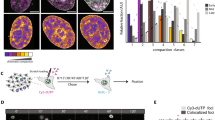
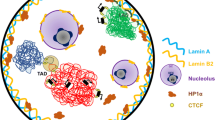
Abstract
In eukaryotes, the organization of DNA wrapped around histones regulates DNA-dependent processes. Changes in epigenetic modifications modulate the compaction of DNA into chromatin and, thus, regulate DNA metabolism in time and space. Hence, to catalog the spatiotemporal epigenetic information and its relation to the dynamic nuclear landscape is of paramount importance. Here, we present a method, based on FiJi and the statistical image analysis tool nucim(R), to classify in 3D the nuclear DNA compaction in single interphase cells. We, furthermore, mapped the distribution of (epi)genetic marks and nuclear proteins/processes to the compaction classes along with their dynamics over the cell cycle. These techniques allow to catalog and quantify the dynamic changes in the epigenome in space and time and in single cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kornberg RD (1974) Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science 184:868–871. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.184.4139.868
Allshire RC, Madhani HD (2018) Ten principles of heterochromatin formation and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:229–244. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.119
Mikkelsen TS, Ku M, Jaffe DB et al (2007) Genome-wide maps of chromatin state in pluripotent and lineage-committed cells. Nature 448:553–560. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06008
Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD et al (2009) Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature 459:108–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07829
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Kuo MH, Allis CD (1998) Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. BioEssays 20:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199808)20:8<615::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-H
Tashiro S, Lanctôt C (2015) The international nucleome consortium. Nucleus 6:89–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/19491034.2015.1022703
Buenrostro JD, Wu B, Litzenburger UM et al (2015) Single-cell chromatin accessibility reveals principles of regulatory variation. Nature 523:486–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14590
Jagannathan M, Cummings R, Yamashita YM (2018) A conserved function for pericentromeric satellite DNA. eLife 7:e34122. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34122
Schermelleh L, Heintzmann R, Leonhardt H (2010) A guide to super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol 190:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201002018
Cremer T, Cremer C (2001) Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat Rev Genet 2:292–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/35066075
Cremer T, Cremer M, Hübner B et al (2015) The 4D nucleome: evidence for a dynamic nuclear landscape based on co-aligned active and inactive nuclear compartments. FEBS Lett 589:2931–2943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.037
Kapuscinski J (1995) DAPI: a DNA-specific fluorescent probe. Biotech Histochem 70:220–233. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520299509108199
Smeets D, Markaki Y, Schmid VJ et al (2014) Three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy of the inactive X chromosome territory reveals a collapse of its active nuclear compartment harboring distinct **st RNA foci. Epigenetics Chromatin 7:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8935-7-8
Schmid VJ, Cremer M, Cremer T (2017) Quantitative analyses of the 3D nuclear landscape recorded with super-resolved fluorescence microscopy. Methods 123:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.03.013
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E et al (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
Martin RM, Leonhardt H, Cardoso MC (2005) DNA labeling in living cells. Cytometry A 67:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20172
Yaffe D, Saxel O (1977) Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature 270:725–727. https://doi.org/10.1038/270725a0
Cardoso MC, Leonhardt H (1996) Immunofluorescence techniques in cell cycle studies. In: Pagano M (ed) Cell cycle—materials and methods. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 15–28
Acknowledgments
We thank Haris Kujundzic for the initial testing of the method, Corella S. Casas-Delucchi for image data, Alexander Rapp, Cathia Rausch, and Maria Arroyo for many useful comments and all present and past members of the laboratory for their contributions over the years. The laboratory of M. Cristina Cardoso is supported by grants from the German Research Foundation (DFG Project-ID 393547839 – SFB 1361, CA 198/9-2, and CA 198/12-1), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), and the Hessian Ministry of Higher Education, Research, Science, and the Arts (HMWK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Pradhan, S.K., Cardoso, M.C. (2023). Analysis of Cell Cycle and DNA Compaction Dependent Subnuclear Distribution of Histone Marks. In: Krämer, O.H. (eds) HDAC/HAT Function Assessment and Inhibitor Development. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2589. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2788-4_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2788-4_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2787-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2788-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols