Abstract
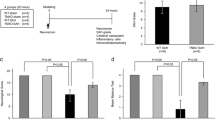
Vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) has been studied, but the mechanisms remain to be unveiled. Tenascin-C (TNC), which is a matricellular protein and reported to increase in spastic cerebral artery wall after SAH, is a ligand for both Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Our previous studies suggested the involvement of TNC and these receptors in vasoconstriction or vasospasm after SAH. In this study, we investigated whether upregulation of TNC and TLR4 is observed and if an EGFR inhibitor has suppressive effects against them in a mice endovascular perforation SAH model. At 24 h after SAH, TNC and TLR4 expressions were widely observed in spastic cerebral arteries, and these expressions were suppressed by the administration of an EGFR inhibitor. From these results, EGFR inhibitors possibly suppress the expression of not only EGFR but also TLR4 at least partly through regulating TNC upregulation. More studies are needed to clarify the precise mechanisms linking these receptors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawakita F, Fujimoto M, Liu L, Nakano F, Nakatsuka Y, Suzuki H. Effects of Toll-like receptor 4 antagonists against cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:6624–33.
Midwood K, Sacre S, Piccinini AM, Inglis J, Trebaul A, Chan E, Drexler S, Sofat N, Kashiwagi M, Orend G, Brennan F, Foxwell B. Tenascin-C is an endogenous activator of Toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nat Med. 2009;15:774–80.
Suzuki H, Kanamaru K, Shiba M, Fujimoto M, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Taki W. Cerebrospinal fluid tenascin-C in cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011;23:310–7.
Shiba M, Suzuki H, Fujimoto M, Shimojo N, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Kanamaru K, Matsushima S, Taki W. Imatinib mesylate prevents cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage via inhibiting tenascin-C expression in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46:172–9.
Fujimoto M, Shiba M, Kawakita F, Liu L, Nakasaki A, Shimojo N, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Suzuki H. Epidermal growth factor-like repeats of tenascin-C-induced constriction of cerebral arteries via activation of epidermal growth factor receptors in rats. Brain Res. 2016;1642:436–44.
Okada T, Suzuki H. Toll-like receptor 4 as a possible therapeutic target for delayed brain injuries after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12:193–6.
Nakano F, Fujimoto M, Kawakita F, Nakazaki A, Liu L, Nakatsuka Y, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Suzuki H. Receptors that mediate tenascin-C-induced constriction of cerebral arteries in rats. In: Sasaki T, Ohkuma H, Kanamaru K, Suzuki M, editors. Neurovascular events after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Tokyo: Narunia; 2017. p. 151–6.
Estany S, Vicens-Zygmunt V, Llatjós R, Montes A, Penín R, Escobar I, Xaubet A, Santos S, Manresa F, Dorca J, Molina-Molina M. Lung fibrotic tenascin-C upregulation is associated with other extracellular matrix proteins and induced by TGFβ1. BMC Pulm Med. 2014;14:120.
Jones PL, Crack J, Rabinovitch M. Regulation of tenascin-C, a vascular smooth muscle cell survival factor that interacts with the alpha v beta 3 integrin to promote epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation and growth. J Cell Biol. 1997;139:279–93.
Mercado-Gómez O, Landgrave-Gómez J, Arriaga-Avila V, Nebreda-Corona A, Guevara-Guzmán R. Role of TGFβ signaling pathway on Tenascin C protein upregulation in a pilocarpine seizure model. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108:1694–704.
De S, Zhou H, DeSantis D, Croniger CM, Li X, Stark GR. Erlotinib protects against LPS-induced endotoxicity because TLR4 needs EGFR to signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:9680–5.
Fujimoto M, Suzuki H, Shiba M, Shimojo N, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Kanamaru K, Matsushima S, Taki W. Tenascin-C induces prolonged constriction of cerebral arteries in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;55:104–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to Drs. Shiba and Suzuki. We thank Chiduru Yamamoto (Department of Neurosurgery, Mie University Graduate School of Medicine) for her assistance.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nakano, F. et al. (2020). Link Between Receptors That Engage in Develo** Vasospasm After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. In: Martin, R., Boling, W., Chen, G., Zhang, J. (eds) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, vol 127. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04615-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04615-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04614-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04615-6
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)