Abstract
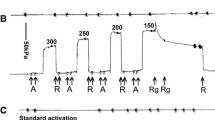
Single fibers from glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle were treated with 1-ethyl-3[3-(dimethylamino) propyl] carbodiimide (EDC), after rigor was induced, to crosslink myosin heads to actin. The optimally pre-stretched (∼1.8%), partially crosslinked fibers produce a large force when MgATP is depleted, and this force is abolished when MgATP is reintroduced, even in high ionic strength solution of 0.5 M (Tawada et al. 1989). We investigated the rate of force decay in the crosslinked, force-producing fibers using pulse photolysis of caged ATP (Goldman et al. 1984). The decay of force was fast, the rate of which depending both on the ionic strength and on the amount of ATP released (0.2–2.2 mM) with the second-order rate constant of 0.5–1 × 105 M-1s-1 at the ionic strength of 0.5 M. At high ionic strength (1–2M) force decayed at lower rate. At low ionic strength (0.1–0.2 M), however, force decayed more rapidly, but force redeveloped subsequently, which is probably caused by uncrosslinked myosin heads.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mornet, D., Bertrand, R., Pantel, P., Audemard, E. & Kassab R. Nature 292, 301–306 (1981).
Tawada, K. & Kimura, M. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility 7, 339–350 (1986).
Tawada, K. & Emoto, Y. in Molecular Mechanisms of Muscle Contraction (eds. Sugi, H. & Pollack, H.) 219–224 (Plenum Press, New York, 1988
Tawada, K., Huang, Y.-P. & Emoto, Y. Muscle Energetics (eds. Paul, R. J., Elzinga, G. & Yamada, K.) 37–43, (Alan R. Liss, New York, 1989
Goldman, Y.E., Hibberd, M G. & Trentham, D.R. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 354, 577–604 (1984).
Horiuti, K., Sakoda, T., Takei, M. & Yamada, K. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motility, 13, 199–205 (1992).
Yamada, K. Emoto, Y., Horiuti, K. & Tawada, K. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 446, 264P (1992).
Tawada, K. & Kawai, M. Biophys. J. 57, 643–647 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1993 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Yamada, K., Emoto, Y., Horiuti, K., Tawada, K. (1993). Effects of Ionic Strength on Force Transients Induced by Flash Photolysis of Caged ATP in Covalently Crosslinked Rabbit Psoas Muscle Fibers. In: Sugi, H., Pollack, G.H. (eds) Mechanism of Myofilament Sliding in Muscle Contraction. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 332. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2872-2_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2872-2_44
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6245-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-2872-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive