Abstract
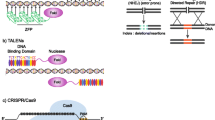
Five distinct gene therapy approaches have been developed for treating AATD. These approaches include knockout of the mutant (PiZ) allele by introduction of double-strand breaks (DSBs) and subsequent creation of insertions and deletions (indels) by DSB repair, homology-directed repair (HDR) targeted to the mutation site, base editing, prime editing, and alternatively targeted knock-in techniques. Each approach will be discussed and a brief summary of a standard CRISPR–Cas9 targeting method will be presented.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ijaz F, Nakazato R, Setou M et al (2022) A pair of primers facing at the double-strand break site enables to detect NHEJ-mediated indel mutations at a 1-bp resolution. Sci Rep 12:11681
Guo T, Feng YL, **ao JJ et al (2018) Harnessing accurate non-homologous end joining for efficient precise deletion in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing. Genome Biol 19:170
Brazelton VA Jr, Zarecor S, Wright DA et al (2015) A quick guide to CRISPR sgRNA design tools. GM Crops Food 6:266–276
Ran FA, Hsu PD, Wright J et al (2013) Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc 8:2281–2308
Song CQ, Wang D, Jiang T et al (2018) In vivo genome editing partially restores alpha1-antitrypsin in a murine model of AAT deficiency. Hum Gene Ther 29:853–860
Carlson JA, Rogers BB, Sifers RN et al (1989) Accumulation of PiZ alpha 1-antitrypsin causes liver damage in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 83:1183–1190
Shen S, Sanchez ME, Blomenkamp K et al (2018) Amelioration of alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency diseases with genome editing in transgenic mice. Hum Gene Ther 29:861–873
Stephens CJ, Kashentseva E, Everett W et al (2018) Targeted in vivo knock-in of human alpha-1-antitrypsin cDNA using adenoviral delivery of CRISPR/Cas9. Gene Ther 25:139–156
Barzel A, Paulk NK, Shi Y et al (2015) Promoterless gene targeting without nucleases ameliorates haemophilia B in mice. Nature 517:360–364
Borel F, Tang Q, Gernoux G et al (2017) Survival advantage of both human hepatocyte xenografts and genome-edited hepatocytes for treatment of α-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Mol Ther 25:2477–2489
Gaudelli NM, Komor AC, Rees HA et al (2017) Programmable base editing of A⋅T to G⋅C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 551:464–471
Komor AC, Kim YB, Packer MS et al (2016) Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533:420–424
Hess GT, Tycko J, Yao D et al (2017) Methods and applications of CRISPR-mediated base editing in eukaryotic genomes. Mol Cell 68:26–43
Packer MS, Chowdhary V, Lung G et al (2022) Evaluation of cytosine base editing and adenine base editing as a potential treatment for alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Mol Ther 30:1396–1406
Werder RB, Kaserman JE, Packer MS et al (2021) Adenine base editing reduces misfolded protein accumulation and toxicity in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficient patient iPSC-hepatocytes. Mol Ther 29:3219–3229
Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR et al (2019) Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 576:149–157
Habib O, Habib G, Hwang GH et al (2022) Comprehensive analysis of prime editing outcomes in human embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 50:1187–1197
Liu P, Liang SQ, Zheng C et al (2021) Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice. Nat Commun 12:2121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gruntman, A.M., Xue, W., Flotte, T.R. (2024). Approaches to Therapeutic Gene Editing in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. In: Bristow, C.L. (eds) Alpha-1 Antitrypsin. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2750. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3605-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3605-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3604-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3605-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols