Abstract
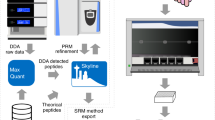
Testing of large populations for virus infection is now a reality worldwide due to the coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. The demand for SARS-CoV-2 testing using alternatives other than PCR led to the development of mass spectrometry (MS)-based assays. However, MS for SARS-CoV-2 large-scale testing have some downsides, including complex sample preparation and slow data analysis. Here, we describe a high-throughput targeted proteomics method to detect SARS-CoV-2 directly from nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs. This strategy employs fully automated sample preparation mediated by magnetic particles, followed by detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein peptides by turbulent flow chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guglielmi G (2020) The explosion of new coronavirus tests that could help to end the pandemic. Nature 583(7817):506–509
Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG et al (2020) A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 395(10223):470–473
Lalli MA, Langmade SJ, Chen X et al (2020) Rapid and extraction-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 from saliva with colorimetric LAMP. medRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.07.20093542. Preprint
Esbin MN, Whitney ON, Chong S et al (2020) Overcoming the bottleneck to widespread testing: a rapid review of nucleic acid testing approaches for COVID-19 detection. RNA 26(7):771–783
No authors listed (2013) Method of the year 2012. Nat Methods 10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2329
Cardozo KHM, Lebkuchen A, Okai GG et al (2020) Establishing a mass spectrometry-based system for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 in large clinical sample cohorts. Nat Commun 11(1):6201. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19925-0
Zecha J, Lee CY, Bayer FP et al (2020) Data, reagents, assays and merits of proteomics for SARS-CoV-2 research and testing. Mol Cell Proteomics 19(9):503–1522
Nikolaev EN, Indeykina MI, Brzhozovskiy AG et al (2020) Mass-spectrometric detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus in scra**s of the epithelium of the nasopharynx of infected patients via Nucleocapsid N protein. J Proteome Res 19(11):4393–4397
Gouveia D, Miotello G, Gallais F et al (2020) Proteoty** SARS-CoV-2 virus from nasopharyngeal swabs: a proof-of-concept focused on a 3 min mass spectrometry window. J Proteome Res 19(11):4407–4416
Ihling C, Tänzler D, Hagemann S et al (2020) Mass spectrometric identification of SARS-CoV-2 proteins from gargle solution samples of COVID-19 patients. J Proteome Res 19(11):4389–4392
Renuse S, Vanderboom PM, Maus AD et al (2021) A mass spectrometry-based targeted assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen from clinical specimens. EBioMedicine 69:103465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103465
Saadi J, Oueslati S, Bellanger L et al (2021) Quantitative assessment of SARS-CoV-2 virus in nasopharyngeal swabs stored in transport medium by a straightforward LC-MS/MS assay targeting Nucleocapsid, membrane, and spike proteins. J Proteome Res 20(2):1434–1443
Carvalho VM (2012) The coming of age of liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry in the endocrinology laboratory. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 883–884:50–58
Arora A, Somasundaram K (2019) Targeted proteomics comes to the Benchside and the bedside: is it ready for us? BioEssays 41:e1800042. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201800042
Sobsey CA, Ibrahim S, Richard VR et al (2020) Targeted and untargeted proteomics approaches in biomarker development. Proteomics 20(9):e1900029. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201900029
Wölfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W et al (2020) Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 581(7809):465–469
Widders A, Broom A, Broom J (2020) SARS-CoV-2: the viral shedding vs infectivity dilemma. Infect Dis Health 25(3):210–215
Tang YW, Schmitz JE, Persing DH et al (2020) The laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 infection: current issues and challenges. J Clin Microbiol 58(6):e00512–e00520. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00512-20
Lippi G, Simundic AM, Plebani M (2020) Potential preanalytical and analytical vulnerabilities in the laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin Chem Lab Med 58(7):1070–1076
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) Interim Guidelines for collecting, handling and testing clinical specimens for COVID-19. Updated Oct 8, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinical-specimens.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2021) Preparation of viral transport medium. SOP DSR-052-05. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/downloads/Viral-Transport-Medium.pdf
Acknowledgments
We thank Erico Santana Gomes Ribeiro for excellent engineering assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Viana, L.G. et al. (2022). Mass Spectrometry Multiplexed Detection of SARS-CoV-2. In: Guest, P.C. (eds) Multiplex Biomarker Techniques. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2511. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2395-4_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2395-4_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2394-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2395-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols