Abstract
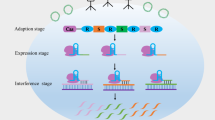
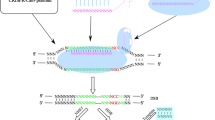
A wide range of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, or neurodegenerative diseases, have been associated with single nucleotide mutations in their causative genes. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system is a flexible and efficient genome engineering technology widely used for researches and therapeutic applications which offers immense opportunity to treat genetic diseases. The complex of Cas9 and the guide RNA acts as an RNA-guided endonuclease. Cas9 recognizes a sequence motif known as a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), and then the guide RNA base pairs with its proximal target region of 20 nucleotides with sequence complementarity. Here we describe the procedure named single nucleotide polymorphism-distinguishable (SNPD)-CRISPR system which can suppress or enhance the expression of disease-causative gene with single nucleotide mutation distinguished from its wild-type. In this study, we used HRAS, one of most famous cancer-causative genes, as an example of a target gene.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishino Y, Krupovic M, Forterre P (1987) History of CRISPR-Cas from encounter with a mysterious repeated sequence to genome editing technology. J Bacteriol 200:e00580–e00517
Mojica FJ, Diez-Villasenor C, Garcia-Martinez J, Soria E (2005) Intervening sequences of regularly spaced prokaryotic repeats derive from foreign genetic elements. J Mol Evol 60:174–182
Bolotin A, Quinquis B, Sorokin A, Ehrlich SD (2005) Clustered regularly interspaced short palindrome repeats (CRISPRs) have spacers of extrachromosomal origin. Microbiology 151:2551–2561
Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2014) Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346:1258096
Gasiunas G, Barrangou R, Horvath P, Siksnys V (2012) Cas9-crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E2579–E2586
Deltcheva E, Chylinski K, Sharma CM, Gonzales K, Chao Y, Pirzada ZA, Eckert MR, Vogel J, Charpentier E (2011) CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III. Nature 471:602–607
**ek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided dna endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–821
Sung P, Klein H (2006) Mechanism of homologous recombination: mediators and helicases take on regulatory functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:739–750
Cox DBT, Platt RJ, Zhang F (2015) Therapeutic genome editing: prospects and challenges. Nat Med 21:121–131
Cradick TJ, Fine EJ, Antico CJ, Bao G (2013) CRISPR/Cas9 systems targeting β-globin and CCR5 genes have substantial off-target activity. Nucleic Acids Res 41:9584–9592
Hsu PD, Scott DA, Weinstein JA, Ran FA, Konermann S, Agarwala V, Li Y, Fine EJ, Wu X, Shalem O, Cradick TJ, Marraffini LA, Bao G, Zhang F (2013) DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 31:827–832
Wang Q, Ui-Tei K (2017) Computational prediction of CRISPR/Cas9 target sites reveals potential off-target risks in human and mouse. In: Hatada I (ed) Genome editing in animals: methods and protocols. Springer, pp 43–53
Komor AC, Kim YB, Packer MS, Zuris JA, Liu DR (2016) Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533:420–424
Gaudelli NM, Komor AC, Rees HA, Packer MS, Badran AH, Bryson DI, Liu DR (2017) Programmable base editing of A·T to G·C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage. Nature 551:464–471
Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR, Sousa AA, Koblan LW, Levy JM, Chen PJ, Wilson C, Newby GA, Raguram A, Liu DR (2019) Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 576:149–157
Qi LS, Larson MH, Gilbert LA, Doudna JA, Weissman JS, Arkin AP, Lim WA (2013) Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell 152:1173–1183
Waryah CB, Moses C, Arooj M, Blancafort P (2018) Zinc fingers, TALEs, and CRISPR systems: a comparison of tools for epigenome editing. Methods Mol Biol 1767:19–63
Rowe HM, Jakobsson J, Mesnard D, Rougemont J, Reynard S, Aktas T, Maillard PV, Layard-Liesching H, Verp S, Mrquis J, Spitz F, Constam DB, Trono D (2010) KAP1 controls endogenous retroviruses in embryonic stem cells. Nature 463:237–240
Croner AC, Meylan S, Ciuffi A, Zangger N, Ambrosini G, Denervaud N, Bucher P, Trono D (2010) KRAB-zinc finger proteins and KAP1 can mediate long-range transcriptional repression through heterochromatin spreading. PLoS Genet 6:41000869
Matsuda E, Agata Y, Sugai M, Katakai T, Gonda H, Shimizu A (2001) Targeting of Krüppel-associated box-containing zinc finger proteins to centromeric heterochromatin. Implication for the gene silencing mechanisms. J Biol Chem 276:14222–14229
Kearns NA, Pham H, Tabak B, Genga RM, Silversterin NJ, Garber M, Maehr R (2015) Functional annotation of native enhancers with a Cas9-histone demethylase fusion. Nat Methods 12:401–403
Thakore PI, D’Ippolito AM, Song L, Safi A, Shivakumar N, Kabadi AM, Reddy TE, Crawford GE, Gersbach CA (2015) Highly specific epigenome editing by CRISPR-Cas9 repressors for silencing of distal regulatory elements. Nat Methods 12:1143–1149
Jiang Y, Triezenburg SJ, Gralla JD (1994) Defective transcriptional activation by diverse VP16 mutants associated with a common inability to form open promoter complexes. J Biol Chem 269:5505–5508
**ao H, Friesen JD, Lis JT (1994) A highly conserved domain of RNA polymerase II shares a functional element with acidic activation domains of upstream transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 14:7507–7516
Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA (2019) COSMIC: the catalogue of somatic mutations in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D941–D947
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, Norville JE, Church GM (2013) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339:823–826
Gilbert LA, Larson MH, Morsut L, Liu Z, Brar GA, Torres SE, Stern-Ginossar N, Brandman O, Whitehead EH, Doudna JA, Lim WA, Weissman JS, Qi LS (2013) CRISPR-mediated modular RNA-guided regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Cell 154:442–451
Ui-Tei K, Maruyama S, Nakano Y (2017) Enhancement of single guide RNA transcription for efficient CRISPR/Cas-based genomic engineering. Genome 60:537–545
Cong LE, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu PD, Wu X, Jiang W, Marrarrini LA, Zhang F (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339:819–823
Naito Y, Hino K, Bono H, Ui-Tei K (2015) CRISPRdirect: software for designing CRISPR/Cas guide RNA with reduced off-target sites. Bioinformatics 31:1120–1123
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (No. 15547651) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Maruyama, S. et al. (2023). SNPD-CRISPR: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism-Distinguishable Repression or Enhancement of a Target Gene Expression by CRISPR System. In: Hatada, I. (eds) Genome Editing in Animals. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2637. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3016-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3016-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3015-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3016-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols