Abstract
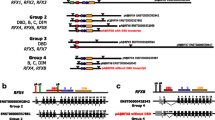
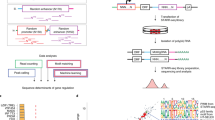
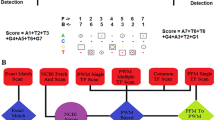
Transcription factors (TFs) bind to specific regions of DNA known as transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) and modulate gene expression by interacting with the transcriptional machinery. TFBSs are typically located upstream of target genes, within a few thousand base pairs of the transcription start site. The binding of TFs to TFBSs influences the recruitment of the transcriptional machinery, thereby regulating gene transcription in a precise and specific manner. This chapter provides practical examples and case studies demonstrating the extraction of upstream gene regions from the genome, identification of TFBSs using PWMEnrich R/Bioconductor package, interpretation of results, and preparation of publication-ready figures and tables. The EOMES promoter is used as a case study for single DNA sequence analysis, revealing potential regulation by the LHX9-FOXP1 complex during embryonic development. Additionally, an example is presented on how to investigate TFBSs in the upstream regions of a group of genes, using a case study of differentially expressed genes in response to human parainfluenza virus type 1 (HPIV1) infection and interferon-beta. Key regulators identified in this context include the STAT1:STAT2 heterodimer and interferon regulatory factor family proteins. The presented protocol is designed to be accessible to individuals with basic computer literacy. Understanding the interactions between TFs and TFBSs provides insights into the complex transcriptional regulatory networks that govern gene expression, with broad implications for several fields such as developmental biology, immunology, and disease research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacob F, Monod J (1961) Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol 3(3):318–356
Crick FH (1958) On protein synthesis. Symp Soc Exp Biol 12:138–163
Dynan WS, Tjian R (1983) The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell 35(1):79–87
Nakabeppu Y, Ryder K, Nathans D (1988) DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by fos. Cell 55(5):907–915
Muley VY, Pathania A (2017) Gene expression. Encyclopedia of animal cognition and behavior. Springer, Cham
Forrest AR, Kawaji H, Rehli M, Baillie JK, de Hoon MJ, Haberle V, Lassmann T (2014) The FANTOM consortium and the RIKEN PMI and CLST (DGT). A promoter-level mammalian expression atlas. Nature 507(7493):462–470
Ren B, Robert F, Wyrick JJ, Aparicio O, Jennings EG, Simon I, Zeitlinger J, Schreiber J, Hannett N, Kanin E, Volkert TL (2000) Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science 290(5500):2306–2309
Muley VY, López-Victorio CJ, Ayala-Sumuano JT, González-Gallardo A, González-Santos L, Lozano-Flores C, Wray G, Hernández-Rosales M, Varela-Echavarría A (2020) Conserved and divergent expression dynamics during early patterning of the telencephalon in mouse and chick embryos. Prog Neurobiol 186:101735
Levine M, Tjian R (2003) Transcription regulation and animal diversity. Nature 424(6945):147–151
Muley VY, König R (2022) Human transcriptional gene regulatory network compiled from 14 data resources. Biochimie 193:115–125
Diamond MI, Miner JN, Yoshinaga SK, Yamamoto KR (1990) Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science 249(4974):1266–1272
Djordjevic M, Sengupta AM, Shraiman BI (2003) A biophysical approach to transcription factor binding site discovery. Genome Res 13(11):2381–2390
Lambert SA, Jolma A, Campitelli LF, Das PK, Yin Y, Albu M, Chen X, Taipale J, Hughes TR, Weirauch MT (2018) The human transcription factors. Cell 172(4):650–665
Vaquerizas JM, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA, Luscombe NM (2009) A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10(4):252–263
Stormo GD (2000) DNA binding sites: representation and discovery. Bioinformatics 16(1):16–23
Mathelier A, Zhao X, Zhang AW, Parcy F, Worsley-Hunt R, Arenillas DJ, Buchman S, Chen CY, Chou A, Ienasescu H, Lim J (2014) JASPAR 2014: an extensively expanded and updated open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D142–D147
Pachkov M, Balwierz PJ, Arnold P, Ozonov E, Van Nimwegen E (2012) SwissRegulon, a database of genome-wide annotations of regulatory sites: recent updates. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D214–D220
Pratt HE, Andrews GR, Phalke N, Huey JD, Purcaro MJ, van der Velde A, Moore JE, Weng Z (2022) Factorbook: an updated catalog of transcription factor motifs and candidate regulatory motif sites. Nucleic Acids Res 50(D1):D141–D149
Stojnic R, Diez D (2015) PWMEnrich: PWM enrichment analysis. R Package Version 4(0):10–8129
Porcelli D, Fischer B, Russell S, White R (2019) Chromatin accessibility plays a key role in selective targeting of Hox proteins. Genome Biol 20:1–9
** H, Stojnic R, Adryan B, Ozdemir A, Stathopoulos A, Frasch M (2013) Genome-wide screens for in vivo Tinman binding sites identify cardiac enhancers with diverse functional architectures. PLoS Genet 9(1):e1003195
Ma X, Ezer D, Navarro C, Adryan B (2015) Reliable scaling of position weight matrices for binding strength comparisons between transcription factors. BMC Bioinform 16(1):1–3
Frith MC, Fu Y, Yu L, Chen JF, Hansen U, Weng Z (2004) Detection of functional DNA motifs via statistical over-representation. Nucleic Acids Res 32(4):1372–1381
Kimura N, Nakashima K, Ueno M, Kiyama H, Taga T (1999) A novel mammalian T-box-containing gene, Tbr2, expressed in mouse develo** brain. Dev Brain Res 115(2):183–193
Boonyaratanakornkit JB, Bartlett EJ, Amaro-Carambot E, Collins PL, Murphy BR, Schmidt AC (2009) The C proteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 (HPIV1) control the transcription of a broad array of cellular genes that would otherwise respond to HPIV1 infection. J Virol 83(4):1892–1910
Huber W, Carey VJ, Gentleman R, Anders S, Carlson M, Carvalho BS, Bravo HC, Davis S, Gatto L, Girke T, Gottardo R (2015) Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat Methods 12(2):115–121
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5(10):1–6
Stojnic R (2022) PWMEnrich.hsapiens.background: H. Sapiens background for PWMEnrich
Shannon P, Richards M (2022) MotifDb: an annotated collection of protein-DNA binding sequence motifs
Team TBD (2020) BSgenome.hsapiens.UCSC.hg19: Full genome sequences for homo sapiens (UCSC version hg19, based on GRCh37.p 13)
Pagès H (2023). BSgenome: software infrastructure for efficient representation of full genomes and their SNPs
Carlson M, Maintainer BP (2015) org.Hs.eg.db: genome wide annotation for human
Lawrence M, Huber W, Pagès H, Aboyoun P, Carlson M, Gentleman R, Morgan MT, Carey VJ (2013) Software for computing and annotating genomic ranges. PLoS Comput Biol 9(8):e1003118
Zhang MQ (1998) Identification of human gene core promoters in silico. Genome Res 8(3):319–326
Gerstein MB, Kundaje A, Hariharan M, Landt SG, Yan KK, Cheng C, Mu XJ, Khurana E, Rozowsky J, Alexander R, Min R (2012) Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data. Nature 489(7414):91–100
Neph S, Vierstra J, Stergachis AB, Reynolds AP, Haugen E, Vernot B, Thurman RE, John S, Sandstrom R, Johnson AK, Maurano MT (2012) An expansive human regulatory lexicon encoded in transcription factor footprints. Nature 489(7414):83–90
Sanyal A, Lajoie BR, Jain G, Dekker J (2012) The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature 489(7414):109–113
Pagès H, Aboyoun P, Gentleman R, DebRoy S (2019) Biostrings: efficient manipulation of biological strings. R Package Version 2(0):10–8129
Elsen GE, Hodge RD, Bedogni F, Daza RA, Nelson BR, Shiba N, Reiner SL, Hevner RF (2013) The protomap is propagated to cortical plate neurons through an Eomes-dependent intermediate map. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(10):4081–4086
Bertuzzi S, Porter FD, Pitts A, Kumar M, Agulnick A, Wassif C, Westphal H (1999) Characterization of Lhx9, a novel LIM/homeobox gene expressed by the pioneer neurons in the mouse cerebral cortex. Mech Dev 81(1–2):193–198
Gehring WJ (1992) The homeobox in perspective. Trends Biochem Sci 17(8):277–280
Banerjee-Basu S, Baxevanis AD (2001) Molecular evolution of the homeodomain family of transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 29(15):3258–3269
Trelles MP, Levy T, Lerman B, Siper P, Lozano R, Halpern D, Walker H, Zweifach J, Frank Y, Foss-Feig J, Kolevzon A (2021) Individuals with FOXP1 syndrome present with a complex neurobehavioral profile with high rates of ADHD, anxiety, repetitive behaviors, and sensory symptoms. Mol Autism 12(1):1–5
Nunez BS, Geng CD, Pedersen KB, Millro-Macklin CD, Vedeckis WV (2005) Interaction between the interferon signaling pathway and the human glucocorticoid receptor gene 1A promoter. Endocrinology 146(3):1449–1457
Petta I, Dejager L, Ballegeer M, Lievens S, Tavernier J, De Bosscher K, Libert C (2016) The interactome of the glucocorticoid receptor and its influence on the actions of glucocorticoids in combatting inflammatory and infectious diseases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80(2):495–522
Cheon H, Holvey-Bates EG, Schoggins JW, Forster S, Hertzog P, Imanaka N, Rice CM, Jackson MW, Junk DJ, Stark GR (2013) IFNβ-dependent increases in STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9 mediate resistance to viruses and DNA damage. EMBO J 32(20):2751–2763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic Supplementary Material
Table S1
Genes differentially expressed by wt HPIV1 or IFNβ compared to mock infection (XLSX 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Muley, V.Y. (2024). Prediction and Analysis of Transcription Factor Binding Sites: Practical Examples and Case Studies Using R Programming. In: Mandal, S. (eds) Reverse Engineering of Regulatory Networks. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2719. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3461-5_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3461-5_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3460-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3461-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols