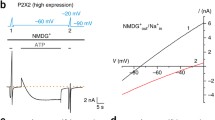
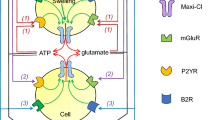
Abstract
P2X7 receptors are ATP-gated ion channels permeable to metal cations, such as Na+, K+, and Ca2+. They also exhibit permeability to various large molecular weight species, reaching up to 900 Da, in a process known as macropore formation, which is a unique functional hallmark across the P2X family. While well-documented in a range of different cell types, the molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon is poorly understood, and has been clouded through the use of electrophysiological methodology prone to artifacts as a result of significant changes in ionic concentrations in asymmetric conditions. In this chapter, we discuss the permeation properties of P2X7, the related methodological challenges and the use of symmetrical organic cation solutions as a useful technique for probing P2X7 permeation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCarthy AE, Yoshioka C, Mansoor SE (2019) Full-length P2X7 structures reveal how Palmitoylation prevents channel desensitization. Cell 179(3):659–670.e613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.017
Di Virgilio F, Schmalzing G, Markwardt F (2018) The elusive P2X7 macropore. Trends Cell Biol 28(5):392–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2018.01.005
Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E, North RA, Buell G (1996) The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272(5262):735. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5262.735
Robinson LE, Shridar M, Smith P, Murrell-Lagnado RD (2014) Plasma membrane cholesterol as a regulator of human and rodent P2X7 receptor activation and sensitization. J Biol Chem 289(46):31983–31994. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.574699
Roger S, Gillet L, Baroja-Mazo A, Surprenant A, Pelegrin P (2010) C-terminal calmodulin-binding motif differentially controls human and Rat P2X7 receptor current facilitation. J Biol Chem 285(23):17514–17524. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.053082
Khakh BS, Bao XR, Labarca C, Lester HA (1999) Neuronal P2X transmitter-gated cation channels change their ion selectivity in seconds. Nat Neurosci 2(4):322–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/7233
Virginio C, MacKenzie A, Rassendren FA, North RA, Surprenant A (1999) Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat Neurosci 2(4):315–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/7225
Cankurtaran-Sayar S, Sayar K, Ugur M (2009) P2X7 receptor activates multiple selective dye-permeation pathways in RAW 264.7 and human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mol Pharmacol 76(6):1323–1332. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.109.059923
Schachter J, Motta AP, Zamorano AS, Silva-Souza HA, Guimarães MZP, Persechini PM (2008) ATP-induced P2X7-associated uptake of large molecules involves distinct mechanisms for cations and anions in macrophages. J Cell Sci 121(19):3261–3270. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.029991
Janks L, Sharma CVR, Egan TM (2018) A central role for P2X7 receptors in human microglia. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1353-8
Janks L, Sprague RS, Egan TM (2019) ATP-gated P2X7 receptors require chloride channels to promote inflammation in human macrophages. J Immunol 202(3):883–898. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1801101
Jiang L-H, Rassendren F, Mackenzie A, Zhang Y-H, Surprenant A, North RA (2005) N-methyl-d-glucamine and propidium dyes utilize different permeation pathways at rat P2X7 receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289(5):C1295–C1302. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00253.2005
Ugur M, Ugur Ö (2019) A mechanism-based approach to P2X7 receptor action. Mol Pharmacol 95(4):442–450. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.118.115022
Peverini L, Beudez J, Dunning K, Chataigneau T, Grutter T (2018) New insights into permeation of large cations through ATP-gated P2X receptors. Front Mol Neurosci 11:265. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00265
Pellegatti P, Falzoni S, Pinton P, Rizzuto R, Di Virgilio F (2005) A novel recombinant plasma membrane-targeted luciferase reveals a new pathway for ATP secretion. Mol Biol Cell 16(8):3659–3665. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e05-03-0222
Duan S, Anderson CM, Keung EC, Chen Y, Chen Y, Swanson RA (2003) P2X7 receptor-mediated release of excitatory amino acids from astrocytes. J Neurosci 23(4):1320–1328. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01320.2003
Mackenzie AB, Young MT, Adinolfi E, Surprenant A (2005) Pseudoapoptosis induced by brief activation of ATP-gated P2X7 receptors. J Biol Chem 280(40):33968–33976. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M502705200
Sorge RE, Trang T, Dorfman R, Smith SB, Beggs S, Ritchie J, Austin J-S, Zaykin DV, Meulen HV, Costigan M, Herbert TA, Yarkoni-Abitbul M, Tichauer D, Livneh J, Gershon E, Zheng M, Tan K, John SL, Slade GD, Jordan J, Woolf CJ, Peltz G, Maixner W, Diatchenko L, Ze S, Salter MW, Mogil JS (2012) Genetically determined P2X7 receptor pore formation regulates variability in chronic pain sensitivity. Nat Med 18(4):595–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2710
Aga M, Johnson CJ, Hart AP, Guadarrama AG, Suresh M, Svaren J, Bertics PJ, Darien BJ (2002) Modulation of monocyte signaling and pore formation in response to agonists of the nucleotide receptor P2X7. J Leukoc Biol 72(1):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.72.1.222
Rat P, Olivier E, Tanter C, Wakx A, Dutot M (2017) A fast and reproducible cell- and 96-well plate-based method for the evaluation of P2X7 receptor activation using YO-PRO-1 fluorescent dye. J Biol Methods 4(1):e64. https://doi.org/10.14440/jbm.2017.136
Riedel T, Lozinsky I, Schmalzing G, Markwardt F (2007) Kinetics of P2X7 receptor-operated single channels currents. Biophys J 92(7):2377–2391. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.091413
Riedel T, Schmalzing G, Markwardt F (2007) Influence of extracellular monovalent cations on pore and gating properties of P2X7 receptor-operated Single-Channel currents. Biophys J 93(3):846–858. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.103614
Li M, Toombes GES, Silberberg SD, Swartz KJ (2015) Physical basis of apparent pore dilation of ATP-activated P2X receptor channels. Nat Neurosci 18(11):1577–1583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4120
Harkat M, Peverini L, Cerdan AH, Dunning K, Beudez J, Martz A, Calimet N, Specht A, Cecchini M, Chataigneau T, Grutter T (2017) On the permeation of large organic cations through the pore of ATP-gated P2X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(19):E3786–E3795. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1701379114
Karasawa A, Michalski K, Mikhelzon P, Kawate T (2017) The P2X7 receptor forms a dye-permeable pore independent of its intracellular domain but dependent on membrane lipid composition. Elife 6:e31186. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31186
Coddou C, Yan Z, Obsil T, Huidobro-Toro JP, Stojilkovic SS (2011) Activation and regulation of purinergic P2X receptor channels. Pharmacol Rev 63(3):641–683. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.003129
Marty A, Neher E (1983) Tight-seal whole-cell recording. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-Channel recording. Springer US, Boston, MA, pp 107–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-7858-1_7
Dolzer J (2021) Patch clamp technology in the twenty-first century. In: Dallas M, Bell D (eds) Patch clamp electrophysiology: methods and protocols. Springer US, New York, NY, pp 21–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0818-0_2
Browne LE, Compan V, Bragg L, North RA (2013) P2X7 receptor channels allow direct permeation of nanometer-sized dyes. J Neurosci 33(8):3557–3566. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2235-12.2013
Di Virgilio F, Giuliani AL, Vultaggio-Poma V, Falzoni S, Sarti AC (2018) Non-nucleotide agonists triggering P2X7 receptor activation and pore formation. Front Pharmacol 9:39. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00039
Fellin T, Pozzan T, Carmignoto G (2006) Purinergic receptors mediate two distinct glutamate release pathways in hippocampal astrocytes. J Biol Chem 281(7):4274–4284. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M510679200
Greenberg S, Di Virgilio F, Steinberg TH, Silverstein SC (1988) Extracellular nucleotides mediate Ca2+ fluxes in J774 macrophages by two distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem 263(21):10337–10343
Steinberg TH, Newman AS, Swanson JA, Silverstein SC (1987) ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem 262(18):8884–8888
Faria RX, Freitas HR, Reis RAM (2017) P2X7 receptor large pore signaling in avian Müller glial cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 49(3):215–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-017-9717-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Dunning, K., Peverini, L., Grutter, T. (2022). Using Symmetrical Organic Cation Solutions to Study P2X7 Ion Permeation. In: Nicke, A. (eds) The P2X7 Receptor. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2510. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2384-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2384-8_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2383-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2384-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols