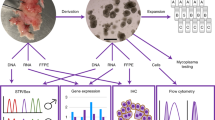
Abstract
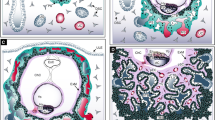
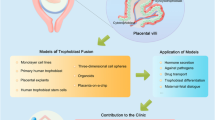
The human placenta provides the site of exchange between the maternal and fetal bloodstreams, acts as an endocrine organ, and has immunological functions. The majority of pregnancy disorders including preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction have their roots in pathological placentation. Yet, the underlying molecular causes of these complications remain largely unknown, not least due to the lack of reliable in vitro models. Recent establishment of 2D human trophoblast stem cells and 3D trophoblast organoids has been a major advancement that opened new avenues for trophoblast research. Here we provide a protocol detailing isolation of cytotrophoblast from the first trimester human placenta, establishment of trophoblast organoids, their culture and differentiation conditions. Overall, we describe an in vitro system that offers an excellent model to study the molecular basis of placental development and disease.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hemberger M, Hanna CW, Dean W (2020) Mechanisms of early placental development in mouse and humans. Nat Rev Genet 21:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0169-4
Turco MY, Moffett A (2019) Development of the human placenta. Development 146:dev163428. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.163428
Knöfler M, Haider S, Saleh L et al (2019) Human placenta and trophoblast development: key molecular mechanisms and model systems. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:3479–3496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03104-6
Okae H, Toh H, Sato T et al (2018) Derivation of human trophoblast stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 22:50–63.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.004
Haider S, Meinhardt G, Saleh L et al (2018) Self-renewing trophoblast organoids recapitulate the developmental program of the early human placenta. Stem Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.07.004
Turco MY, Gardner L, Kay RG et al (2018) Trophoblast organoids as a model for maternal-fetal interactions during human placentation. Nature 564:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0753-3
Lancaster MA, Huch M (2019) Disease modelling in human organoids. Dis Model Mech 12. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.039347
Schutgens F, Clevers H (2020) Human organoids: tools for understanding biology and treating diseases. Annu Rev Pathol 15:211–234. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032611
Kim J, Koo B-K, Knoblich JA (2020) Human organoids: model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:571–584. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0259-3
Saha B, Ganguly A, Home P et al (2020) TEAD4 ensures postimplantation development by promoting trophoblast self-renewal: an implication in early human pregnancy loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:17864–17875. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002449117
Meinhardt G, Haider S, Kunihs V et al (2020) Pivotal role of the transcriptional co-activator YAP in trophoblast stemness of the develo** human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:13562–13570. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2002630117
Hornbachner R, Lackner A, Haider S et al (2021) MSX2 safeguards syncytiotrophoblast fate of human trophoblast stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118(37):e2105130118
Kliman HJ, Nestler JE, Sermasi E et al (1986) Purification, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of cytotrophoblasts from human term placentae. Endocrinology 118:1567–1582. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-118-4-1567
Tarrade A, Lai Kuen R, Malassiné A et al (2001) Characterization of human villous and extravillous trophoblasts isolated from first trimester placenta. Lab Investig 81:1199–1211. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3780334
Sandra, Haider Andreas Ian, Lackner Bianca et al (2022) Transforming growth factor-β signaling governs the differentiation program of extravillous trophoblasts in the develo** human placenta Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 119(28). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2120667119
Kaela M, Varberg Esteban M, Dominguez Boryana et al (2023) Extravillous trophoblast cell lineage development is associated with active remodeling of the chromatin landscape Abstract Nature Communications 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40424-5
Chen, Dong Shuhua, Fu Rowan M et al (2022) A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen identifies essential and growth-restricting genes in human trophoblast stem cells Abstract Nature Communications 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30207-9
Mariyan J, Jeyarajah Gargi, Jaju Bhattad Rachel D et al (2022) The multifaceted role of GCM1 during trophoblast differentiation in the human placenta Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 119(49). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2203071119
Kaela M, Varberg Khursheed, Iqbal Masanaga et al (2021) ASCL2 reciprocally controls key trophoblast lineage decisions during hemochorial placenta development Significance Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118(10). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2016517118
Liheng, Yang Eleanor C, Semmes Cristian et al (2022) Innate immune signaling in trophoblast and decidua organoids defines differential antiviral defenses at the maternal-fetal interface eLife. https://doi.org/1110.7554/eLife.79794
(2024) Trophoblast organoids with physiological polarity model placental structure and function ABSTRACT Journal of Cell Science 137(5). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.261528
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (grant P-34588-B awarded to SH and grant P-31738-B26 awarded to PL). We are grateful to Gudrun Meinhardt and Henrieta Papuchova for valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Haider, S., Knöfler, M., Latos, P.A. (2024). Trophoblast Organoids as a Novel Tool to Study Human Placental Development and Function. In: Raha, S. (eds) Trophoblasts. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2728. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3495-0_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3495-0_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3494-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3495-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols