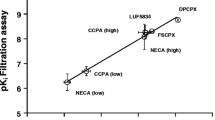
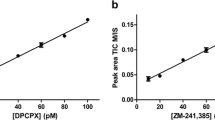
Abstract
Designed to measure binding interactions between small molecules and receptor proteins, radioligand binding approaches may also be applied to interactions between monoamine oxidase (MAO) and its ligands. The technique may be used with tissue homogenates or with mitochondrial membranes and can provide information about binding site density, ligand affinity, binding rate constants, and binding events at sites that do not impact absorbance characteristics of the flavin cofactor and that may not be amenable to spectrophotometric studies. This overview describes the use of a cell harvester in a common filtration approach to measure binding to MAO of radiolabeled substrates, inhibitors, or allosteric ligands in saturation analyses and to take advantage of the principles of competition to obtain quantitative binding data for unlabeled ligands that may bind with much lower affinity. The quality and reproducibility of data are impacted by factors such as choice of ligand concentrations, pipetting technique, graphing and regression approaches, and scintillation counting parameters, and consideration is given to these and other factors that may influence the results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall DW, Logan BW, Parsons GH (1969) Further studies on the inhibition of monoamine oxidase by M and B 9302 (clorgyline). I. Substrate specificity in various mammalian species. Biochem Pharmacol 18:1447–1454
Haefely W, Burkard WP, Cesura AM, Kettler R, Lorez HP, Martin JR, Richards JG, Scherschlicht R, Da Prada M (1992) Biochemistry and pharmacology of moclobemide, a prototype RIMA. Psychopharmacology 106:S6–S14
Hulme EC, Trevethick MA (2010) Ligand binding assays at equilibrium: validation and interpretation. Brit J Pharmacol 161:1219–1237
Hulme EC (1992) Receptor-ligand interactions: a practical approach. Practical approach series. IRL Press at Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York
Weiland GA, Molinoff PB (1981) Quantitative-analysis of drug-receptor interactions .1. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci 29:313–330
Belloli S, Morari M, Murtaj V, Valtorta S, Moresco RM, Gilardi MC (2020) Translation imaging in Parkinson’s disease: focus on Neuroinflammation. Front Aging Neurosci 12:152
Lyles GA, Callingham BA (1982) In vitro and in vivo inhibition by benserazide of clorgyline-resistant amine oxidases in rat cardiovascular tissues. Biochem Pharmacol 31:1417–1424
Costa MR, Breakefield XO (1979) Electrophoretic characterization of monoamine oxidase by [3H]pargyline binding in rat hepatoma cells with A and B activity. Mol Pharmacol 16:242–249
Yu PH (1981) Studies on the pargyline-binding site of different types of monoamine oxidase. Can J Biochem 59:30–37
Summers KM, Brown GK, Craig IW, Littlewood J, Peatfield R, Glover V, Rose FC, Sandler M (1982) Platelet monoamine oxidase: specific activity and turnover number in headache. Clin Chim Acta 121:139–146
Billett EE, Mayer RJ (1986) Monoclonal antibodies to monoamine oxidase B and another mitochondrial protein from human liver. Biochem J 235:257–263
Balsa MD, Gomez N, Unzeta M (1989) Characterization of monoamine oxidase activity present in human granulocytes and lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 992:140–144
Fritze J, Koronakis P, Konradi C, Riederer P (1989) Isoelectric focusing of monoamine oxidase subtypes as identified by MAO inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol 172:147–154
Riley LA, Waguespack MA, Denney RM (1989) Characterization and quantitation of monoamine oxidases A and B in mitochondria from human placenta. Mol Pharmacol 36:54–60
Riley LA, Denney RM (1991) Problems with the measurement of monoamine oxidase A protein concentration in mitochondrial preparations. Revised molecular activities and implications for estimating ratios of MAO A: MAO B molecules from radiochemical assay data. Biochem Pharmacol 42:1953–1959
Parkinson D, Callingham BA (1980) The binding of [3H] pargyline to rat liver mitochondrial monoamine oxidase. J Pharm Pharmacol 32:49–54
Anderson MC, Tipton KF (1994) Estimation of monoamine oxidase concentrations in soluble and membrane-bound preparations by inhibitor binding. J Neural Transm Suppl 41:47–53
Parsons B, Rainbow TC (1984) High-affinity binding-sites for [3H]MPTP may correspond to Monamine oxidase. Eur J Pharmacol 102:375–377
Crumeyrolle-Arias M, Medvedev A, Cardona A, Barritault D, Glover V (2003) In situ imaging of specific binding of [3H]isatin in rat brain. J Neurochem 84:618–620
Karolewicz B, Klimek V, Zhu H, Szebeni K, Nail E, Stockmeier CA, Johnson L, Ordway GA (2005) Effects of depression, cigarette smoking, and age on monoamine oxidase B in amygdaloid nuclei. Brain Res 1043:57–64
Nelson DL, Herbet A, Glowinski J, Hamon M (1979) [3H]Harmaline as a Specific Ligand of MAO A .2. Measurement of the turnover rates of MAO A during ontogenesis in the rat-brain. J Neurochem 32:1829–1836
Galva MD, Bondiolotti GP, Olasmaa M, Picotti GB (1995) Effect of aging on Lazabemide binding, monoamine-oxidase activity and monoamine metabolites in human frontal-cortex. J Neural Transm-Gen 101:83–94
Russ H, Pindur U, Przuntek H (1986) The interaction of 1-Alkyl-4, 4-Diphenylpiperidines with the 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine receptor-binding site. J Neural Transm 65:157–166
Cesura AM, Galva MD, Imhof R, Kyburz E, Picotti GB, Da Prada M (1989) [3H]Ro 19-6327: a reversible ligand and affinity labelling probe for monoamine oxidase-B. Eur J Pharmacol 162:457–465
Cesura AM, Bos M, Galva MD, Imhof R, Daprada M (1990) Characterization of the binding of [3H] Ro-41-1049 to the active-site of human monoamine oxidase-A. Mol Pharmacol 37:358–366
Li X-M, Juorio AV, Paterson IA, Boulton A (1992) Absence of 2-phenyethylamine binding after monoamine oxidase inhibition in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 210:189–193
Lesniak A, Aarnio M, Jonsson A, Norberg T, Nyberg F, Gordh T (2016) High-throughput screening and radioligand binding studies reveal monoamine oxidase-B as the primary binding target for D-deprenyl. Life Sci 152:231–237
Cesura AM, Galva MD, Imhof R, Daprada M (1987) Binding of [3H] Ro 16-6491, a reversible inhibitor of monoamine-oxidase type-B, to human-brain mitochondria and platelet membranes. J Neurochem 48:170–176
Vermeiren C, Motte P, Viot D, Mairet-Coello G, Courade JP, Citron M, Mercier J, Hannestad J, Gillard M (2018) The tau positron-emission tomography tracer AV-1451 binds with similar affinities to tau fibrils and monoamine oxidases. Movement Dis 33:273–281
Tesson F, Prip-Buus C, Lemoine A, Pegorier JP, Parini A (1991) Subcellular distribution of imidazoline-guanidinium-receptive sites in human and rabbit liver. Major localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem 266:155–160
Alemany R, Olmos G, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1997) Labelling of I2B-imidazoline receptors by [3H]2-(2-benzofuranyl)-2- imidazoline (2-BFI) in rat brain and liver: characterization, regulation and relation to monoamine oxidase enzymes. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 356:39–47
Hosseini AR, Jackman GP, King PR, Louis WJ, Gundlach AL (1998) Pharmacology and subcellular distribution of [3H]rilmenidine binding sites in rat brain. J Autonom Nerv Syst 72:129–136
Raddatz R, Savic SL, Bakthavachalam V, Lesnick J, Jasper JR, McGrath CR, Parini A, Lanier SM (2000) Imidazoline-binding domains on monoamine oxidase B and subpopulations of enzyme. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:1135–1145
McDonald GR, Olivieri A, Ramsay RR, Holt A (2010) On the formation and nature of the imidazoline I(2) binding site on human monoamine oxidase-B. Pharmacol Res 62:475–488
Bonivento D, Milczek EM, McDonald GR, Binda C, Holt A, Edmondson DE, Mattevi A (2010) Potentiation of ligand binding through cooperative effects in monoamine oxidase B. J Biol Chem 285:36849–36856
Li M, Hubálek F, Newton-Vinson P, Edmondson DE (2002) High-level expression of human liver monoamine oxidase A in Pichia pastoris: comparison with the enzyme expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Protein Expr Purif 24:152–162
Newton-Vinson P, Hubalek F, Edmondson DE (2000) High-level expression of human liver monoamine oxidase B in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 20:334–345
Holt A, Palcic MM (2006) A peroxidase-coupled continuous absorbance plate-reader assay for flavin monoamine oxidases, copper-containing amine oxidases and related enzymes. Nat Protoc 1:2498–2505
Martin IL, Davies M, Dunn SM (2007) Characterization of receptors by radiolabelled ligand binding techniques. In: Baker G, Dunn S, Holt A (eds) Practical neurochemistry methods. Handbook of neurochemistry and molecular neurobiology, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, NY, pp 257–274
Hulme EC, Birdsall NJM (1992) Strategy and tactics in receptor binding studies. In: Hulme EC (ed) Receptor-ligand interactions. A practical approach. The practical approach series. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, pp 63–176
Cheng Y, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Cheng HC (2004) The influence of cooperativity on the determination of dissociation constants: examination of the Cheng-Prusoff equation, the Scatchard analysis, the Schild analysis and related power equations. Pharmacol Res 50:21–40
Tan AK, Ramsay RR (1993) Substrate-specific enhancement of the oxidative half-reaction of monoamine oxidase. Biochemistry 32:2137–2143
Ramsay RR (1991) Kinetic mechanism of monoamine oxidase A. Biochemistry 30:4624–4629
Husain M, Edmondson DE, Singer TP (1982) Kinetic studies on the catalytic mechanism of liver monoamine oxidase. Biochemistry 21:595–600
Ritchie RJ, Prvan T (1996) Current statistical methods for estimating the km and Vmax of Michaelis-Menten kinetics. Biochem Educ 24:196–206
Cornish-Bowden A, Eisenthal R (1974) Statistical considerations in estimation of enzyme kinetic-parameters by direct linear plot and other methods. Biochem J 139:721–730
McDonald GR, Hudson AL, Dunn SM, You H, Baker GB, Whittal R, Martin JW, Jha A, Edmondson DE, Holt A (2008) Bioactive contaminants leach from disposable laboratory plasticware. Science 322:917
Olivieri A, Degenhardt OS, McDonald GR, Narang D, Paulsen IM, Kozuska JL, Holt A (2012) On the disruption of biochemical and biological assays by chemicals leaching from disposable laboratory plasticware. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90:697–703
Kessler MJ (1989) Statistics of liquid scintillation counting. In: Kessler MJ (ed) Liquid scintillation analysis. Science and technology. Packard Instrument Company, Waltham, MA
Acknowledgements
I thank Professor David Colquhoun for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Holt, A. (2023). Conventional Receptor Radioligand Binding Techniques Applied to the Study of Monoamine Oxidase. In: Binda, C. (eds) Monoamine Oxidase. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2558. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2643-6_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2643-6_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2642-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2643-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols