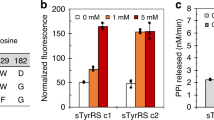
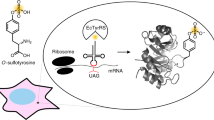
Abstract
Protein tyrosine O-sulfation (PTS) plays a crucial role in numerous extracellular protein-protein interactions. It is involved in diverse physiological processes and the development of human diseases, including AIDS and cancer. To facilitate the study of PTS in live mammalian cells, an approach for the site-specific synthesis of tyrosine-sulfated proteins (sulfoproteins) was developed. This approach takes advantage of an evolved Escherichia coli tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase to genetically encode sulfotyrosine (sTyr) into any proteins of interest (POI) in response to a UAG stop codon. Here, we give a step-by-step account of the incorporation of sTyr in HEK293T cells using the enhanced green fluorescent protein as an example. This method can be widely applied to incorporating sTyr into any POI to investigate the biological functions of PTS in mammalian cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettelheim FR (1954) Tyrosine O-sulfate in a peptide from fibrinogen. J Am Chem Soc 76:2838–2839. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01639a073
Kehoe JW, Bertozzi CR (2000) Tyrosine sulfation: a modulator of extracellular protein-protein interactions. Chem Biol 7(3):R57–R61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(00)00093-4
Moore KL (2003) The biology and enzymology of protein tyrosine O-sulfation. J Biol Chem 278(27):24243–24246. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R300008200
Farzan M, Mirzabekov T, Kolchinsky P, Wyatt R, Cayabyab M, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Sodroski J, Choe H (1999) Tyrosine sulfation of the amino terminus of CCR5 facilitates HIV-1 entry. Cell 96(5):667–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80577-2
Stone MJ, Chuang S, Hou X, Shoham M, Zhu JZ (2009) Tyrosine sulfation: an increasingly recognized post-translational modification of secreted proteins. New Biotechnol 25(5):299–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2009.03.011
Thompson RE, Liu X, Ripoll-Rozada J, Alonso-Garcia N, Parker BL, Pereira PJB, Payne RJ (2017) Tyrosine sulfation modulates activity of tick-derived thrombin inhibitors. Nat Chem 9(9):909–917. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2744
Li X, Hitomi J, Liu CC (2018) Characterization of a sulfated anti-HIV antibody using an expanded genetic code. Biochemistry 57(20):2903–2907. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00374
Koeller KM, Smith MEB, Wong CH (2000) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of PSGL-1 glycopeptides: sulfation on tyrosine affects glycosyltransferase-catalyzed synthesis of the O-glycan. Bioorg Med Chem 8(5):1017–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(00)00041-9
Kitagawa K, Aida C, Fujiwara H, Yagami T, Futaki S, Kogire M, Ida J, Inoue K (2001) Facile solid-phase synthesis of sulfated tyrosine-containing peptides: total synthesis of human big gastrin-II and cholecystokinin (CCK)-39. J Org Chem 66(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo000895y
Stone MJ, Payne RJ (2015) Homogeneous sulfopeptides and sulfoproteins: synthetic approaches and applications to characterize the effects of tyrosine sulfation on biochemical function. Acc Chem Res 48(8):2251–2261. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00255
Liu CC, Schultz PG (2006) Recombinant expression of selectively sulfated proteins in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 24(11):1436–1440. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1254
He X, Chen Y, Beltran DG, Kelly M, Ma B, Lawrie J, Wang F, Dodds E, Zhang L, Guo J, Niu W (2020) Functional genetic encoding of sulfotyrosine in mammalian cells. Nat Commun 11(1):4820. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18629-9
Ju T, Niu W, Cerny R, Bollman J, Roy A, Guo J (2013) Molecular recognition of sulfotyrosine and phosphotyrosine by the Src homology 2 domain. Mol BioSyst 9(7):1829–1832. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3mb70061e
Liu W, Brock A, Chen S, Chen S, Schultz PG (2007) Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 4(3):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1016
He X, Ma B, Chen Y, Guo J, Niu W (2022) Genetic encoding of a nonhydrolyzable phosphotyrosine analog in mammalian cells. Chem Commun 58(39):5897–5900. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cc01578a
Elsasser SJ, Ernst RJ, Walker OS, Chin JW (2016) Genetic code expansion in stable cell lines enables encoded chromatin modification. Nat Methods 13(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3701
Chatterjee A, **ao H, Bollong M, Ai H-W, Schultz PG (2013) Efficient viral delivery system for unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(29):11803–11808. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1309584110
Si L, Xu H, Zhou X, Zhang Z, Tian Z, Wang Y, Wu Y, Zhang B, Niu Z, Zhang C, Fu G, **ao S, **a Q, Zhang L, Zhou D (2016) Generation of influenza a viruses as live but replication-incompetent virus vaccines. Science 354(6316):1170–1173. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah5869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
He, X., Chen, Y., Guo, J., Niu, W. (2023). Site-Specific Incorporation of Sulfotyrosine into Proteins in Mammalian Cells. In: Tsai, YH., Elsässer, S.J. (eds) Genetically Incorporated Non-Canonical Amino Acids. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2676. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3251-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3251-2_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3250-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3251-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols