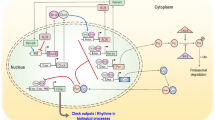
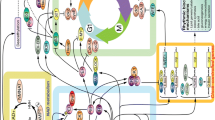
Abstract
Biological processes are highly structured in time as endogenously derived rhythms of short, intermediate, and long periods, with the circadian (24h) time structure most studied. Staging of key physiological and biochemical circadian rhythms gives rise to 24-h patterns in the exacerbation of chronic medical conditions, including arthritis, asthma, ulcer, and hypertension, plus manifestation of acute severe morbid and mortal events, such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and sudden cardiac death. Body rhythms may also significantly affect patient response to diagnostic tests and pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicities of diverse classes of medications. This chapter reviews circadian and other period biological rhythm dependencies of the pathophysiology of disease and pharmacology of medications as the basis for chronotherapeutics and development of time-modulated drug-delivery systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reinberg A, Smolensky MH (1983) Biologic rhythms and medicine. cellular, metabolic, pathophysiologic, and pharmacologic aspects. Springer, Heidelberg
Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) (1992) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg
Haus E, Touitou Y (1992) Principles of clinical chronobiology. In: Touitou Y Haus E (eds) Biological rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. New York, Springer, pp 6–34
Donahue JL, Lowenthal DT (1997) Nocturnal polyuria in the elderly person. Am J Med Sci 314:232–238
Kallas HE, Chintanadilok J, Maruenda J, Donahue JL, Lowenthal DT (1999) A clinical investigation of nocturnal polyuria in patients with nocturia: a diurnal variation in arginine vasopressin secretion and its relevance to mean blood pressure. Drugs Aging 15:429–437
Smolensky MH, Halberg F (1977) Circadian rhythm in airway patency and lung volumes. In: McGovern JP, Smolensky MH, Reinberg A, Thomas CC (eds) Chronobiology in allergy and immunology. Springfield, Illinois, pp 117–138
Halberg F, Simpson H (1967) Circadian acrophases of human 17-hydroxycorticosteroid excretion referred to midsleep rather than midnight. Hum Biol 39:405–413
Reinberg A (1979) Chronobiologic field trials of oil refinery shift workers. Chronobiologia 6(Suppl 1):1–119
Reinberg A, Smolensky MH (1992) Night and shift work and transmeridian and space flights. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 242–255
Dardente H, Cermakian N (2007) Review: molecular circadian rhythms in central and peripheral clocks in mammals. Chronobiol Int 24:195–214
Duguay D, Cermakian N (2009) The crosstalk between physiology and circadian clock proteins. Chronobiol Int 26:1479–1513
Hanifin JP, Brainard GC (2007) Photoreception for circadian, neuroendocrine, and neurobehavioral regulation. J Physiol Anthropol 26:87–94
Maronde E, Stehle JH (2007) The mammalian pineal gland: known facts, unknown facets. Trends Endocrinol Metab 18:142–149
Golombek DA, Rosenstein RE (2010) Physiology of circadian entrainment. Physiol Rev 90:1063–1102
Wever RA (1979) The circadian system of man, results of experiments under temporal isolation. Springer, New York
Pezuk P, Mohawk JA, Yoshikawa T, Sellix MT, Menaker M (2010) Circadian organization is governed by extra-SCN pacemakers. J Biol Rhythms 25:432–441
Khalsa SB, Jewett ME, Cajochen C, Czeisler CA (2003) A phase response curve to single bright light pulses in human subjects. J Physiol 549:945–952
Lagoguey M, Reinberg A, Legrand JC (1981) Variations chronobiologiques de la response testiculaire a l’HCG chez l’homme adulte sain. Ann Endocrinol 41:59–60
Lagoguey M, Reinberg A (1981) Circadian and circannual changes of pituitary hormones in healthy human males. In: Van Cauter E, Copinschi G (eds) Human pituitary hormones. Martinus Nijhoff Publ, The Hague, pp 261–285
Reinberg A (1983) Clinical chronopharmacology: an experimental basis for chronotherapy. In: Reinberg A, Smolensky MH (eds) Biologic rhythms and medicine. cellular, metabolic, pathophysiologic, and pharmacologic aspects. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 243–248
Smolensky MH, Peppas N (2007) Chronobiology, drug delivery, and chronotherapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:828–851
Folkard S (2008) Do permanent night workers show circadian adjustment? A review based on the endogenous melatonin rhythm. Chronobiol Int 25:215–224
Horne JA, Östberg O (1976) A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness–eveningness in human circadian rhythms. Int J Chronobiol 4:97–110
Duffy JF, Rimmer DW, Czeisler CA (2001) Association of intrinsic circadian period with morningness–eveningness, usual wake time, and circadian phase. Behav Neurosci 115:895–899
Roenneberg T, Wirtz-Justice A, Merrow M (2003) Life between the clocks: daily temporal patterns of human chronotypes. J Biol Rhythms 18:80–90
Baehr EK, Revelle W, Eastman CI (2000) Individual differences in the phase and amplitude of the human circadian temperature rhythm: with an emphasis on morningness–eveningness. J Sleep Res 9:117–127
Bailey SL, Heitkemper MM (2001) Circadian rhythmicity of cortisol and body temperature: morningness–eveningness effects. Chronobiol Int 18:249–261
Duffy JF, Dijk DJ, Hall EF, Czeisler CA (1999) Relationship of endogenous circadian melatonin and temperature rhythms to self-reported preference for morning or evening activity in young and older people. J Investig Med 47:141–150
Burgess HJ, Sharkey KM, Eastman CI (2002) Bright light, dark and melatonin can promote circadian adaptation in night shift workers. Sleep Med Rev 6:407–420
Lewy AJ, Bauer VK, Ahmed S, Thomas KH, Cutler NL, Singer CM, Moffit MT, Sack RL (1998) The human phase response curve (PRC) to melatonin is about 12 hours out of phase with the PRC to light. Chronobiol Int 15:71–83
Minors DS, Waterhouse JM, Wirz-Justice A (1991) A human phase-response curve to light. Neurosci Lett 133:36–40
Brismar K, Hylander B, Eliasson K, Rössner S, Wetterberg L (1988) Melatonin secretion related to side-effects of beta-blockers from the central nervous system. Acta Med Scand 223:525–530
Nathan PJ, Maguire KP, Burrows GD, Norman TR (1997) The effect of atenolol, a beta1-adrenergic antagonist, on nocturnal plasma melatonin secretion: evidence for a dose-response relationship in humans. J Pineal Res 23:131–135
Stoschitzky K, Sakotnik A, Lercher P, Zweiker R, Maier R, Liebmann P, Lindner W (1999) Influence of beta-blockers on melatonin release. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 55:111–115
Stoschitzky K, Stoschitzky G, Brussee H, Bonelli C, Dobnig H (2006) Comparing beta-blocking effects of bisoprolol, carvedilol and nebivolol. Cardiology 106:199–206
Conlon M, Lightfoot N, Kreiger N (2007) Rotating shift work and risk of prostate cancer. Epidemiology 18:182–183
Deacon S, English J, Tate J, Arendt J (1998) Atenolol facilitates light-induced phase shifts in humans. Neurosci Lett 242:53–56
Schernhammer ES, Laden F, Speizer FE, Willett WC, Hunter DJ, Kawachi I, Colditz GA (2002) Rotating night shifts and risk of breast cancer in women participating in the nurses’ health study. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1563–1568
Schernhammer ES, Laden F, Speizer FE, Willett WC, Hunter DJ, Kawachi I, Fuchs CS, Colditz GA (2003) Night-shift work and risk of colorectal cancer in the nurses’ health study. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:825–828
Lewy A, Emens JS, Lefler BJ, Yuhas K, Jackman AR (2005) Melatonin entrains free-running blind people according to a physiological dose–response curve. Chronobiol Int 22:1093–1106
Lewy AJ, Emens J, Jackman A, Yuhas K (2006) Circadian uses of melatonin in humans. Chronobiol Int 23:403–412
Hoban TM, Sack RL, Lewy AJ, Miller LS, Singer CM (1989) Entrainment of a free-running human with bright light? Chronobiol Int 6:347–353
Costa G, Di Milia L (2008) Aging and shift work. A complex problem to face. Chronobiol Int 25:165–181
Haus E, Smolensky MH (2006) Biological clocks and shift work: circadian dysregulation and potential long-term effects. Cancer Causes Control 17:489–500
Knutsson A (2003) Health disorders of shift workers. Occup Med 53:103–108
Morikawa Y, Nakagawa H, Miura K, Ishizaki M, Tabata M, Nishijo M, Higashiguchi K, Yoshita K, Sagara T, Kido T, Naruse Y, Nogawa K (1999) Relationship between shift work and onset of hypertension in a cohort of manual workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 25:100–104
Oishi M, Suwazono Y, Sakata K, Okubo Y, Harada H, Kobayashi E, Uetani M, Nogawa K (2005) A longitudinal study on the relationship between shift work and the progression of hypertension in Japanese male workers. J Hypertens 23:2173–2178
WHO-IARC (2010) Painting, firefighting, and shiftwork/IARC working group on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans (2007: Lyon, France). v. 98
Lee RE, Smolensky MH, Leach CS, Mc Govern JP (1997) Circadian rhythms in the cutaneous reactivity to histamine and selected antigens, including phase relationship to urinary cortisol excretion. Ann Allergy 38:231–236
Smolensky MH, Lemmer B, Reinberg A (2007) The chronobiology and chronotherapy of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:852–882
Gaultier C, Reinberg A, Girard F (1975) Circadian changes in lung resisatnce and dynamic compliance in healthy and asthmatic children. Effects of two bronchodilators. Respir Physiol 31:169–182
JNC 7 (2003) The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. JAMA 289:2560-2671
Drance SM (1960) The significance of the diurnal tension variations in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Arch Ophthalmol 64:494–501
Saccà SC, Rolando M, Marletta A, Macrí A, Cerqueti P, Ciurlo G (1998) Fluctuations of intraocular pressure during the day in open glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma and normal subjects. Opthalmologica 212:115–119
Jarrett RJ (1972) Circadian variations in blood glucose levels, in glucose tolerance and in plasma immunoreactive insulin levels. Acta Diabetol Lat 9:263–275
Zimmet PZ, Wall JR, Rome R, Stimmler L, Jarrett RJ (1974) Diurnal variation in glucose tolerance: associated changes in plasma insulin, growth hormone and non-esterified fatty acids. Br Med J 1:485–488
Solberg HE (1987) Approved recommendation (1986) on the theory of reference values, Part 1. The concept of reference values. Report of Expert Panel on Theory of Reference Values (EPTRV) of the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry (IFCC). Clin Chim Acta 165:111–118
PetitClerc C, Solberg HE (1987) Approved recommendation on the theory of reference values, Part 2. Selection of individuals for the production of reference values. Report of Expert Panel on Theory of Reference Values (EPTRV) of the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry (IFCC). J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 25:639–644
Haus E, Touitou Y (1992) Chronobiology in laboratory medicine. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biological rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Heidelberg, Springer, pp 673–708
Halberg F, Lee JK, Nelson WL (1978) Time-qualified reference intervals – chronodesms. Experientia 34:713–716
Haus E (1987) Requirements for chronobiotechnology and chronobiologic engineering in laboratory medicine. In: Scheving LE, Halberg F, Ehret CF (eds) Chronobiotechnology and chronobiological engineering. Appl Sci 120:331–372
DePrins J, Hecquet B (1992) Data processing in chronobiological studies. In: Touitou Y Haus E(eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 90–113
Halberg F, Cornelissen G, Sothern RB, Wallach LA, Halberg E, Ahlgren A, Kuzel M, Radke A, Barbosa J, Goetz F, Buckley J, Mandel J, Schuman L, Haus E, Lakatua D, Sackett L, Berg H, Kawasaki T, Ueno M, Uezono K, Matsouka M, Omae T, Tarquini B, Cagnoni M, Garcia Sainz M, Perez Vega E, Griffiths K, Wilson D, Donati L, Tatti P, Vasta M, Locatelli I, Camagna A, Lauro R, Tritsch G, Wendt HW (1981) International geographic studies of oncological interest on chronobiological variables. In: Kaiser HN (ed) Neoplasms-comparative pathology of growth in animals, plants, and man. Wiley, New York, pp 553–596
Halberg F, Lagoguey A, Reinberg A (1983) Human circannual rhythms over a broad spectrum of physiological processes. Int J Chronobiol 8:225–268
Haus E, Lakatua DJ, Halberg F, Halberg E, Cornelissen G, Sackett LL, Berg HG, Kawasaki T, Ueno M, Uezono K, Matsouka M, Omae T (1980) Chronobiological studies of plasma prolactin in women and Kyuishu, Japan and Minnesota USA. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 51:632–640
Haus E, Lakatua DJ, Sackett-Lundeen L, Swoyer J (1984) Chronobiology in laboratory medicine. In: Reitveld WT (ed) Clinical aspects of chronobiology. Baarn, Bakker, pp 13–82
Haus E, Lakatua DJ, Swoyer J, Sackett-Lundeen L (1983) Chronobiology in hematology and immunology. Am J Anatomy 168:467–517
Haus E, Nicolau GY, Lakatua DJ, Sackett-Lundeen L (1988) Reference values for chronopharmacology. Annu Rev Chronopharmacol 4:333–424
Kanabrocki EL, Sothern RB, Scheving LE, Vesely DL, Tsai TH, Shelstad J, Cournoyer C, Greco J, Mermall H, Ferlin H, Nemchausky BM, Bushnell DL, Kaplan E, Kahn S, Augustine G, Holmes E, Rumbyrt J, Sturtevant RP, Sturtevant F, Bremer F, Third JLHG, McCormick JB, Mudd CA, Dawson S, Sackett-Lundeen L, Haus E, Halberg F, Pauly JE, Olwin JH (1990) Reference values for circadian rhythms of 98 variables in clinically healthy men in the fifth decade of life. Chronobiol Int 7:445–461
Kanabrocki EL, Sothern RB, Scheving LE, Vesely DL, Tsai TH, Shelstad J, Cournoyer C, Greco J, Mermall H, Nemchausky BM, Bushnell DL, Kaplan E, Kahn S, Augustine G, Holmes E, Rumbyrt J, Sturtevant RP, Sturtevant F, Bremer F, Third JLHG, McCormick JB, Mudd CA, Dawson S, Olwin JH, Sackett-Lundeen L, Haus E, Halberg F, Pauly JE, Hrushesky WJM (1990) Circadian reference data for men in fifth decade of life. In: Hayes, DK, Pauly, JE, Reiter, RE (eds) Chronobiology: its role in clinical medicine, general biology and agriculture. Prog Clin Biol Res, Wiley/Liss, New York, 341A:771–781
Touitou Y, Fèvre M, Lagoguey M, Carayon A, Bogdan A, Reinberg A, Beck H, Cesselin F, Touitou C (1981) Age- and mental health-related circadian rhythms of plasma levels of melatonin, prolactin, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone in man. J Endocrinol 91:467–475
Touitou Y, Motohashi Y, Pati A, Lévi F, Reinberg A, Ferment O (1986) Comparison of cortical circadian rhythms documented in samples of saliva, capillary (fingertips) and venous blood from healthy subjects. Annu Rev Chronopharmacol 3:297–299
Touitou Y, Sulon J, Bogdan A, Touitou C, Reinberg A, Beck H, Sodoyez JC, Demey-Ponsart E, Van Cauwenberge H (1982) Adrenal circadian system in young and elderly human subjects: a comparative study. J Endocrinol 93:201–210
Touitou Y, Touitou C, Bogdan A, Reinberg A, Auzeby A, Beck H, Guillet PH (1986) Differences between young and elderly subjects in seasonal and circadian variations of total plasma proteins and blood volume as reflected by hemoglobin, hematocrit and erythrocyte counts. Clin Chem 32:801–804
Touitou Y, Touitou C, Bogdan A, Reinberg A, Motohashi Y, Auzeby A, Beck H (1989) Circadian and seasonal variations of electrolytes in aging humans. Clin Chil Acta 180:245–254
Reinberg A, Lagoguey M, Cesselin F, Touitou Y, Legrand JC, Delassalle A, Antreassian J, Lagoguey A (1978) Circadian and circannual rhythms in plasma hormones and other variables in five healthy young human males. Acta Endocrinol 88:417–427
Hanson EJ (1970) Multiple time series. Wiley, New York
MacNeill IB (1974) Tests for periodic components in multiple time series. Biometrika 61:57–70
Van Cauter E (1979) Method for characterization of 24-hr temporal variations of blood components. Am J Physiol 237:E255–E264
DePrins J, Cornelissen G, Malberg W (1986) Statistical procedures in chronobiology and chronotherapeutics. Annu Rev Chronopharmacol 2:27–141
Halberg F, Panofsky H (1961) I. Thermo-variance spectra; method and clinical illustrations. Exp Med Surg 19:284–309
Panofsky H, Halberg F (1961) II. Thermo-variance spectra; simplified computational example and other methodology. Exp Med Surg 19:323–338
Halberg F, Engeli M, Hamburger C, Hillman D (1965) Spectral resolution of low-frequency, small amplitude rhythms in excreted ketosteroids; probable androgen-induced circaseptan desynchronization. Acta Endocrinol 103(Suppl):5–54
Nelson WL, Tong YL, Lee JK, Halberg F (1979) Methods for cosinor rhythmometry. Chronobiologia 6:305–323
Halberg F, Tong YL, Johnson EA (1967) Circadian system phase – an aspect of temporal morphology; procedures and illustrative examples. In: von Mayersbach H (ed) The cellular aspects of biorhythms. Heidelberg, Springer, pp 20–48
Bingham C, Arbogast B, Cornelissen-Guillaume G, Lee JK, Halberg F (1982) Inferential statistical methods for estimating and comparing cosinor parameters. Chronobiologia 9:397–439
Arendt J (1995) Melatonin and the mammalian pineal gland. Chapman Hill, London
Mirick DK, Davis S (2008) Melatonin as a biomarker of circadian dysregulation (review). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:3306–3313
Touitou Y, Motohashi Y, Reinberg A, Touitou C, Bourdeleau P, Bogdan A, Auzéby A (1990) Effect of shift work on the night-time secretory patterns of melatonin, prolactin, cortisol, and testosterone. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 60:288–292
Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE (2009) Urinary melatonin levels and postmenopausal breast cancer risk in the Nurses’ Health Study cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:74–79
Schernhammer ES, Rosner B, Willett WC, Laden F, Colditz GA, Hankinson SE (2004) Epidemiology of urinary melatonin in women and its relation to other hormones and night work. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:936–943
Arendt J (1992) The pineal. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 348–362
Walker RF, Read GF, Wilson DW, Riad-Fahmy D, Griffiths K (1990) Chronobiology in laboratory medicine: principles and clinical applications illustrated from measurements of neutral steroids in saliva. In: Hayes DK, Pauly JE, Reiter RE (eds) Chronobiology: its role in clinical medicine, general biology and agriculture. Prog Clin Biol Res, Wiley/Liss, New York, 341A:105–117
Miles A, Philbrick DRS, Thomas DR, Grey J (1987) Diagnostic and clinical implications of plasma and salivary melatonin assay. Clin Chem 33:1295–1297
Archer SN, Viola AU, Kyriakopoulou V, von Schantz M, Dijk DJ (2008) Inter-individual differences in habitual sleep timing and entrained phase of endogenous circadian rhythms of BMAL1, PER2 and PER3 mRNA in human leukocytes. Sleep 31:608–617
Boivin DB, James FO, Wu A, Cho-Park PF, **ong H, Sun ZS (2003) Circadian clock genes oscillate in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Blood 102:4143–4145
Hida A, Kusanagi H, Satoh K, Kato T, Matsumoto Y, Echizenya M, Shimizu T, Higuchi S, Mishima K (2009) Expression profiles of PERIOD 1, 2 and 3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from older subjects. Life Sci 84:33–37
Takimoto M, Hamada A, Tomoda A, Ohdo S, Omura T, Sakato H, Kawatani J, Jodoi T, Nakagawa H, Terazono H, Koyanagi S, Higuchi S, Kimura M, Tukikawa H, Irie S, Saito H, Miike T (2005) Daily expression of clock genes in whole blood cells in healthy subjects and a patient with circadian rhythm sleep disorder. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:1273–1279
Teboul M, Barrat-Petit MA, Li XM, Claustrat B, Formento JL, Delaunay F, Lévi F, Milano G (2005) Atypical patterns of circadian clock gene expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Mol Med 83:693–699
Azama T, Yano M, Oishi K, Kadota K, Hyun K, Tokura H, Nishimura S, Matsunaga T, Iwanaga H, Miki H, Okada K, Hiraoka N, Miyata H, Takiguchi S, Fujiwara Y, Yasuda T, Ishida N, Monden M (2007) Altered expression profiles of clock genes hPer1 and hPer2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of cancer patients undergoing surgery. Life Sci 80:1100–1108
Waterhouse J, Edwards B, Mugarza J, Flemming R, Minors D, Calbraith D, Williams G, Atkinson G, Reilly T (1999) Purification of masked temperature data from humans: some preliminary observations on a comparison of the use of an activity diary, wrist actimetry, and heart rate monitoring. Chronobiol Int 16:461–475
Waterhouse J, Weinert D, Minors D, Atkinson G, Reilly T, Folkard S, Owens D, Macdonald I, Sytnik N, Tucker P (1999) The effect of activity on the waking temperature rhythm in humans. Chronobiol Int 16:343–357
Reinberg A, Ghata J, Halberg F, Apelbaum M, Gervais P, Boudon P, Abulker C, Dupont J (1974) Treatment schedules modify circadian timing in human adrenocortical insufficiency. In: Scheving LE, Halberg F, Pauly JE (eds) Chronobiology. Igaku Shoin Ltd, Tokyo, pp 168–173
Angeli A (1974) Circadian ACTH-adrenal rhythm in man. Chronobiologia 1(Suppl):253–268
Grant PH, Forsham PH, DiRaimando VC (1965) Suppression of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids in plasma and urine after single and divided doses of triamcinolone. N Engl J Med 273:1115–1118
Harter JG, Reddy WJ, Thorn GW (1963) Studies on an intermittent corticosteroid dosage regimen. N Engl J Med 296:591–595
Alten R, Döring G, Cutolo M, Gromnica-Ihle E, Witte S, Straub R, Buttgereit F (2010) Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with nighttime-release prednisone. J Rheumatol 37:2025–2031
Buttgereit F, Döring G, Schaeffler A, Witte S, Sierakowski S, Gromnica-Ihle E, Jeka S, Krueger K, Szechinski J, Alten R (2008) Efficacy of modified-release versus standard prednisone to reduce duration of morning stiffness of the joints in rheumatoid arthritis (CAPRA-1): A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 371:205–214
To H, Irie S, Tomonari M, Watanabe Y, Kitahara T, Sasaki H (2009) Therapeutic index of methotrexate depends on circadian cycling of tumor necrosis factor-α in collagen-induced arthritis rats and mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 61:1333–1338
To H, Yoshimatsu H, Tomonari M, Ida H, Tsurumoto T, Tsuji Y, Sonemoto E, Shimasaki N, Koyanagi S, Sasaki H, Ieiri I, Higuchi S, Kawakami A, Ueki Y, Eguchi K (2011) Methotrexate chronotherapy is effective against rheumatoid arthritis. Chronobiol Int 28:267–274
Haus E, Cusulos M, Sackett-Lundeen L, Swoyer J (1990) Circadian variations in blood coagulation parameters, alpha-antitrypsin antigen and platelet aggregation and retention in clinically healthy subjects. Chronobiol Int 7:203–216
Haus E, Smolensky MH (1999) Biologic rhythms in the immune system. Chronobiol Int 16:581–622
Fernandes G (1992) Chronobiology of immune functions: cellular and humoral aspects. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Heidelberg, Springer, pp 493–503
Wrba H, Dutter A, Sánchez de la Peña S, Wu J, Carandente F, Cornélissen G, Halberg F (1990) Secular or circadian effects of placebo and melatonin on murine breast cancer? In: Hayes DK, Pauly JE, Reiter RE (eds) Chronobiology: its role in clinical medicine, general biology, and agriculture. Wiley/Liss, Washington, pp 31–40
Wrba H, Halberg F, Dutter A (1986) Melatonin circadian-stage-dependently delays breast tumor development in mice injected daily for several months. Chronobiologia 13:123–128
Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA (1999) Gout and hyperuricemia. Am Fam Physician 59:925–934
Sydenham T (1850) The works of Thomas Sydenham. Translated from the Latin by R.G. Lathan
Rigas B, Torosis J, McDougall CJ, Vener KJ, Spiro HM (1990) The circadian rhythm of biliary colic. J Clin Gastroenterol 12:409–414
Manfredini R, Gallerani K, Cecilia O, Boari B, Fersini C, Portaluppi F (2002) Circadian pattern in occurrence of renal colic in an emergency department; an analaysis of patients notes. BMJ 324:767
Bellamy N, Sothern RB, Campbell J (2004) Aspects of diurnal rhythmicity in pain, stiffness, and fatigue in patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 31:379–389
Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Miller KA, Feigenbaum SL (1981) Primary fibromyalgia: clinical study of 50 patients with matched controls. Semin Arthritis Rheum 11:151–171
Moore JG, Halberg F (1987) Circadian rhythm of gastric acid secretion in active duodenal ulcer: Chronobiological statistical characteristics and comparison of acid sectretory and plasma gastrin patterns with healthy subjects and post-vagotomy and pyloroplasty patients. Chronobiol Int 4:101–110
Cugini P, Di Palma L, Battisti P, Leone G, Materia E, Parenzi A, Romano M, Ferrera U, Moretti M (1990) Ultradian, circadian and infradian periodicity of some cardiovascular emergencies. Am J Cardiol 66:240–243
Kroetz C (1940) Ein biologiescher 24-Stunden-Rhythmus des Blutkreislaufs bei Gesundheit und bei Herzschwache zugleich ein Beitrag zur tageszeitlichen Haufung einiger akuter Kreislaufstorungen. Munch Med Wschr 87:314–317
Turner-Warwick M (1998) Epidemiology of nocturnal asthma. Am J Med 85:6–8
Dethlefsen U, Repges R (1985) Ein neues Therapieprinzip bei nachtlichem Asthma. Med Klin 80:44–47
Ebata T, Aizawa H, Kamide R, Niimura M (1999) The characteristics of nocturnal scratching in adults with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 141:82–86
Smolensky MH, Tatar SE, Bergman SA, Losman JG, Barnard CN, Dasco CC, Kraft IA (1976) Circadian rhythmic aspects of human cardiovascular function: A review by chronobiologic statistical methods. Chronobiologia 3:337–371
Portaluppi F, Hermida RC (2007) Circadian rhythms in cardiac arrhythmias and opportunities for their chronotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:940–951
Tikkinen KA, Johnson TMn, Tammela TL, Sintonen H, Huhtala H, Auvinen A (2010) Nocturia frequency, bother, and quality of life: how much is too often? A population-based study in Finland. Eur Urol 57:488–496
Cruz IA, Drummond M, Wimck JC (2011) Obstructive sleep apnea symptoms beyond sleepiness and snoring: effects of nasal APAP therapy. Sleep Breath doi.10.1007/s11325-011-0502-4
Natarajan R (2010) Review of periodic limb movement and restless leg syndrome. J Postgrad Med 56:157–162
Portaluppi F, Cortelli P, Buonaura GC, Smolensky MH, Fabbain F (2009) Do restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movements of sleep play a role in nocturnal hypertension and increased cardiovascular disease risk in renal patients. Chronobiol Int 26:1206–1221
Kelmanson IA (1991) Circadian variation of the frequency of sudden infant death syndrome and of sudden death from life-threatening conditions in infants. Chronobiologia 18:181–186
Reinberg AE, Gervais P, Levi F, Smolensky M, Del Cerro L, Ugolini C (1988) Circadian and circannual rhythms of allergic rhinitis: an epidemiologic study involving chronobiologic methods. J Allergy Clin Immunol 81:51–62
Smolensky MH, Reinberg A, Labrecque G (1995) Twenty-four hour pattern in symptom intensity of viral and allergic rhinitis: Treatment implications. J Allergy Immunol 95:1084–1096
Bellamy N, Sothern RB, Campbell J, Buchanan WW (1991) Circadian rhythm in pain, stiffness, and manual dexterity in rheumatoid arthritis: relation between discomfort and disability. Ann Rhuem Dis 50:243–348
Fox AW, Davis RL (1998) Migraine chronobiology. Headache 38:436–441
Solomon GD (1992) Circadian rhythms and migraine. Cleveland Clin J Med 59:326–329
Mulcahy D, Keegan J, Cunningham D, Quyyumi A, Crean P, Park A, Wright C, Fox K (1998) Circadian variation of total ischemic burden and its alteration with anti-anginal agents. Lancet 2:755–759
Rocco MB, Barry J, Campbell S, Nabel E, Cook EF, Goldman L, Selwyn AP (1987) Circadian variation of transient myocardial ischemia in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 75:395–400
Cohen MC, Rohtla KM, Lavery CE, Muller JE, Mittleman MA (1997) Meta analysis of the morning excess of acute myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death. Am J Cardiol 79:1512–1516
Shaw E, Tofler GH (2009) Circadian rhythm and cardiovascular disease. Curr Atheroscler Rep 11:289–295
Elliott WJ (1998) Circadian variation in the timing of stoke onset. A meta-analysis. Stroke 29:992–996
Gallerani M, Manfredini R, Fersini C (1993) Chronoepidemiology in human disease. Ann Inst Super Sanita 29:569–579
Gallerani M, Manfredini R, Ricci L, Grandi E, Cappato R, Calò G, Pareschi PL, Fersini C (1992) Sudden death from pulmonary thromboembolism: chronobiological aspects. Eur Heart J 6:305–323
Rossenwasser AM, Wirz-Justice A (1997) Circadian rhythms and depression: clinical and experimental models. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms, handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Springer, Berlin, pp 457–486
Wehr TA (1982) Circadian rhythm disturbances in depression and mania. In: Brown FM, Graeber RC (eds) Rhythmic aspects of behavior. Lawrence Erlbaum Ass, New Jersey, pp 399–428
Mooney M, Green C, Hatsukami D (2006) Nicotine self-administration: cigarette versus nicotine gum diurnal topography. Hum Psychopharamcol 21:539–548
Mützell S (1998) Alcohol consumption, clinical findings and retrospective psycho social data in a random sample of men in suburban Stockholm. Scand J Prim Health Care 6:185–192
Bellamy N, Sothern RB, Campbell J (1990) Rhythmic variations in pain perception in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Rheumatol 17:364–372
Bellamy N, Sothern RB, Campbell J, Buchanan WW (2002) Rhythmic variations in pain, stiffness, and manual dexterity in osteoarthristis. Ann Rheum Dis 61:1075–1080
Manfredini R, Gallerani M, Salmi R, Calò G, Pasin M, Bigoni M, Fersini C (1994) Circadian variation in the time of onset of acute intestinal bleeding. J Emerg Med 12:5–9
Svanes C, Sothern RB, Sorbye H (1998) Rhythmic patterns in incidence of peptic ulcer perforation over 5.5 decades in Norway. Chronobiol Int 15:241–264
Kim YK, Oh WH, Park KH, Kim JM, Kim DH (2010) Circadian blood pressure and intraocular pressure patterns in normal tension glaucoma patients with undisturbed sleep. Korean J Opththalmol 24:23–28
Liu JH, Bouligny RP, Kripke DF, Weinreb RN (2003) Nocturnal elevation of intraocular pressure is detectable in the sitting position. Invest Opththalmol Vis Sci 44(10):4439–4442
Baxil CW, Walczak TS (1997) Effects of sleep and sleep stage on epileptic and nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsia 38:56–62
Langdon-Down M, Brain WR (1929) Time of day in relation to convulsion in epilepsy. Lancet 1:1029–1032
Bjorvatn B, Pallesen S (2009) A practical approach to circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Sleep Med Rev 13:47–60
Pandi-Perumal SR, Trakht I, Spence DW, Srinivasan V, Dagan Y, Cardinali DP (2008) The roles of melatonin and light in the pathophysiology and treatment of circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 4:436–447
Lamont EW, James FO, Boivin DB, Cermakian N (2007) From circadian clock genes to pathologies. Sleep Med Rev 8:547–556
Aoki H, Ozeki Y, Yamada N (2001) Hypersensitivity of melatonin suppression in response to light in patients with delayed sleep phase syndrome. Chronobiol Int 18:263–271
Shanware NP, Hutchinson JA, Kim SH, Zhan L, Bowler MJ, Tibbetts RS (2011) Casein kinease1-dependent phosphorylation of familial advanced sleep phase syndrome-associated residues controls PERIOD 2 stability. J Biochem 286:12766–12774
Reinberg A, Ashkanazi I (2008) Internal desynchronization of circadian rhythms and tolerance to shift work. Chronobiol Int 25:625–643
Hack LM, Lockley SW, Arendt J, Skene DJ (2003) The effects of low-dose melatonin on the free-running rhythm of blind subjects. J Biol Rhythms 18:420–429
Kennaway DJ (2010) Clock genes at the heart of depression. J Pyschopharmacol 24:5–14
Kripke D, Drennan MD, Elliott JA (1992) The complex circadian pacemaker in affective disorder. In: Touitou Y Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinic and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 265–276
Parry BL, Meliska CJ, Sorenson DL, Martínez LF, López AM, Elliott JA, Hauger RL (2011) Reduced phase-advance of plasma melatonin after bright morning light in the luteal, but not follicular, menstrual cycle phase in premenstrual dysphoric disorder: an extended study. Chronobiol Int 28:415–424
Utge SJ, Soronen P, Loukola A, Kronholm E, Ollilia HM, Pirkola S, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Partonen T, Paunio T (2010) Systemic analysis of circadian genes in a population-based sample reveals association of TIMELESS with depression and sleep disturbance. PLos One 5:e9259
Reinberg AE (1991) Concepts of circadian chronopharmacology. In: Hrushesky WJM, Langer R, Theeuwes F (eds) Temporal control of drug delivery. Ann N Y Acad Sci 618:102–115
Lemmer B (ed) (1989) Chronopharmacology: cellular and biochemical interactions. Marcel Dekker, New York
Lemmer B (2005) Chronopharmacology and controlled drug release. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2:667–681
Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) (1997) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms. Springer, Heidelberg
Bélanger PM (1993) Chronopharmacology in drug research and therapy. Adv Drug Res 24:1–80
Bélanger PM, Bruguerolle B, Labrecque G (1997) Rhythms in pharmacokinetics: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms: handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Springer, Berlin, pp 177–204
Bruguerolle B (1998) Chronopharmacokinetics. Current status. Clin Pharmacokinet 35:83–94
Lemmer B (2006) Clinical chronopharmacology of the cardiovascular system: hypertension and coronary heart disease. Clin Ther 157:41–52
Lemmer B, Bruguerolle B (1994) Chronopharmacokinetics. Are they clinically relevant? Clin Pharmacokinet 26:419–427
Moore J, Merki H (1997) Gastrointestinal tract. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms, handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Berlin, Springer, pp 351–373
Reinberg AE, Smolensky MH (1982) Circadian changes in drug disposition in man. Clin Pharmacokinet 7:401–420
Witte K, Lemmer B (1997) Rhythms in second message mechanism. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms, handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Berlin, Springer, pp 135–156
Sanders SW, Moore JG, Buchi KN, Bishop AL (1988) Circadian variation in the pharmacodynamic effect of intrvenous ranitidine. Annu Rev Chronopharmacol 5:335–338
Sanders SW, Moore JG, Buchi KN, Bishop AL (1989) Pharmacodynamics of intravenous ranitidine after bolus and continuous infusion in patients with healed duodenal ulcer. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46:545–551
White C, Smolensky MH, Sanders SW, Buchi KN, Moore JG (1991) Day-night and individual differences in response to constant-rate ranitidine infusion. Chronobiol Int 8:56–66
Decousus H (1992) Chronobiology in hemostasis. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 554–565
Decousus H, Croze M, Lévi F, Perpoint B, Jaubert J, Bonadona JF, Reinberg A, Queneau P (1985) Circadian changes in anticoagulant effect of heparin infused at a constant rate. Br Med J 290:341–344
Haus E (2007) Chronobiology of hemostasis and inferences for the chronotherapy of coagulation disorders and thrombosis prevention. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:966–984
Bruguerolle B, Labrecque G (2007) Rhythm patterns in pain and their chronotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:883–895
Smolensky MH, Hermida R, Ayala DE, Portaluppi F (2010) Administration-time-dependent effects of antihypertension medications: basis for the chronotherapy of hypertension (review). Blood Press Monitor 15:173–180
Portaluppi F, Smolensky MH (2010) Perspectives on the chronotherapy of hypertension based on the results of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int 27:1652–1667
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, Fernández JR (2010) Influence of circadian time of hypertension treatment on cardiovascular risk: Results of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int 27:1629–1651
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Fontao MJ, Mojón A, Fernández JR (2010) Chronotherapy with valsartan/amlodipine fixed combination: improved blood pressure control of essential hypertension with bedtime dosing. Chronobiol Int 27:1287–1303
Os I, Bratland B, Dahlhöf B, Syvertsen JO, Tretli S (1994) Female preponderance for lisinopril cough in hypertension. Am J Hypertens 7:1012–1015
Oparil S, Miller AP (2005) Gender and hypertension. J Clin Hypertens 7:305–309
Kloner RA, Sowers JR, DiBona GF, Gaffney M, Wein M (1996) Sex- and age-related antihypertensive effects of amlodipine. The Amlodipine Cardiovascular Community Trial Study Group. Am J Cardiol 77:713–722
Canzanello VJ, Baranco-Pryor E, Rahbari-Oskoui F, Schwartz GL, Boerwinkle E, Turner ST, Chapman AB (2008) Predictors of blood pressure response to the angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 21:61–66
Saunders E, Cable G, Neutel J (2008) Predictors of blood pressure response to angiotensin receptor blocker/diuretic combination therapy: a secondary analysis of the irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide blood pressure reductions in diverse populations (INCLUSIVE) study. J Clin Hypertens 10:27–33
Ayala DE, Hermida RC (2010) Sex differences in the administration-time-dependent effects of low-dose aspirin on ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. Chronobiol Int 27:354–362
Hermida RC, Calvo C, Ayala DE, Domínquez MJ, Covelo M, Fernández JR, Mojón A, López JE (2003) Administration time-dependent effects of valsartan on ambulatory blood pressure of hypertensive subjects. Hypertension 42:283–290
Cambar J, L’Azou B, Cal C (1992) Chronotoxicology. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 139–150
Cambar J, Pons M (1997) New trends in chronotoxicology. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms, handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Springer, Berlin, pp 557–588
Halberg F (1960) Temporal coordination of physiologic function. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 25:289–310
Beauchamp D, Labrecque G (2007) Chronobiology and chronotoxicology of antibiotics and aminoglycosides. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:896–903
Ceresa F, Angeli A, Buccuzzi G, Molino G (1969) Once-a-day neurally stimulated and basal ACTH secretion phases in man and their response to corticoid inhibition. J Clin Endocrinol 29:1074–1082
Haus E (2007) Chronobiology in the endocrine system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:985–1014
McHugh RB, Smolensky MH, Halberg F (1975) Biological rhythm experimentation: a longitudinal design and analysis. Chronobiologia 2:1–12
Smolensky MH, Reinberg A (1976) The chronotherapy of corticosteroids: a practical application of chronobiological findings to clinical and hospital nursing. J Nursing Clinics 11:609–620
Hermida RC, Ayala DC, Mojón A, Fernández JR (2008) Chronotherapy with nifedipin GITS in hypertensive patients: improved efficacy and safety with bedtime dosing. Am J Hypertens 21:948–954
Bernard S, Cajavec Bernard B, Lévi F, Herzel H (2010) Tumor growth rate determines the timing of optimal chronomodulated treatment schedules. PLOS Comput Biol 6(3):e1000712
Hrushesky WJM, März WJ (1992) Chronochemotherapy of malignant tumors: Temporal aspects of antineoplastic drug toxicity. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 611–634
Lévi F (1997) Chronopharmacology of anticancer agents. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Physiology and pharmacology of biological rhythms, handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 125. Springer, Berlin, pp 299–350
Lévi F, Focan C, Karaboué A, de la Valette V, Focan-Henrard D, Baron B, Kreutz F, Giacchetti S (2007) Implications of circadian clocks for the rhythmic delivery of cancer medications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:1015–1035
Mormont C, Boughattas N, Lévi F (1989) Mechanisms of circadian rhythms in the toxicity and efficacy of anticancer drugs: relevance for the development of new analogues In: Lemmer B (ed) Chronopharmacology: cellular and biochemical interactions. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 395–437
Sauerbier I (1992) Rhythms in drug-induced teratogensis. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Heidelberg, Springer, pp 151–157
Smolensky MH (1998) Knowledge and attitudes of American physicians and public about medical chronobiology and chronotherapeutics. Findings of two 1996 Gallup surveys. Chronobiol Int 15:377–394
Arendt J, Aldhous M, Marks V (1986) Alleviation of jet-lag by melatonin: preliminary results of a controlled double-blind trial. Br Med J 292:1170
D'Alonzo GE, Smolensky MH, Feldman S, Gianotti LA, Emerson MB, Staudinger H, Steinijans VM (1990) Twenty-four-h lung function in adult patients with asthma: chronoptimized theophylline therapy once-daily dosing in the evening versus conventional twice-daily dosing. Am Rev Respir Dis 142:84–90
Neuenkirchen H, Wilkens JH, Oellerich M, Sybrecht GW (1985) Nocturnal asthma: effect of a once per evening dose of sustained-release theophylline. Eur J Respir Dis 66:196–204
Merki HS, Witzel L, Hare K, Scheurle E, Bauerfeind P, Blum AL (1987) Single dose treatment with H2-receptor antagonists: Is bedtime too late? Gut 28:451–454
Stalenhoff AFH, Mol MJTM, Stuyt PMJ (1989) Efficacy and tolerability of simvastatin. Am J Med 87:39s–43s
Sica D, Frishman WH, Manowitz N (2003) Pharmacokinetics of propranolol after single and multiple dosing with sustained released propranolol or propranolol CR (Innopran XL™), a new chronotherapeutic formulation. Heart Dis 5:176–181
Sista S, Lai J, Eradiri O, Albert K (2003) Pharmacokinetics of a novel diltiazem HCL extended-release tablet formulation for evening administration. J Clin Pharmacol 43:1149–1157
Smith DHG, Neutel JM, Weber MA (2001) A new chronotherapeutic oral drug absorption system for verapamil optimizes blood pressure control in the morning. Am J Hypertens 14:14–19
Smolensky MH, Hermida R, Portaluppi F, Haus E, Reinberg A (2005) Chronotherapeutics in the treatment of hypertersion. In: Oparil S, Weber MA (eds) Hypertension: a companion to Brenner and Rector’s the kidney, 2nd edn. Philadelphia, Elsevier Saunders, pp 530–542
White WB, Anders RJ, MacInyre JM, Black HR, Sica DA (1995) Nocturnal dosing of a novel delivery system of verapamil for systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 76:375–380
Kunkel G, Steinijans VW, Borner K (1987) Chrono-optimization of the time of evening administration of theophylline with unequally divided twice daily dosing. Chronobiol Int 4:364–368
Postma DS, Koëter GH, vd Mark TW, Reig RP, Sluiter HJ (1985) The effects of oral slow-release terbutaline on the circadian variation in spirometry and arterial blood gas levels in patients with chronic air flow obstruction. Chest 87:653–657
Portaluppi F, Manfredini R, Fersini C (1999) From a static to a dynamic concept of risk: the circadian epidemiology of cardiovascular risk. Chronobiol Int 16:33–50
Black HR, Elliott WJ, Neaton JD, Grandits G, Grambsch P, Grimm RH, Hansson L, Lacoucière Y, Muller J, Sleight P, Weber MA, White WB, Williams G, Wittes J, Zanchetti A, Fakouhi TD (1998) Rationale and design for the Controlled ONset Verapamil INvestigation of Cardiovascular Endpoints (CONVINCE) trial. Control Clin Trials 19:370–390
Black HR, Elliott WJ, Grandits G, Grambsch P, Lucente T, White WB, Neaton JD, Grimm RH, Hansson L, Lacourciere Y, Muller J, Sleight P, Weber MA, Williams G, Wittes J, Zanchetti A, Anders RJ, Group CR (2003) Principal results of the Controlled Onset Verapamil Investigation of Cardiovascular End Points (CONVINCE) trial. JAMA 289:2073–2082
Black HR, Elliott WJ, Grandits G, Grambsch P, Lucente T, Neaton JD, Grimm RH, Hansson L, Lacourcière Y, Muller JE, Sleight P, Weber MA, White WB, Williams GH, Wittes J, Zanchett A, Anders RJ, Group CR (2005) Results of the Controlled ONset Verapamil INvestigation of Cardiovascular Endpoints (CONVINCE) trial by geographical region. J Hypertens 23:1099–1106
Hermida RC (2007) Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in the prediction of cardiovascular events of chronotherapy: rationale and design of the MAPEC study. Chronobiol Int 24:749–775
Bennett BM, Leitman DC, Schroeder H, Kawamoto JH, Nakatsu K, Murad F (1989) Relationship between biotransformation of glyceryl trinitrate and cyclic GMP accumulation in various cultured cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 250:316–322
Fung H-L, Chung S-J, Bauer JA, Chong S, Kowaluk EA (1992) Biochemical mechanisms of organic nitrate action. Am J Cardiol 70:4B–10B
Salvemini D, Pistelli A, Vane J (1993) Conversion of glyceryl trinitrate to nitric oxide in tolerant and non-tolerant smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 108:162–169
Waldman SA, Rapoport RM, Ginsburg R, Murad F (1986) Densitization to nitroglycerin in vascular smooth muscle from rat and human. Biochem Pharmacol 35:3525–3531
Enbright GE (1914) The effects of nitroglycerin on those engaged in its manufacture. J Am Med Assoc 62:201–202
Stewart D (1888) Remarkable tolerance to nitroglycerin. Philadelphia Polyclinic 6:43
Chen Z, Zhang J, Stamler JS (2002) Identification of the enzymatic mechanism of nitroglycerin bioactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8306–8311
Katz RJ (1990) Mechanism of nitrate tolerance: a review. Cardiovasc Drugs Therapy 4:247–252
Hinz B, Schroeder H (1998) Nitrate tolerance is specific for nitric acid esters and its recovery requires intact protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:232–235
Kenkare S, Benet LZ (1996) Tolerance to nitroglycerin in rabbit aorta. Biochem Pharmacol 51:1357–1361
Thadhani U (1992) Role of nitrates in angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 70:43B–53B
Kimura E, Hosoda S, Katoh K, Endo M, Yasue H, Asada S, Kuroiwa A (1978) Panel discussion on the variant form of angina pectoris. Jpn Circ J 42:455–476
Kuroiwa A (1978) Symptomology of variant angina. Jpn Circ J 42:459–478
Conn PM, Crowley WFJ (1994) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its analogs. Annu Rev Med 45:391–405
Huirne JA, Lambalk CB (2001) Gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor antagonists. Lancet 358:1793–1803
Belchetz PE, Plant TM, Nakai Y, Keogh EJ, Knobil E (1978) Hypophysial response to continuous and intermittent delivery of hypopthalamic gonadotropin releasing hormone. Science 202:632–633
Knobil E (1980) The role of signal pattern in the hypothalamic control of gonadotropin secretion. In: Ortavant R, Reinberg A (eds) Rhythmes et reproduction. Paris, Masson, pp 75–80
Nakai Y, Plant TM, Hess DL, Keoch EJ, Knobil E (1978) On the sites of negative and positive feedback action of estradiol in the control of gonadotropin secretion in the Rhesus monkey. Endocrinology 102:1008–1014
Filicori M, Santoro N, Merriam GR, Crowley WFJ (1986) Characterization of the physiological pattern of episodic gonadotropin secretion throughout the human menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 62:1136–1144
Reame N, Sauder SE, Kelch RP, Marshall JC (1984) Pulsatile gonadotropin secretion during the human menstrual cycle: evidence for altered frequency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59:328–337
Hall JE, Schoenfeld DA, Martin KA, Crowley WFJ (1992) Hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion and follicle-stimulating hormone dynamics during the luteal-follicular transition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 74:600–607
Knobil E (1980) The neuroendocrine control of the menstrual cycle. Recent Prog Horm Res 36:53–88
Crowley WFJ, Vale W, Rivier J, MacArthur JW (1981) LH and RH in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. In: Zatuchini GI, Schelter JD, Sciarra JJ (eds) LH-RH peptides as female and male contraceptives. Philadelphia, Harper, pp 321–333
Santen RJ, Manni A, Harvey H (1986) Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs for the treatment of breast and prostatic carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 7:129–145
Macklon NS, Stouffer RL, Giudice LC, Fauser BC (2006) The Science behind 25 years of ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization. Endocr Rev 27:170–207
Gompel A, Poitout P (1997) Inducteurs de l’ovulation. In: Maurais-Jarvis P, Schaison P, Touraine P (eds) Médecine de la reproduction. Paris, Flammarion, pp 604–616
Gompel A (2003) Induction de l’ovulation par administration pulsatile de Gn-RH par pompe portable. In: Reinberg AE (ed) Chronobiologie Médicale et Chronothérapeutique. Paris, Flammarion, pp 177–180
Leyendecker G, Wildt L, Hansmann M (1980) Pregnancies following chronic intermittent (pulsatile) administration of Gn-Rh by means of a portable pump (“Zyklomat”) – a new approach to the treatment of infertility in hypothalamic amenorrhea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 51:1214–1216
Hayes FJ, Seminara SB, Crowley WF Jr (1998) Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am 27:739–763
Santoro N, Filicori M, Crowley WF Jr (1986) Hypogonadotropic disorders in men and women: diagnosis and therapy with pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Endocr Rev 7:11–23
Spratt DI, Crowley WF Jr, Butler JP, Hoffman AR, Conn PM, Badger TM (1985) Pituitary luteinizing hormone responses to intravenous and subcutaneous administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in men. JCE & M 61:890–895
Farhy LS, Veldhuis JD (2005) Deterministic construct of amplifying actions of ghrelin on pulsatile growth hormone secretion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R1649–R1663
Giustina A, Veldhuis JD (1998) Pathophysiology of the neuroregulation of growth hormone secretion in experimental animals and the human. Endocr Rev 19:717–797
Veldhuis JD, Bowers CY (2003) Three-peptide control of pulsatile and entropic feedback-sensitive modes of growth hormone secretion: modulation by estrogen and aromatizable androgen (review). J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 16(Suppl 3):587–605
Veldhuis JD, Roelfsema F, Keenan DM, Pincus S (2011) Gender, age, body mass index, and IGF-1 individually and jointly determine distinct GH dynamics: analyses in one hundred healthy adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:115–121
Isgaard J, Carlsson L, Isaksson O, Jansson J (1988) Pulsatile intravenous growth hormone (GH) infusion to hypophysectomized rats increases insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acid in skeletal tissues more effectively than continuous GH infusion. Endocrinology 123:2605–2610
Jaffe CA, Turgeon DK, Lown K, Demott-Friberg R, Watkins PB (2002) Growth hormone secretion pattern is an independent regulator of growth hormone actions in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E1008–E1015
Veldhuis JD, Bowers CY (2010) Integrating GHS into the ghrelin system (Review). Int J Peptides 2010:879503
Veldhuis JD, Roemmich JN, Richmond EJ, Bowers CY (2006) Somatotropic and gonadotropic axes linkages in infancy, childhood, and the puberty-adult transition. Endocr Rev 27:101–140
Litman T, Halberg F, Ellis S, Bittner JJ (1958) Pituitary growth hormone and mitoses in immature mouse liver. Endocrinology 62:361–364
Veldhuis JD, Keenan DM, Pincus SM (2008) Motivations and methods for analyzing pulsatile hormone secretion (review). Endocr Rev 29:823–864
Wu FC, Butler GE, Kelnar CJ, Huhtaniemi I, Veldhuis JD (1996) Ontogeny of pulsatile gonadotropin releasing hormone secretion from midchildhood, through puberty, to adulthood in the human male: a study using deconvolution analysis and an ultrasensitive immunofluorometric assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1798–1805
Farhy LS, Veldhuis JD (2004) Putative GH pulse renewal: periventricular somatostatinergic control of an arcuate-nuclear somatostatin and GH-releasing hormone oscillator. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286:R1030–R1042
Farhy LS, Straume M, Johnson ML, Kovatchev B, Veldhuis JD (2002) Unequal autonegative feedback by GH models the sexual dimorphism in GH secretory dynamics. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R753–R764
Veldhuis JD, Evans WS, Shah N, Story S, Bray MJ, Anderson SM (1999) Proposed mechanisms of sex-steroid hormone neuromodulation of the human GH-IGP-I axis. In: Veldhuis JD, Giustina A (eds) Sex-steroid interactions with growth hormone. Springer, New York, pp 93–121
Arvat E, Ceda GP, Di Vito L, Ramunni J, Gianotti L, Broglio F, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E (1998) Age-related variations in the neuroendocrine control, more than impaired receptor sensitivity, cause the reduction in the GH-releasing activity of GHRPs in human aging. Pituitary 1:51–58
Van Cauter E, Plat L, Copinschi G (1998) Interrelations between sleep and the somatotropic axis. Sleep 21:553–566
Ho KY, Evans WS, Blizzard RM, Veldhuis JD, Merriam GR, Samojlik E, Furlanetto R, Rogol AD, Kaiser DL, Thorner MO (1987) Effects of sex and age on the 24-h profile of growth hormone secretion in man: importance of endogenous estradiol concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64:51–58
Holl RW, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Taylor WM, Thorner MO (1991) Thirty-second sampling of plasma growth hormone in man: correlation with sleep stages. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:854–861
Krueger JM, Obál F Jr (1993) Growth hormone-releasing hormone and interleukin-1 in sleep regulation. FASEB J 7:645–652
Ocampo-Lim B, Guo W, DeMott-Friberg R, Barkan AL, Jaffe CA (1996) Nocturnal growth hormone (GH) secretion is eliminated by infusion of GH-releasing hormone antagonist. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:4396–4399
Gronfier C, Luthringer R, Follenius M, Schaltenbrand N, Macher JP, Muzet A, Brandenberger G (1996) A quantitative evaluation of the relationships between growth hormone secretion and delta wave electroencephalographic activity during normal sleep and after enrichment in delta waves. Sleep 19:817–824
Van Cauter E, Plat L, Scharf MB, Leproult R, Cespedes S, L’Hermite-Balériaux M, Copinschi G (1997) Simultaneous stimulation of slow-wave sleep and growth hormone secretion by gamma-hydroxybutyrate in normal young men. J Clin Invest 100:745–753
Anderson LA, McTernan PG, Barnett AH, Kumar S (2001) The effects of androgens and estrogens on preadipocyte proliferation in human adipose tissue: influence of gender and site. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5045–5051
Leung KC, Johannsson G, Leong GM, Ho KK (2004) Estrogen regulation of growth hormone action. Endocr Rev 25:693–721
Davey HW, Wilkins RJ, Waxman DJ (1999) STAT5 signaling in sexually dimorphic gene expression and growth patterns. Am J Hum Genet 65:959–965
Rudling M, Norstedt G, Olivecrona H, Reihner E, Gustafsson JA, Angelin B (1992) Importance of growth hormone for the induction of hepatic low density lipoprotein receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:6983–6987
Laron Z (2004) Laron syndrome (primary growth hormone resistance or insensitivity): the personal experience 1958–2003. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:1031–1044
Roelfsema F, Biermasz NR, Veldman RG, Veldhuis JD, Frölich M, Stokvis-Brantsma WH, Wit JM (2000) Growth hormone (GH) secretion in patients with an inactivating defect of the GH-releasing hormone (GHRH) receptor is pulsatile: evidence for a role for non-GHRH inputs into the generation of GH pulses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2459–2464
van Coevorden A, Mockel J, Laurent E, Kerkhofs M, L’Hermite-Balériaux M, Decoster C, Nève P, Van Cauter E (1991) Neuroendocrine rhythms and sleep in aging men. Am J Physiol 260(4 Pt 1):E651–E661
Veldhuis JD, Liem AY, South S, Weltman A, Weltman J, Clemmons DA, Abbott R, Mulligan T, Johnson ML, Pincus S, Straume M, Iranmanesh A (1995) Differential impact of age, sex steroid hormones, and obesity on basal versus pulsatile growth hormone secretion in men as assessed in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescence assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:3209–3222
Martin FC, Yeo AL, Sonksen PH (1997) Growth hormone secretion in the elderly: aging and the somatopause. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 11:223–250
Biermasz NR, Pereira AM, Frölich M, Romijn JA, Veldhuis JD, Roelfsema F (2004) Octreotide represses secretory-burst mass and nonpulsatile secretion but does not restore event frequency or orderly GH secretion in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 286:E25–E30
Hartman ML, Pincus SM, Johnson ML, Matthews DH, Faunt LM, Vance ML, Thorner MO, Veldhuis JD (1994) Enhanced basal and disorderly growth hormone secretion distinguish acromegalic from normal pulsatile growth hormone release. J Clin Invest 95:1277–1288
Faje AT, Barkan AL (2010) Basal, but not pulsatile, growth hormone secretion determines the ambient circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2486–2491
Dimaraki EV, Jaffe CA, DeMott-Friberg R, Chandler WF, Barkan AL (2002) Acromegaly with apparently normal GH secretion: implications for diagnosis and follow-up. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3537–3542
van den Berg G, Pincus SM, Frölich M, Veldhuis JD, Roelfsema F (1998) Reduced disorderliness of growth hormone release in biochemically inactive acromegaly after pituitary surgery. Eur J Endocrinol 138:164–169
Cordido F, Garcia-Buela J, Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Martinez T, Vidal O (2010) The decreased growth hormone response to growth hormone releasing hormone in obesity is associated to cardiometabolic risk factors. Mediators Inflamm 2010:1–8
Utz AL, Yamamoto A, Hemphill L, Miller KK (2008) Growth hormone deficiency by growth hormone releasing hormone-arginine testing criteria predicts increased cardiovascular risk markers in normal young overweight and obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:2507–2514
Sen F, Demirturk M, Abaci N, Golcuk E, Oflaz H, Elitok A, Kutluturk F, Issever H, Unaltuna NE, Ozbey NC (2008) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase intron 4a/b polymorphism and early atherosclerotic changes in hypopituitary GH-deficient adult patients. Eur J Endocrinol 158:615–622
Hong JW, Kim JY, Kim YE, Lee EJ (2011) Metabolic parameters and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in hypopituitary men. Horm Metab Res 43:48–54
Barclay JL, Nelson CN, Ishikawa M, Murray LA, Kerr LM, McPhee TR, Powell EE, Waters MJ (2011) GH-dependent STAT5 signaling plays an important role in hepatic lipid metabolism. Endocrinology 152:181–192
Christ ER, Cummings MH, Russell-Jones DL (1998) Dyslipidaemia in adult growth hormone (GH) deficiency and the effect of GH replacement therapy: a review. Trends Endocrinol Metab 9:200–206
Monson JP, Jönsson P, Koltowska-Häggström M, Kourides I (2007) Growth hormone (GH) replacement decreases serum total and LDL-cholesterol in hypopituitary patients on maintenance HMG CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) therapy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 67:623–628
Pijl H, Langendonk JG, Burggraaf J, Frölich M, Cohen AF, Veldhuis JD, Meinders AE (2001) Altered neuroregulation of GH secretion in viscerally obese premenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5509–5515
Boero L, Cuniberti L, Magnani N, Manavela M, Yapur V, Bustos M, Rosso LG, Meroño T, Marziali L, Viale L, Evelson P, Negri G, Brites F (2010) Increased oxidized low density lipoprotein associated with high ceruloplasmin activity in patients with active acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 72:654–660
Mihailescu DV, Vora A, Mazzone T (2011) Lipid effects of endocrine medications. Curr Atheroscler, Rep, 13
Cersosimo E, Danou F, Persson M, Miles JM (1996) Effects of pulsatile delivery of basal growth hormone on lipolysis in humans. Am J Physiol 271:E123–E126
Surya S, Horowitz JF, Goldenberg N, Sakharova A, Harber M, Cornford AS, Symons K, Barkan AL (2009) The pattern of growth hormone delivery to peripheral tissues determines insulin-like growth factor-1 and lipolytic responses in obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2828–2834
Johansson JO, Oscarsson J, Bjarnason R, Bengtsson BA (1996) Two weeks of daily injections and continuous infusion of recombinant human growth hormone (GH) in GH-deficient adults. I. Effects on insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), GH and IGF binding proteins, and glucose homeostasis. Metabolism 45:362–369
Jørgensen JO, Møller N, Lauritzen T, Christiansen JS (1990) Pulsatile versus continuous intravenous administration of growth hormone (GH) in GH-deficient patients: effects on circulating insulin-like growth factor-I and metabolic indices. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70:1616–1623
Laursen T, Lemming L, Jorgensen JO, Klausen IC, Christiansen JS (1998) Different effects of continuous and intermittent patterns of growth hormone administration on lipoprotein levels in growth hormone-deficient patients. Horm Res 50:284–291
Oscarsson J, Ottosson M, Johansson JO, Wiklund O, Mårin P, Björntorp P, Bengtsson BA (1996) Two weeks of daily injections and continuous infusion of recombinant human growth hormone (GH) in GH-deficient adults. II. Effects on serum lipoproteins and lipoprotein and hepatic lipase activity. Metabolism 45:370–377
Marshall L, Mölle M, Böschen G, Steiger A, Fehm HL, Born J (1996) Greater efficacy of episodic than continuous growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) administration in promoting slow-wave sleep (SWS). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:1009–1013
Johnson TN, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Tucker GT (2006) Prediction of the clearance of eleven drugs and associated variability in neonates, infants and children. Clin Pharmacokinet 45:931–956
Nelson DR, Zeldin DC, Hoffman SM, Maltais LJ, Wain HM, Nebert DW (2004) Comparison of cytochrome P450 (CYP) genes from the mouse and human genomes, including nomenclature recommendations for genes, pseudogenes and alternative-splice variants. Pharmacogenetics 14:1–18
Thorner MO, Rogol AD, Blizzard RM, Klingensmith GJ, Najjar J, Misra R, Burr I, Chao G, Martha P, Mc Donald J (1988) Acceleration of growth rate in growth hormone-deficient children treated with human growth hormone-releasing hormone. Pediatr Res 24:145–151
Laursen T, Jørgensen JO, Jakobsen G, Hansen BL, Christiansen JS (1995) Continuous infusion versus daily injections of growth hormone (GH) for 4 weeks in GH-deficient patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:2410–2418
Hümmelink R, Sippell WG, Benoit KG, Danielson K, Faijerson Y (1993) Intranasal administration of growth hormone-releasing hormone (1–29)-NH2 in children with growth hormone deficiency: effects on growth hormone secretion and growth. Acta Pediatr 388:23–26
Steyn D, du Plessis L, Kotzé A (2010) Nasal delivery of recombinant human growth hormone: in vivo evaluation with Pheroid technology and N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. J Pharm Pharm Sci 13:263–273
Takeda A, Copper K, Bird A, Baxter L, Frampton GK, Gospodarevskaya E, Welch K, Bryant J (2010) Recombinant human growth hormone for the treatment of growth disorders in children: a systemic review and economic evaluation (Review). Health Technol Assess 14:1–209
Endocrine Society (2011) Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin Endocrinol Metabol 96:1587–1609
Burman P, Johansson AG, Siegbahn A, Vessby B, Karlsson FA (1997) Growth hormone (GH)-deficient men are more responsive to GH replacement than women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:550–555
Cook DM, Ludlam WH, Cook MB (1999) Route of estrogen administration helps to determine growth hormone (GH) replacement dose in GH-deficient adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:3956–3960
Johansson AG, Engström BE, Ljunghall S, Karlsson FA, Burman P (1999) Gender differences in the effects of long term growth hormone (GH) treatment on bone in adults with GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2002–2007
Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, Schilling LM, Cole KY, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Gormley GJ, Thorner MO (1996) Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:4249–4257
Ionescu M, Frohman LA (2006) Pulsatile secretion of growth hormone (GH) persists during continuous stimulation by CJC-1295, a long-acting GH-releasing hormone analog. J Clin Endocroniol Metab 91:4792–4797
Micic D, Casabiell X, Gualillo O, Pombo M, Dieguez C, Casanueva FF (1999) Growth hormone secretagogues: the clinical future. Horm Res 51:29–33
Nass R, Pezzoli SS, Oliveri MC, Patrie JT, Harrell FEJ, Clasey JL, Heymsfield SB, Bach MA, Vance ML, Thorner MO (2008) Effects of an oral ghrelin mimetic on body composition and clinical outcomes in healthy older adults: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 149:601–611
Stanley TL, Chen CY, Branch KL, Makimura H, Grinspoon SK (2011) Effects of a growth hormone-releasing hormone analog on endogenous GH pulsatility and insulin sensitivity in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:150–158
Méjean L, Kolopp M, Drouin P (1992) Chronobiology, nutrition, and diabetes. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Biologic rhythms in clinical and laboratory medicine. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 375–385
Gualandi-Signorini AM, Giorgi G (2001) Insulin formulations – a review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 5:73–83
Dessau E, Cameron F, Lee HB, Bequette BW, Zisser H, Jovanovic L, Chase HP, Wilson DM, Buckingham BA, Doyle FJ (2010) Real-time hypoglycemia prediction suite using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 33:1249–1254
Keenan DB, Cartaya R, Mastrototaro JJ (2010) Accuracy of a new real-time continuous glucose monitoring algorithm. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4:111–118
Keenan DB, Cartaya R, Mastrototaro JJ (2010) The pathway to the closed-loop artificial pancreas: research and commercial perspectives. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 7:445–451
Lee H, Buckingham BA, Wilson DM, Bequette BW (2009) A closed-loop artificial pancreas using model predictive control and a sliding meal size estimator. J Diabetes Sci Technol 3:1082–1090
Parker RS, Doyle FJ, Peppas NA (1999) A model-based algorithm for blood glucose control in type I diabetes. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46:148–157
Bratusch-Marrain PR, Komjati M, Waldhäusl WK (1986) Efficacy of pulsatile versus continuous insulin administration on hepatic glucose production and glucose utilization in type I diabetic humans. Diabetes 35:922–926
Courtney CH, Atkinson AB, Ennis CN, Sheridan B, Bell PM (2003) Comparison of the priming effects of pulsatile and continuous insulin delivery on insulin action in man. Metabolism 52:1050–1055
Meier JJ, Veldhuis JD, Butler PC (2005) Pulsatile insulin secretion dictates systemic insulin delivery by regulating hepatic insulin extraction in humans. Diabetes 54:1649–1656
Mirouze J, Selam JL, Pham TC (1977) Le pancréas artificial extra-corporel; nouvelle orientation du traitement insulinique. In: XIV Congrès Internat. Thérapeutique, Expansion Scientifique, Montpellier, France, pp 79–91
Mirouze J, Selam JL, Pham TC, Orsetti A (1977) Evaluation of exogenous insulin homeostatis by the artificial pancrease in insulin dependent diabetes. Diabetologia 13:273–278
Paolisso G, Scheen AJ, Giugliano D, Sgambato S, Albert A, Varricchio M, D'Onofrio F, Lefèbvre PJ (1991) Pulsatile insulin delivery has greater metabolic effects than continuous hormone administration in man; importance of pulse frequency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:607–615
Matthews DR, Naylor BA, Jones RG, Ward GM, Turner RC (1983) Pulsatile insulin has greater hypoglycemic effect than continuous delivery. Diabetes 32:617–621
Berman N, Chou HF, Berman A, Ipp E (1993) A mathematical model of oscillatory insulin secretion. Am J Physiol 264:R839–R851
Jaspan JB, Lever E, Polonsky KS, Van Cauter E (1986) In vivo pulsatility of pancreatic islet peptides. Am J Physiol 251:E215–E226
Lefebvre PJ, Paolisso G, Scheen AJ, Henquin JC (1987) Pulsatility of insulin and glucagon release: physiological significance and pharmacological implications. Diabetologia 30:443–452
Gibson T, Stimmler L, Jarrett RJ, Rutland P, Shiu M (1975) Diurnal variation in the effects of insulin in blood glucose, plasma non-esterified fatty acids and growth hormone. Diabetologia 11:83–88
Debry G, Mejean L, Villaume C, Drouin P, Martin JM, Pointel JP, Gay G (1977) Chronobiologie et nutrition humaine. In: XIV Congrès Internat. Thérapeutique, Expansion Scientifique, Montpellier, France, pp 225–245
Mirouze J, Collard F (1973) Continous blood glucose monitoring in brittle diabetes. In: Proceedings 8th Int’l. Congr. Diabetes Fed., pp 532–545
Haus E, Nicolau G, Halberg F, Lakatua D, Sackett-Lundeen L (1983) Circannual variations in plasma insulin and C-peptide in clinically healthy subjects. Chronobiologia 10:132
Cawood EH, Bancroft J, Steel JM (1993) Perimenstrual symptoms in women with diabetes mellitus and the relationship to diabetic control. Diabet Med 10:444–448
Ruegemer JJ, Squires RW, Marsh HM, Haymond MW, Cryer PE, Rizza RA, Miles JM (1990) Differences between pre-breakfast and late afternoon glycemic response to exercise in IDDM patients. Diabetes Care 13:104–110
Aye T, Block J, Buckingham B (2010) Toward closing the loop: an update on insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 39:609–624
Linkeschova R, Raoul M, Bott U, Berger M, Spraul M (2002) Less severe hypoglycemia, better metabolic control, and improved quality of life in type I diabetes mellitus with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy; an observational study of 100 consecutive patients followed for a mean of 2 years. Diabet Med 19:746–751
Olinder AL, Nyhlin KT, Smide B (2011) Clarifying responsibility for self-management of diabetes in adolescents using insulin pumps – a qualitative study. J Adv Nurs 67:1547–1557
Revert A, Rossetti P, Calm R, Vehí J, Bondia J (2010) Combining basal-bolus insulin infusion for tight postprandial glucose control: an in silico evaluation in adults, children, and adolescents. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4:1424–1437
Walsh J, Roberts R, Bailey T (2010) Guidelines for insulin dosing in continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion using new formulas from a retrospective study of individuals with optimal glucose levels. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4:1174–1181
Cukierman-Yaffe T, Konvalina N, Cohen O (2011) Key elements for successful intensive insulin pump therapy in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 92:69–73
Schwartz FL, Vernier SJ, Shubrook JH, Marling CR (2010) Evaluating the automated blood glucose pattern detection and case-retrieval modules of the 4 Diabetes Support System. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4:1563–1569
Dudde R, Vering T, Piechotta G, Hintsche R (2006) Computer-aided continuous drug infusion: setup and test of a mobile closed-loop system for the continuous automated infusion of insulin. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 10:395–402
Scaramuzza AE, Iafusco D, Rabbone I, Bonfanti R, Lombardo F, Schiaffini R, Buono P, Toni S, Cherubini V, Zuccoti GV, Diabetes Study Group of the Italian Society of S. Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology T (2011) Use of integrated real-time continuous glucose monitoring/insulin pump system in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a 3-year follow-up study. Diabetes Technol Ther 13:99–103
Welsh JB, Kannard B, Nogueira K, Kaufman FR, Shah R (2010) Insights from a large observational database of continuous glucose monitoring adoption, insulin pump usage and glycemic control: the CareLinkTM database. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 7:413–416
Mastrototaro J, Shin J, Marcus A, Sulur G (2008) The accuracy and efficacy of real-time continuous glucose monitoring sensor in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 10:385–390
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Iglesias M (2003) Administration time-dependent influence of aspirin on blood pressure in pregnant women. Hypertension 41:651–656
Peppas N, Leobandung W (2004) Stimuli-sensitive hydrogels: ideal carriers for chronobiology and chronotherapy. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 15:124–144
Rathbone MJ, Hadgraft J, Roberts MS (eds) (2003) Modified-release drug delivery technology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Youan B-BC (ed) (2009) Chronopharmaceutics. Wiley, Hoboken
Moschou EA, Peteu SF, Bachas LG, Madou MJ, Daunert S (2004) Artificial muscle material with fast electroactuation under neutral pH conditions. Chem Mater 16:2499–2502
Prescott JH, Lipka S, Baldwin S, Sheppard NFJ, Maloney JM, Coppeta J, Yomtov B, Staples MA, Satini JTJ (2006) Chronic, programmed polypeptide delivery from an implanted, multireservoir microchip device. Nat Biotechnol 24:437–438
Santini JT, Cima MJ, Langer R (1999) A controlled release microchip. Nat Biotechnol 397:335–338
Haus E, Touitou Y (1992) Chronobiology in circulating blood cells and platelets. In: Touitou Y, Haus E (eds) Chronobiology in laboratory medicine. Heidelberg, Springer, pp 504–526
Ohdo S, Koyanagi S, Matsunaga N, Hamdan A (2011) Molecular basis of chronopharmaceutics. J Pharm Sci 100:3560–3576
Mandal AS, Biswas N, Karim KM, Guha A, Chatterjee S, Behera M, Kuotsu K (2010) Drug delivery systems based on chronobiology--a review. J Control Release 147:314–325
Khan Z, Pillay V, Choonara YE, du Toit L (2010) Drug delivery technologies for therapeutic applications. Pharmaceut Develop Technol 14:602–612
Sewlall S, Pillay V, Danckwerts MP, Choonara YE, Ndesendo VM, du Toit LC (2010) A timely review of state-of-the-art chronopharmaceuticals synchronized with biological rhythms. Curr Drug Deliv 7:370–388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer US
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Smolensky, M.H., Siegel, R.A., Haus, E., Hermida, R., Portaluppi, F. (2012). Biological Rhythms, Drug Delivery, and Chronotherapeutics. In: Siepmann, J., Siegel, R., Rathbone, M. (eds) Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery. Advances in Delivery Science and Technology. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0881-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0881-9_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-0880-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-0881-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)