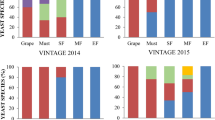
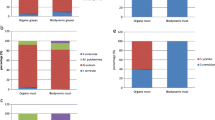
Abstract
Although humankind has been involved in winemaking since the very beginning of civilization, it was not until the second half of the last century that Pasteur (1857) demonstrated the microbial origin of spontaneous fermentations. Years later, Hansen (1903) established the taxonomic basis for a rational approach to the study of yeasts associated with grapes and to those actually involved in the fermentation process. By the middle of the present century studies in microbial ecology have shown that the vinification process involves a sequential proliferation of different types of yeast and bacteria coming either from the vineyard itself or from the cellar (Mrak and McClung, 1940; Castelli, 1954 and Galzy, 1958)
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Aidroos, K. and Bussey H. 1977, Chromosomal mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae affecting the cell wall binding site for killer factor. Can. J. Microbiol. 24:228–237.
Barre, P. 1980, Role du facteur killer dans la concurrence entre souches de levures. Bull. O.I.V. 52:560–567.
Barre, P. 1984, Le mecanisme killer dans la concurrence entre souches de levures. Evaluation et prise en compte. Bull. O.I.V. 641:635–643.
Belin, J.M. 1972, Reserches sur la repartition des levures a la surface de la grappe de raisin. Vitis 11:135–145.
Beech, F.W. and Thomas, S. 1985, Action antimicrobienne de l’anhidride sulfureux. Bull. O.I.V. 58:564–581.
Benda, J. 1970, Natural and controlled microbial processes in grape must in young wine. Bayer Ladwisch. Jahrh. 47:19–29.
Benda, J. 1985, Yeast in winemaking-investigating so-called killer yeasts during fermentation. Der Deutsche Weinbau. Wisbaden. 40:166–171.
Bevan, E. A. and MacKover, M. 1963, The physiologycal basis of the killer character in yeast. In: Geerts, S.J. (ed.) Proc.Intern.Congress of Genet. Le Hage. 11:127.
Bisiach, M., Minervini, G. and Zerbetto, F. 1986, Possible integrated control of grapevine sour rot. Vitis 25:118–128.
Blanco, P., Sieiro, C., Diaz, A. and Villa, T.G. 1994, Production and Partial Characterization of an Endopoly-galacturonase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can. J. Microbiol. 40:974–977.
Bouix, M., Leveau, J.Y, et Cuinier C. 1981, Determination de l’origine de levures de vinification par une methode de differenciation fine des souches. Conn. Vigne Vin. 15:41–52.
Bruenn, J., Bobek, L., Brennan, V. and Held, W. 1980, Yeast viral RNA polymerase is a transcriptase. Nucleic Acid Res. 8:2985–2997.
Bussey, H. 1981, Physiology of killer factor in yeast. Adv. Microbiol. Physiol. 23:93–122.
Cansado, J., Velazquez, J.B., Sieiro, C., Calo, P., Longo, E. and Villa, T.G. 1992, Role of killer strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in spontaneous fermentations, pp. 127–142 In: Villa, T.G. and Abalde, J. (eds.) Profiles on Biotechnology Santiago University Press. Spain.
Cansado, J., Longo, E., Calo, P., Sieiro, C., Velazquez, J.B. and Villa, T.G. 1991, Role of killer character in spontaneous fermentations from NW Spain: ecology, distribution and significance Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.34:643–647.
Castelli, T. 1954, Les agents de la fermentation vinaire. Arch. Microbiol. 20:323–342.
Ciolfi, G. 1984, Effect of pH on the killer phenotype in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Riv. Vitic. Enol. 37:76–79.
Cuinier, C. 1980, Origine des levures assurant l’elaboration d’un vin blanc de Tourraine. Identification des species. Connaiss. Vigne Vin 14:111–126.
Davenport, R.R. 1976, Distribution of yeasts and yeast-like organisms from aerial surfaces of develo** apples and grapes, pp.325–359 In: Dickinson, C.H. and Preecee, T.F. (eds.) Microbiology of Aerial Plant Surfaces, Academic Press. London.
dela Peña, P., Barros, F., Gascón, S., Lazo, P.S. and Ramos, S. 1981, Effect of yeast killer toxin on sensitive cells of S. cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 256:10420–10425.
Domerq, S. 1956, Etude et classification des levures de vin de la Gironde. These de Docteur-Ingenieur. Universite de Bordeaux
Esteban, R. and Fujimura, T. 1992, RNA expresion vectors based on the killer dsRNA viruses from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, pp. 33–42 In: Villa, T.G. and Abalde, J. (eds.) Profiles on Biotechnology Santiago University Press, Spain.
Farris, G.A., Forteleoni, M. and Fatichenti, F. 1987, Effects microbiologique de la recolte mecanique. Rev. Fr. Oenol. 110:42–45.
Federici, F. 1985, Production, purification and partial characterization of an endopolygalacturonase from Cryptococcus albidus var. albidus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 51:139–150.
Fleet, G.H., Lafon-Lafourcade, S. and Ribereau-Gayon, 1984, Evolution of yeast and lactic acid bacteria during fermentation and storage of Bordeaux wines. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 48:1034–1038.
Fleet, G.H. 1990, Which yeast species really conduct the fermentation?, pp. 153–156 In: Williams, P.I., Davison, D. and Lee, T.H. (eds.) Proceedings of the Seventh Australian Wine Industry, Australian Industrial Publishers, Adelaide, S.A.
Fogarty, W.M. and Kelly, C.T. 1983, Pectic enzymes, pp. 131–182 In: Fogarty, W.M. (ed.) Microbial Enzymes and Biotechnology, Applied Science Publishers, London.
Frezier, V. and Dubourdieu, D. 1992, Ecology of yeast strain S. cerevisiae during a spontaneous fermentation in a Bordeaux winery. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 43:375–380.
Fujimura, T., Esteban, R. and Wickner, R.B. 1986, In vitro L-A double-stranded RNA synthesis in virus-like particles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83:4433–4437.
Fujimura, T. and Wickner, R.B. 1988, Gene overlap results in a viral protein having an RNA binding domain and a major coat protein domain. Cell. 55:663–671.
Gacto, M., Vicente Soler, J and Pardo, C. 1992, Production and characterization of pectic enzymes from yeasts, pp. 173–181 In: Villa, T.G. and Abalde, J. (eds.) Profiles on Biotechnology, Santiago University Press, Spain.
Galzy, P. 1958, Origine de la microflore des vins. Proc. Agric. Vitic. 75:58–65.
Gillian, M.H. and Fleet, G.H. 1985, Growth of natural flora during fermentation of inoculated wines. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 50:727–728.
Girond, S., Blazy-Mougen, F. and Michell, G 1989, Influence de quelque pesticides viticoles sur les levures et la fermentation. Rev. Fr. Oenol. 119:14–22.
Gonzalez-Candelas, L., Cortell, A. and Ramon D. 1995, Construction of a recombinant wine yeast strain expressing a fungal pectate lyase gene. FEMS Microbiol. Let. 126:263–270.
Goto, S. 1980, Changes in the wild yeast flora of sulfited grape musts. J. Inst. Enol. Vitic. 15:29–32.
Goto, S., Oguri, H. and Yamazaki, M. 1984, Yeast population in botrytised grapes. J. Inst. Enol. Vitic. 19:1–5.
Guerzoni, E. and Marchetti, R. 1987, Analysis of the yeast flora associated with grape sour rot and the chemical disease markers. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 53:571–576.
Hansen, E.C. 1903, Neue Untersuchungen uber den Kreislanf der Hefernanten in der natur. Zentr. Bakteriol. 10:1–8.
Heard, G.M. and Fleet, G.H. 1987, Occurrence and growth of killer yeasts during wine fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53:2171–2174.
Icho, T. and Wickner, R.B. 1989, The double-stranded RNA genome of yeast virus L-A encodes its own putative RNA polymerase by fusing two open reading frames J. Biol. Chem. 252:6716–6723.
Kunkee, R.E. and Amerine, M.H. 1970, Yeast in winemaking, pp. 5–71 In: Rose, A.H. and Harrison, J.S. (eds.) The Yeasts, Academic Press, New York.
Longo, E., Velazquez, J.B., Cansado, J., Calo, P. and Villa, T.G. 1990, Role of killer effect in fermentations conducted by mixed strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Let. 71:331–336.
Longo, E., Cansado, J., Agrelo, D. and Villa, T.G. 1991, Effect of climatic conditions on yeast diversity in grape musts from northwest Spain. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 42:141–144.
Longo, E., Cansado, J., Sieiro, C., Calo, P., Velazquez, J.B. and Villa T.G. 1992, Influence of the curing of the killer phenotype in Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine strains on their fermentative behaviour World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 8:147–150.
McKay, A.M. 1990, Degradation of polygalacturonic acid by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Let. Appl. Microbiol. 11:41–44.
Marchetti, R., Guerzoni, E. and Gentile, M. 1984, Reserche sur l’étiologie d’une nouvelle maladie de la grappe:la pourriture acide. Vitis. 23:55–65
Mrak, E.M. and McClung, S. 1940, Yeasts occurring on grapes and grape products in California. J. Bacteriol. 40:395–399.
Monteil, H., Blazy-Mangen, F. and Michel, G. 1986, Influence des pesticides sur la croissance des levures des raisins et des vins. Science des Aliments. 6:349–360.
Naumova, G.I. and Naumov T.I. 1973, Comparative genetics of yeasts. XIII. Study of antagonistic interrelations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetika 9:85–90.
Ouchi, K., Wickner, R.B., Tohe, A. and Akiyama H. 1979, Breeding of killer yeast for saké brewing by cytoduction J. Ferment. Technol. 57:483–487.
Palfree, R.G.E. and Bussey, H. 1979, Yeast killer toxin: purification and characterization of the protein from S. cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 93:487–493.
Pasteur, L. 1857, Memoires sur la fermentation alcoolique. CR Acad. Scs. Paris. XLV:1032–1036.
Perez-Gonzalez, J.A., Gonzalez, R., Querol, A., Sendra, J. and Ramon, D. 1993, Construction of a recombinant wine yeast strain expressing β-(1,4)-endoglucanase and its use in microvinification processes Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59:2801–2806.
Phaff, H.J., Miller, M.W. and Mrak, E.M. 1978, The Life of Yeasts. Harvard University Press. Cambridge. Mass. USA.
Radler, F. and Schmitt, M. 1987, Killer toxins of yeasts: inhibitors of fermentation and their adsorption. J. Food. Protect. 50:234–238.
Ribereau-Gayon, P., Peynaud, E., et Sudraud, P. 1978. Sciences et Techniques du Vin (vol. 2) Dunod. Paris.
Ribereau-Gayon, P. 1985, New developments in wine microbiology. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 36:1–10.
Rossini, G., Federici, F. and Martini, A. 1982, Yeast flora of grape berries during ripening. Microb. Ecol. 8:83–89.
Rossini, G. 1986, Effect of killer strains on winemaking yeast starters. Ann. Fc. Agrar. Univ. Stud. Perugia. 38:345–354.
Sapis-Domerq, S., Bertrand, A., Mur, F. and Sarre, C. 1977, Influence des produits de traitement de la vigne sur la microflore des raisins et des vins. Conn. Vigne Vin. 11:227–242.
Seki, T., Choi, E. and Ryu, D. 1985, Construction of killer wine yeast strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49:1211–1215
Soumalainen, H. and Lehtonen, M. 1979, The production of aroma compounds by yeasts. J. Inst. Brewing 85:149–156.
Starmer, W.T., Ganter, P.F., Aberdeen, V., Lachance, M.A. and Phaff, H.J. 1987, The ecological role of killer yeast in natural communities of yeasts. Can. J. Microbiol. 33:783–796.
Sturley, S.L., Elliot, Q., Le Vietre, J., Tipper, D.J. and Bostian, K.A. 1986, Map** of functional domains within the S. cerevisiae type I killer preprotoxin. EMBO J. 5:3381–3389.
Suihko, M.L., Lehtinen, U., Zurbriggen, B., Kilpola, A., Nowles, J. and Penttla, M. 1991, Construction and analysis of recombinant glucanolytic brewer’s yeast strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35:781–787.
Templeton, M.D., Sarrock, K.R., Bowen J.K., Crowhurst, R.N. and Rikkerink, E.H.A. 1994, The pectin lyase gene (pnl) family from Glomerella cingulata: characterization of pnlA and its expression in yeast. Gene 142:141–146.
Tiourina, L.V., Bourjan, N.I. and Skarikova T.K. 1980, Emploi des cultures pures du phenotype killer dans la fermentation des mouts de raisin. Bull. O.I.V. 593:573–576.
Tipper, D.J. and Schmitt, M.J. 1991, Yeast ds-RNA viruses replication and killer phenotypes. Mol. Microbiol. 5:2331–2338.
van Zyl, J.A. and Du Plessis, L. 1961, The microbiology of South African winemaking. Part 1. The yeasts occuring in vineyards, musts and wines. S. Afr. J. Agric. Sci. (Pretoria) 4:393–401.
Welsh, D.J. and Leibowitz, M.J. 1980, Transcription of killer virion double-stranded RNA in vitro. Nucleic Acid Res. 8:2365–2375.
Wickner, R.B. 1992, Yeast RNA virologyer systems, pp. 263–269 In: Broach, J.R., Pringle, J.R. and Jones, E.W. (eds.) The Molecular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces, vol. 1, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, USA.
Young, T.W. 1980, The genetic manipulation of killer character into brewing yeast. J. Inst. Brew. 87:292–295.
Zhu, H. and Bussey, H. 1991, Mutational analysis of the functional domains of yeast K1 killer toxin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:175–181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Villa, T.G., Longo, E. (1996). Microbiology of Grape Surfaces and its Importance for Wine Quality. In: Morris, C.E., Nicot, P.C., Nguyen-The, C. (eds) Aerial Plant Surface Microbiology. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-585-34164-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-585-34164-4_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-306-45382-3
Online ISBN: 978-0-585-34164-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive