou, J., Yang, M., Su, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, L., Li, Q., Geng, F.: Noble metal-comparable SERS enhancement from semiconducting metal oxides by making oxygen vacancies. Nat. Commun. 6, 7800 (2015)
Yu, Z., Yun, F.F., Wang, Y., Yao, L., Dou, S., Liu, K., Jiang, L., Wang, X.: Desert Beetle-inspired superwettable patterned surfaces for water harvesting. Small 13(36), 1701403 (2017)
Kim, N.-J., Kim, J., Park, J.-B., Kim, H., Yi, G.-C., Yoon, S.: Direct observation of quantum tunnelling charge transfers between molecules and semiconductors for SERS. Nanoscale 11(1), 45–49 (2019)
Wang, X., Shi, W., She, G., Mu, L.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) on transition metal and semiconductor nanostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(17), 5891–5901 (2012)
Kini, S., Ganiga, V., Kulkarni, S.D., Chidangil, S., George, S.D.: Sensitive detection of mercury using the fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe/CdS quantum dots and Rhodamine 6G. J. Nanoparticle Res. 20(9), 232 (2018)
Basheer, N.S., Kumar, B.R., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Thermal lens probing of distant dependent fluorescence quenching of Rhodamine 6G by silver nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 137, 225–229 (2013)
Kumar, B.R., Basheer, N.S., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Thermal-lens study on the distance-dependent energy transfer from Rhodamine 6G to gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Thermophys. 34(10), 1982–1992 (2013)
John, J., Thomas, L., Kurian, A., Nampoori, V., George, S.D.: Role of decoration method of gold nanoparticles on the thermal and optical properties of mesoporous silica-Rhodamine 6G hybrids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 244, 171–179 (2017)
John, J., Thomas, L., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Modulating fluorescence quantum yield of highly concentrated fluorescein using differently shaped green synthesized gold nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 172, 39–46 (2016)
John, J., Thomas, L., George, N.A., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Tailoring of optical properties of fluorescein using green synthesized gold nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(24), 15813–15821 (2015)
Kumar, B.R., Basheer, N.S., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Study of concentration-dependent quantum yield of Rhodamine 6G by gold nanoparticles using thermal-lens technique. Appl. Phys. B 115(3), 335–342 (2014)
Basheer, N.S., Kumar, B.R., Kurian, A., George, S.D.: Silver nanoparticle size–dependent measurement of quantum efficiency of Rhodamine 6G. Appl. Phys. B 113(4), 581–587 (2013)
Lane, L.A., Qian, X., Nie, S.: SERS nanoparticles in medicine: from label-free detection to spectroscopic tagging. Chem. Rev. 115(19), 10489–10529 (2015)
Cardinal, M.F., Vander Ende, E., Hackler, R.A., McAnally, M.O., Stair, P.C., Schatz, G.C., Van Duyne, R.P.: Expanding applications of SERS through versatile nanomaterials engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(13), 3886–3903 (2017)
Cao, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, Y., Huang, Z., Long, N.V., Fu, C.: Engineering of SERS substrates based on noble metal nanomaterials for chemical and biomedical applications. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 50(6), 499–525 (2015)
Si, S., Liang, W., Sun, Y., Huang, J., Ma, W., Liang, Z., Bao, Q., Jiang, L.: Facile fabrication of high‐density sub‐1‐nm gaps from Au nanoparticle monolayers as reproducible SERS substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26(44), 8137–8145 (2016)
Reguera, J., Langer, J., de Aberasturi, D.J., Liz-Marzán, L.M.: Anisotropic metal nanoparticles for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(13), 3866–3885 (2017)
Turkevich, J., Stevenson, P.C., Hillier, J.: A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 11, 55–75 (1951)
Lee, P., Meisel, D.: Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J. Phys. Chem. 86(17), 3391–3395 (1982)
Benz, F., Chikkaraddy, R., Salmon, A., Ohadi, H., De Nijs, B., Mertens, J., Carnegie, C., Bowman, R.W., Baumberg, J.J.: SERS of individual nanoparticles on a mirror: size does matter, but so does shape. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7(12), 2264–2269 (2016)
Quester, K., Avalos-Borja, M., Vilchis-Nestor, A.R., Camacho-López, M.A., Castro-Longoria, E.: SERS properties of different sized and shaped gold nanoparticles biosynthesized under different environmental conditions by Neurospora crassa extract. PloS one 8(10), e77486 (2013)
Nguyen, B.H., Nguyen, V.H., Tran, H.N.: Rich variety of substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Adv. Natl. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7(3), 033001 (2016)
Solís, D.M., Taboada, J.M., Obelleiro, F., Liz-Marzán, L.M., García de Abajo, F.J.: Optimization of nanoparticle-based SERS substrates through large-scale realistic simulations. ACS Photon.4(2), 329–337 (2017)
Betz, J.F., Wei, W.Y., Cheng, Y., White, I.M., Rubloff, G.W.: Simple SERS substrates: powerful, portable, and full of potential. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(6), 2224–2239 (2014)
Mavani, K., Shah, M.: Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using sodium borohydride as a reducing agent. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2(3), 1–5 (2013)
Song, K.C., Lee, S.M., Park, T.S., Lee, B.S.: Preparation of colloidal silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26(1), 153–155 (2009)
Mulfinger, L., Solomon, S.D., Bahadory, M., Jeyarajasingam, A.V., Rutkowsky, S.A., Boritz, C.: Synthesis and study of silver nanoparticles. J. Chem. Edu. 84(2), 322 (2007)
Leopold, N., Lendl, B.: A new method for fast preparation of highly surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active silver colloids at room temperature by reduction of silver nitrate with hydroxylamine hydrochloride. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(24), 5723–5727 (2003)
Sun, D., Zhang, G., Jiang, X., Huang, J., **g, X., Zheng, Y., He, J., Li, Q.: Biogenic flower-shaped Au–Pd nanoparticles: synthesis, SERS detection and catalysis towards benzyl alcohol oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(6), 1767–1773 (2014)
Hunyadi, S.E., Murphy, C.J.: Bimetallic silver–gold nanowires: fabrication and use in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Mater. Chem. 16(40), 3929–3935 (2006)
Fan, M., Lai, F.-J., Chou, H.-L., Lu, W.-T., Hwang, B.-J., Brolo, A.G.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) from Au: Ag bimetallic nanoparticles: the effect of the molecular probe. Chem. Sci. 4(1), 509–515 (2013)
Muniz-Miranda, M., Gellini, C., Canton, P., Marsili, P., Giorgetti, E.: SERS and catalytically active Ag/Pd nanoparticles obtained by combining laser ablation and galvanic replacement. J. Alloy. Compd. 615, S352–S356 (2014)
Yang, Y., Shi, J., Kawamura, G., Nogami, M.: Preparation of Au–Ag, Ag–Au core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Scr. Mater. 58(10), 862–865 (2008)
Li, J.F., Huang, Y.F., Ding, Y., Yang, Z.L., Li, S.B., Zhou, X.S., Fan, F.R., Zhang, W., Zhou, Z.Y., Ren, B.: Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464(7287), 392 (2010)
Guo, P., Sikdar, D., Huang, X., Si, K.J., **ong, W., Gong, S., Yap, L.W., Premaratne, M., Cheng, W.: Plasmonic core–shell nanoparticles for SERS detection of the pesticide thiram: size-and shape-dependent Raman enhancement. Nanoscale 7(7), 2862–2868 (2015)
**e, W., Herrmann, C., Kömpe, K., Haase, M., Schlücker, S.: Synthesis of bifunctional Au/Pt/Au core/shell nanoraspberries for in situ SERS monitoring of platinum-catalyzed reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(48), 19302–19305 (2011)
Shanthil, M., Thomas, R., Swathi, R., George Thomas, K.: Ag@ SiO2 core–shell nanostructures: distance-dependent plasmon coupling and SERS investigation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3(11), 1459–1464 (2012)
Yang, Y., Liu, J., Fu, Z.-W., Qin, D.: Galvanic replacement-free deposition of Au on Ag for core–shell nanocubes with enhanced chemical stability and SERS activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(23), 8153–8156 (2014)
Pande, S., Ghosh, S.K., Praharaj, S., Panigrahi, S., Basu, S., Jana, S., Pal, A., Tsukuda, T., Pal, T.: Synthesis of normal and inverted gold–silver core–shell architectures in β-cyclodextrin and their applications in SERS. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(29), 10806–10813 (2007)
Wang, J., Zhu, T., Tang, M., Cai, S., Liu, Z.: Fabricating surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active substrates by assembling colloidal Au nanoparticles with self-assembled monolayers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, L1381–L1384 (1996)
Hu, X., Cheng, W., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Wang, E., Dong, S.: Fabrication, characterization, and application in SERS of self-assembled polyelectrolyte-gold nanorod multilayered films. J. Phys. Chem. B 109(41), 19385–19389 (2005)
Chen, J., Guo, L., Qiu, B., Lin, Z., Wang, T.: Application of ordered nanoparticle self-assemblies in surface-enhanced spectroscopy. Mater. Chem. Front. 2(5), 835–860 (2018)
Pu, H., **ao, W., Sun, D.-W.: SERS-microfluidic systems: a potential platform for rapid analysis of food contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 70, 114–126 (2017)
Kant, K., Abalde-Cela, S.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy and microfluidics: towards ultrasensitive label-free sensing. Biosensors 8(3), 62 (2018)
Willner, M.R., McMillan, K.S., Graham, D., Vikesland, P.J., Zagnoni, M.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering based microfluidics for single-cell analysis. Anal. Chem. 90(20), 12004–12010 (2018)
Wu, Y., Jiang, Y., Zheng, X., Jia, S., Zhu, Z., Ren, B., Ma, H.: Facile fabrication of microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman scattering devices via lift-up lithography. R. Soc. Open Sci. 5(4), 172034 (2018)
Jahn, I., Žukovskaja, O., Zheng, X.-S., Weber, K., Bocklitz, T., Cialla-May, D., Popp, J: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and microfluidic platforms: challenges, solutions and potential applications. Analyst 142(7), 1022–1047 (2017)
Yang, S., Dai, X., Stogin, B.B., Wong, T.-S.: Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113(2), 268–273 (2016)
Marquestaut, N., Martin, A., Talaga, D., Servant, L., Ravaine, S., Reculusa, S., Bassani, D.M., Gillies, E., Lagugné-Labarthet, F.: Raman enhancement of azobenzene monolayers on substrates prepared by Langmuir–Blodgett deposition and electron-beam lithography techniques. Langmuir 24(19), 11313–11321 (2008)
Abu Hatab, N.A., Oran, J.M., Sepaniak, M.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrates created via electron beam lithography and nanotransfer printing. ACS Nano 2(2), 377–385 (2008)
Kahl, M., Voges, E., Kostrewa, S., Viets, C., Hill, W.: Periodically structured metallic substrates for SERS. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 51(1–3), 285–291 (1998)
Petti, L., Capasso, R., Rippa, M., Pannico, M., La Manna, P., Peluso, G., Calarco, A., Bobeico, E., Musto, P.: A plasmonic nanostructure fabricated by electron beam lithography as a sensitive and highly homogeneous SERS substrate for bio-sensing applications. Vib. Spectrosc. 82, 22–30 (2016)
Yue, W., Wang, Z., Yang, Y., Chen, L., Syed, A., Wong, K., Wang, X.: Electron-beam lithography of gold nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 22(12), 125007 (2012)
Yu, Q., Guan, P., Qin, D., Golden, G., Wallace, P.M.: Inverted size-dependence of surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanohole and nanodisk arrays. Nano Lett. 8(7), 1923–1928 (2008)
Brolo, A.G., Gordon, R., Leathem, B., Kavanagh, K.L.: Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 20(12), 4813–4815 (2004)
Sivashanmugan, K., Liao, J.-D., You, J.-W., Wu, C.-L.: Focused-ion-beam-fabricated Au/Ag multilayered nanorod array as SERS-active substrate for virus strain detection. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 181, 361–367 (2013)
Sree Satya Bharati, M., Byram, C., Soma, V.R.: Femtosecond laser fabricated Ag@ Au and Cu@ Au alloy nanoparticles for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy based trace explosives detection. Front. Phys. 6, 28 (2018)
Quilis, N.G., Lequeux, M., Venugopalan, P., Khan, I., Knoll, W., Boujday, S., de La Chapelle, M.L., Dostalek, J.: Tunable laser interference lithography preparation of plasmonic nanoparticle arrays tailored for SERS. Nanoscale 10(21), 10268–10276 (2018)
Solak, H.H., David, C., Gobrecht, J., Golovkina, V., Cerrina, F., Kim, S.O., Nealey, P.: Sub-50 nm period patterns with EUV interference lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 67, 56–62 (2003)
Zhang, P., Yang, S., Wang, L., Zhao, J., Zhu, Z., Liu, B., Zhong, J., Sun, X.: Large-scale uniform Au nanodisk arrays fabricated via x-ray interference lithography for reproducible and sensitive SERS substrate. Nanotechnology 25(24), 245301 (2014)
Hwang, J., Yang, M.: Sensitive and reproducible gold SERS sensor based on interference lithography and electrophoretic deposition. Sensors 18(11), 4076 (2018)
Jha, S.K., Ekinci, Y., Agio, M., Löffler, J.F.: Towards deep-UV surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy of explosives: ultrasensitive, real-time and reproducible detection of TNT. Analyst 140(16), 5671–5677 (2015)
Izquierdo-Lorenzo, I., Jradi, S., Adam, P.-M.: Direct laser writing of random au nanoparticle three-dimensional structures for highly reproducible micro-SERS measurements. RSC Adv. 4(8), 4128–4133 (2014)
Byram, C., Moram, S.S.B., Shaik, A.K., Soma, V.R.: Versatile gold based SERS substrates fabricated by ultrafast laser ablation for sensing picric acid and ammonium nitrate. Chem. Phys. Lett. 685, 103–107 (2017)
Dick, L.A., McFarland, A.D., Haynes, C.L., Van Duyne, R.P.: Metal film over nanosphere (MFON) electrodes for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): improvements in surface nanostructure stability and suppression of irreversible loss. J. Phys. Chem. B 106(4), 853–860 (2002)
Haynes, C.L., Van Duyne, R.P.: Nanosphere Lithography: A Versatile Nanofabrication Tool for Studies of Size-Dependent Nanoparticle Optics. ACS Publications (2001)
Quero, G., Zito, G., Managò, S., Galeotti, F., Pisco, M., De Luca, A., Cusano, A.: Nanosphere lithography on fiber: towards engineered lab-on-fiber SERS optrodes. Sensors 18(3), 680 (2018)
Wallace, G.Q., Tabatabaei, M., Lagugné-Labarthet, F.: Towards attomolar detection using a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy platform fabricated by nanosphere lithography. Can. J. Chem. 92(1), 1–8 (2013)
Kahraman, M., Daggumati, P., Kurtulus, O., Seker, E., Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.: Fabrication and characterization of flexible and tunable plasmonic nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 3, 3396 (2013)
Lee, C., Robertson, C.S., Nguyen, A.H., Kahraman, M., Wachsmann-Hogiu, S.: Thickness of a metallic film, in addition to its roughness, plays a significant role in SERS activity. Sci. Rep. 5, 11644 (2015)
George, J.E., Unnikrishnan, V., Mathur, D., Chidangil, S., George, S.D.: Flexible superhydrophobic SERS substrates fabricated by in situ reduction of Ag on femtosecond laser-written hierarchical surfaces. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 272, 485–493 (2018)
Ji, N., Ruan, W., Wang, C., Lu, Z., Zhao, B.: Fabrication of silver decorated anodic aluminum oxide substrate and its optical properties on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and thin film interference. Langmuir 25(19), 11869–11873 (2009)
Kassu, A., Farley, C., Sharma, A., Kim, W., Guo, J.: Effect of pore size and film thickness on gold-coated nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensor. Sensors 15(12), 29924–29937 (2015)
Tran, B., Nam, N., Son, S., Lee, N.: Nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide internalized with gold nanoparticles for on-chip PCR and direct detection by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Analyst 143(4), 808–812 (2018)
Terekhov, S., Mojzes, P., Kachan, S., Mukhurov, N., Zhvavyi, S., Panarin, A.Y., Khodasevich, I., Orlovich, V., Thorel, A., Grillon, F.: A comparative study of surface‐enhanced Raman scattering from silver‐coated anodic aluminum oxide and porous silicon. J. Raman Spectrosc. 42(1), 12–20 (2011)
Toccafondi, C., La Rocca, R., Scarpellini, A., Salerno, M., Das, G., Dante, S.: Thin nanoporous alumina-based SERS platform for single cell sensing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 738–745 (2015)
Zhang, C., Yi, P., Peng, L., Lai, X., Chen, J., Huang, M., Ni, J.: Continuous fabrication of nanostructure arrays for flexible surface enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Sci. Rep. 7, 39814 (2017)
Sun, L., Hu, H., Zhan, D., Yan, J., Liu, L., Teguh, J.S., Yeow, E.K., Lee, P.S., Shen, Z.: Plasma modified MoS2 nanoflakes for surface enhanced Raman scattering. Small 10(6), 1090–1095 (2014)
Lu, X., Luo, X., Zhang, J., Quek, S.Y., **ong, Q.: Lattice vibrations and Raman scattering in two-dimensional layered materials beyond graphene. Nano Res. 9(12), 3559–3597 (2016)
Zhang, S., Zhang, N., Zhao, Y., Cheng, T., Li, X., Feng, R., Xu, H., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Tong, L.: Spotting the differences in two-dimensional materials–the Raman scattering perspective. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47(9), 3217–3240 (2018)
Ling, X., Zhang, J.: First-layer effect in graphene-enhanced Raman scattering. Small 6(18), 2020–2025 (2010)
Ling, X., Moura, L., Pimenta, M.A., Zhang, J.: Charge-transfer mechanism in graphene-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(47), 25112–25118 (2012)
Ling, X., **e, L., Fang, Y., Xu, H., Zhang, H., Kong, J., Dresselhaus, M.S., Zhang, J., Liu, Z.: Can graphene be used as a substrate for Raman enhancement? Nano Lett. 10(2), 553–561 (2009)
Ling, X., Fang, W., Lee, Y.-H., Araujo, P.T., Zhang, X., Rodriguez-Nieva, J.F., Lin, Y., Zhang, J., Kong, J., Dresselhaus, M.S.: Raman enhancement effect on two-dimensional layered materials: graphene, h-BN and MoS2. Nano Lett. 14(6), 3033–3040 (2014)
Kim, N.-Y., Leem, Y.-C., Hong, S.-H., Park, J.-H., Yim, S.-Y.: Ultrasensitive and stable plasmonic surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates covered with atomically thin monolayers: effect of the insulating property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2019)
**a, M.: 2D materials-coated plasmonic structures for SERS applications. Coatings 8(4), 137 (2018)
Yi, N., Zhang, C., Song, Q., **ao, S.: A hybrid system with highly enhanced graphene SERS for rapid and tag-free tumor cells detection. Sci. Rep. 6, 25134 (2016)
Jahn, M., Patze, S., Hidi, I.J., Knipper, R., Radu, A.I., Mühlig, A., Yüksel, S., Peksa, V., Weber, K., Mayerhöfer, T.: Plasmonic nanostructures for surface enhanced spectroscopic methods. Analyst 141(3), 756–793 (2016)
Lee, S., Choi, I.: Fabrication Strategies of 3D Plasmonic Structures for SERS. BioChip J. 13(1), 30–42 (2019)
Liu, H., Yang, L., Liu, J.: Three-dimensional SERS hot spots for chemical sensing: Towards develo** a practical analyzer. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 80, 364-372 (2016)
Gómez‐Graña, S., Pérez‐Juste, J., Alvarez‐Puebla, R.A., Guerrero‐Martínez, A., Liz‐Marzán, L.M.: Self‐assembly of Au@ Ag nanorods mediated by Gemini surfactants for highly efficient SERS‐active supercrystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 1(7), 477–481 (2013)
Henzie, J., Andrews, S.C., Ling, X.Y., Li, Z., Yang, P.: Oriented assembly of polyhedral plasmonic nanoparticle clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110(17), 6640–6645 (2013)
Lim, D.-K., Jeon, K.-S., Hwang, J.-H., Kim, H., Kwon, S., Suh, Y.D., Nam, J.-M.: Highly uniform and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering from DNA-tailorable nanoparticles with 1-nm interior gap. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(7), 452 (2011)
Lim, D.-K., Jeon, K.-S., Kim, H.M., Nam, J.-M., Suh, Y.D.: Nanogap-engineerable Raman-active nanodumbbells for single-molecule detection. Nat. Mater. 9(1), 60 (2010)
Barrow, S.J., Wei, X., Baldauf, J.S., Funston, A.M., Mulvaney, P.: The surface plasmon modes of self-assembled gold nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 3, 1275 (2012)
Chirumamilla, M., Toma, A., Gopalakrishnan, A., Das, G., Zaccaria, R.P., Krahne, R., Rondanina, E., Leoncini, M., Liberale, C., De Angelis, F.: 3D nanostar dimers with a sub‐10‐nm gap for single‐/few‐molecule surface‐enhanced Raman scattering. Adv. Mater. 26(15), 2353–2358 (2014)
Cinel, N.A., Bütün, S., Ertaş, G., Özbay, E.: ‘Fairy Chimney’‐shaped tandem metamaterials as double resonance SERS substrates. Small 9(4), 531–537 (2013)
Qian, C., Ni, C., Yu, W., Wu, W., Mao, H., Wang, Y., Xu, J.: Highly‐ordered, 3D petal‐like array for surface‐enhanced Raman scattering. Small 7(13), 1801–1806 (2011)
Yan, B., Thubagere, A., Premasiri, W.R., Ziegler, L.D., Dal Negro, L., Reinhard, B.M.: Engineered SERS substrates with multiscale signal enhancement: nanoparticle cluster arrays. ACS Nano 3(5), 1190–1202 (2009)
Alba, M., Pazos‐Perez, N., Vaz, B., Formentin, P., Tebbe, M., Correa‐Duarte, M.A., Granero, P., Ferré‐Borrull, J., Alvarez, R., Pallares, J.: Macroscale plasmonic substrates for highly sensitive surface‐enhanced Raman scattering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52(25), 6459–6463 (2013)
Zhang, W., Jiang, L., Piper, J.A., Wang, Y.: SERS nanotags and their applications in biosensing and bioimaging. J. Anal. Test. 2(1), 26–44 (2018)
Hashim, A.I., Zhang, X., Wojtkowiak, J.W., Martinez, G.V., Gillies, R.J.: Imaging pH and metastasis. NMR Biomed. 24(6), 582–591 (2011)
Tannock, I.F., Rotin, D.: Acid pH in tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res. 49(16), 4373–4384 (1989)
Liu, Y., Yuan, H., Fales, A.M., Vo‐Dinh, T.: pH‐sensing nanostar probe using surface‐enhanced Raman scattering (SERS): Theoretical and experimental studies. J. Raman Spectrosc. 44(7), 980–986 (2013)
Kneipp, J., Kneipp, H., Wittig, B., Kneipp, K.: Following the dynamics of pH in endosomes of live cells with SERS nanosensors. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(16), 7421–7426 (2010)
Gühlke, M., Heiner, Z., Kneipp, J.: Combined near-infrared excited SEHRS and SERS spectra of pH sensors using silver nanostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(39), 26093–26100 (2015)
Wang, Y., Rauf, S., Grewal, Y.S., Spadafora, L.J., Shiddiky, M.J., Cangelosi, G.A., Schlücker, S., Trau, M.: Duplex microfluidic SERS detection of pathogen antigens with nanoyeast single-chain variable fragments. Anal. Chem. 86(19), 9930–9938 (2014)
Wang, X., Choi, N., Cheng, Z., Ko, J., Chen, L., Choo, J.: Simultaneous detection of dual nucleic acids using a SERS-based lateral flow assay biosensor. Anal. Chem. 89(2), 1163–1169 (2016)
Wang, Y., Ravindranath, S., Irudayaraj, J.: Separation and detection of multiple pathogens in a food matrix by magnetic SERS nanoprobes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 399(3), 1271–1278 (2011)
Levin, C.S., Kundu, J., Janesko, B.G., Scuseria, G.E., Raphael, R.M., Halas, N.: Interactions of ibuprofen with hybrid lipid bilayers probed by complementary surface-enhanced vibrational spectroscopies. J. Phys. Chem. B 112(45), 14168–14175 (2008)
Šimáková, P., Kočišová, E., Procházka, M.: Sensitive Raman spectroscopy of lipids based on drop deposition using DCDR and SERS. J. Raman Spectrosc. 44(11), 1479–1482 (2013)
Kong, K.V., Lam, Z., Lau, W.K.O., Leong, W.K., Olivo, M.: A transition metal carbonyl probe for use in a highly specific and sensitive SERS-based assay for glucose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(48), 18028–18031 (2013)
Shafer-Peltier, K.E., Haynes, C.L., Glucksberg, M.R., Van Duyne, R.P.: Toward a glucose biosensor based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(2), 588–593 (2003)
Dinish, U., Balasundaram, G., Chang, Y.-T., Olivo, M.: Actively targeted in vivo multiplex detection of intrinsic cancer biomarkers using biocompatible SERS nanotags. Sci. Rep. 4, 4075 (2014)
Yuan, H., Liu, Y., Fales, A.M., Li, Y.L., Liu, J., Vo-Dinh, T.: Quantitative surface-enhanced resonant Raman scattering multiplexing of biocompatible gold nanostars for in vitro and ex vivo detection. Anal. Chem. 85(1), 208–212 (2012)
Wang, Y., Seebald, J.L., Szeto, D.P., Irudayaraj, J.: Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoprobes in zebrafish embryos: in vivo and multiplex imaging. ACS Nano 4(7), 4039–4053 (2010)
Yaseen, T., Pu, H., Sun, D.-W.: Functionalization techniques for improving SERS substrates and their applications in food safety evaluation: a review of recent research trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 72, 162–174 (2018)
Hu, Y., Feng, S., Gao, F., Li-Chan, E.C., Grant, E., Lu, X.: Detection of melamine in milk using molecularly imprinted polymers–surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 176, 123–129 (2015)
Pang, S., Labuza, T.P., He, L.: Development of a single aptamer-based surface enhanced Raman scattering method for rapid detection of multiple pesticides. Analyst 139(8), 1895–1901 (2014)
He, L., Deen, B.D., Pagel, A.H., Diez-Gonzalez, F., Labuza, T.P: Concentration, detection and discrimination of Bacillus anthracis spores in orange juice using aptamer based surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 138(6), 1657–1659 (2013)
He, L., Deen, B., Rodda, T., Ronningen, I., Blasius, T., Haynes, C., Diez-Gonzalez, F., Labuza, T.P.: Rapid detection of ricin in milk using immunomagnetic separation combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. 76(5), N49-N53 (2011)
Kamra, T., Chaudhary, S., Xu, C., Montelius, L., Schnadt, J., Ye, L.: Covalent immobilization of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles on a gold surface using carbodiimide coupling for chemical sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 461, 1–8 (2016)
Kamra, T., Zhou, T., Montelius, L., Schnadt, J., Ye, L.: Implementation of molecularly imprinted polymer beads for surface enhanced Raman detection. Anal. Chem. 87(10), 5056–5061 (2015)
Chang, L., Ding, Y., Li, X.: Surface molecular imprinting onto silver microspheres for surface enhanc24 June 2013ed Raman scattering applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 50, 106–110 (2013)
Sarfo, D.K., Izake, E.L., O’Mullane, A.P., Ayoko, G.A.: Fabrication of nanostructured SERS substrates on conductive solid platforms for environmental application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1–36 (2019)
Li, D., Qu, L., Zhai, W., Xue, J., Fossey, J.S., Long, Y.: Facile on-site detection of substituted aromatic pollutants in water using thin layer chromatography combined with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(9), 4046–4052 (2011)
Fikiet, M.A., Khandasammy, S.R., Mistek, E., Ahmed, Y., Halámková, L., Bueno, J., Lednev, I.K.: Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a review of recent applications in forensic science. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 197, 255-260 (2018)
Kamińska, A., Kowalska, A., Albrycht, P., Witkowska, E., Waluk, J.: ABO blood groups’ antigen–antibody interactions studied using SERS spectroscopy: towards blood ty**. Anal. Methods 8(7), 1463–1472 (2016)
Halouzka, V., Halouzkova, B., Jirovsky, D., Hemzal, D., Ondra, P., Siranidi, E., Kontos, A.G., Falaras, P., Hrbac, J.: Copper nanowire coated carbon fibers as efficient substrates for detecting designer drugs using SERS. Talanta 165, 384–390 (2017)
Kline, N.D., Tripathi, A., Mirsafavi, R., Pardoe, I., Moskovits, M., Meinhart, C., Guicheteau, J.A., Christesen, S.D., Fountain III, A.W.: Optimization of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy conditions for implementation into a microfluidic device for drug detection. Anal. Chem. 88(21), 10513–10522 (2016)
Xu, Z., Jiang, J., Wang, X., Han, K., Ameen, A., Khan, I., Chang, T.-W., Liu, G.L.: Large-area, uniform and low-cost dual-mode plasmonic naked-eye colorimetry and SERS sensor with handheld Raman spectrometer. Nanoscale 8(11), 6162–6172 (2016)
Dong, R., Weng, S., Yang, L., Liu, J.: Detection and direct readout of drugs in human urine using dynamic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and support vector machines. Anal. Chem. 87(5), 2937–2944 (2015)
Chen, N., Ding, P., Shi, Y., **, T., Su, Y., Wang, H., He, Y.: Portable and reliable surface-enhanced Raman scattering silicon chip for signal-on detection of trace trinitrotoluene explosive in real systems. Anal. Chem. 89(9), 5072–5078 (2017)
López-López, M., Merk, V., García-Ruiz, C., Kneipp, J.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the analysis of smokeless gunpowders and macroscopic gunshot residues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408(18), 4965–4973 (2016)
Pozzi, F., Leona, M.: Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy in art and archaeology. J. Raman Spectrosc. 47(1), 67–77 (2016)
Shadi, I.T., Chowdhry, B.Z., Snowden, M.J., Withnall, R.: Semi-quantitative analysis of alizarin and purpurin by surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy (SERRS) using silver colloids. J. Raman Spectrosc. 35(8–9), 800–807 (2004)
Canamares, M., Garcia-Ramos, J., Domingo, C., Sanchez-Cortes, S.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering study of the adsorption of the anthraquinone pigment alizarin on Ag nanoparticles. J. Raman Spectrosc. 35(11), 921–927 (2004)
Chen, K., Leona, M., Vo‐Dinh, K.C., Yan, F., Wabuyele, M.B., Vo‐Dinh, T.: Application of surface‐enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) for the identification of anthraquinone dyes used in works of art. J. Raman Spectrosc. Int. J. Orig. Work Aspects Raman Spectrosc. Includ. Higher Order Process. Brill. Rayleigh Scatt. 37(4), 520–527 (2006)
Pozzi, F., Cesaratto, A., Leona, F.: Recent advances on the analysis of polychrome works of art: SERS of synthetic colorants and their mixtures with natural dyes. Front. Chem. 7, 105 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledge the Manipal Academy of Higher Education for the support through Dr. TMA Pai Endowment Chair in Applied Nanosciences. He is also grateful to Mr. Aravind M and Ms. Alina Peethan for their support in creating the illustrations shown in the chapter. Support from Prof. Santhosh Chidangil of Department of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Manipal Academy of Higher Education is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
George, S.D. (2020). Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates: Fabrication, Properties, and Applications. In: Inamuddin, Boddula, R., Asiri, A. (eds) Self-standing Substrates. Engineering Materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29522-6_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29522-6_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-29521-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-29522-6
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)