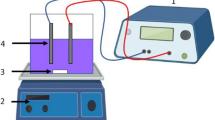
Abstract
Selenium (Se) is an important nutritional element which exists at very low concentrations, easily accumulates via the food chain and creates adverse effects such as a deprived reproduction rate and diminutive growth in human and aquatic organisms. So, it has become a severe concern around the world. We explore electrocoagulation using Al and Fe electrodes and activated sludge process (ASP) in batch process and also in an integrated process to remove Se. The optimized parameters of the current density in the batch process were: 6.7 and 5.7 mA/cm2 for Al and Fe, respectively. The mass transfer coefficient has been estimated through numerical modelling for batch and integrated processes using the equations K = \({\text{0}}{\text{.0146}}C_{{{\text{Se}}}}^{{{\text{0}}{\text{.3651}}}}{{I}^{{{\text{0}}{\text{.8916}}}}}\) and K = \({\text{295}}{\text{.387}}C_{{{\text{Se}}}}^{{{\text{6}}{\text{.607}}}}{{I}^{{{\text{3}}{\text{.587}}}}}\); the energy consumption and metal dissolution were 138240 and 384 MWh/m3, 60 and 3.58 g, respectively. The response surface methodology (RSM) was implemented in Box−Benken design to assess the parametric optimization, and the validation of experimental data was done using ANOVA and regression analysis. The obtained p-values and model F-values were 0.000 and 63.09 for Al and 0.000 and 79.98 for Fe, which indicated the significance of the model. The chemical oxygen demand (COD) reduction values estimated along with Se reduction in real effluent treatment were above 90 and 60% in electrolytic and 80% in an integrated ASP with very high-cost efficiency. The results assure that this proposed hybrid work will provide a higher reduction, improved energy and cost efficiency for the effluent with indeterminate influent Se and COD concentration. The proposed model also helps to make predictions of removal efficiency without requiring an extensive time and cost burden.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Zoroufchi, B.Kh., McPhedran, K.N., and Soltan, J., Selenium removal from water using adsorbents: A critical review, J. Hazard. Mater., 2022, vol. 424, p. 127603. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjhazmat.2021.127603
Lichtfouse, E., Morin-Crini, N., Bradu, C., Boussouga, Y.A., Aliaskari, M., Schafer, A.I., and Crini, G., Methods for selenium removal from contaminated waters: A review, Environ. Chem. Lett., 2022, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 2019–2041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01419-8
Nishimura, T., Hashimoto, H., and Nakayama, M., Removal of selenium(VI) from aqueous solution with polyamine-type weakly basic ion exchange resin, Sep. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 42, no. 14, pp. 3155–3167. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390701513107
Zelmanov, G. and Semiat, R., Selenium removal from water and its recovery using iron (Fe3+) oxide/hydroxide-based nanoparticles sol (NanoFe) as an adsorbent, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2013, vol. 103, pp. 167–172. https://doi.org/10.10167j.seppur.2012.10.037
Das, S., Lindsay, M.B., Essilfie-Dughan, J., and Hendry, M.J., Dissolved selenium(VI) removal by zero-valent iron under toxic conditions: Influence of sulfate and nitrate, ACS Omega, 2017, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 1513–1522. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.6b00382
Jadhav, A.S., Ramteke, P., Singh, S.K., and Labhasetwar, N.K., Sustainable selenium remediation from water using aluminium-iron mixed oxide: Batch and column adsorption studies, J. Water Process Eng., 2022, vol. 48, p. 102824. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjwpe.2022.102824
Flores, O.J., Nava, J.L., Carreno, G., Elorza, E., and Martinez, F., Arsenic removal from groundwater by electrocoagulation in a pre-pilot-scale continuous filter press reactor, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2013, vol. 97, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/jxes.2013.04.029
Rani, A. and Chang, C.T., Modeling and optimization of wastewater treatment processes, in Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Strategic Perspectives in Solid Waste and Wastewater Management, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2021, pp. 373−396.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821009-3.00006-3
Hansen, H.K., Pena, S.F., Gutierrez, C., Lazo, A., Lazo, P., and Ottosen, L.M., Selenium removal from petroleum refinery wastewater using an electrocoagulation technique, J. Hazard. Mater., 2019, vol. 364, pp. 78–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjhazmat.2018.09.090
Fadaei, A. and Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A., Selenium removal from water and wastewater by different technologies: A systematic review, Iran. J. Public Health, 2023, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 64–77. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijph.v52i1.11667
Liu, Y., Hedwig, S., Schaffer, A., Lenz, M., and Martinez, M., 2021 Sulfur amino acid status controls selenium methylation in Pseudomonas tolaasii: Identification of a novel metabolite from promiscuous enzyme reactions, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2021, vol. 87, no. 12, p. e00104. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00104-21
Stefaniak, J., Dutta, A., Verbinnen, B., Shakya, M., and Rene, E.R., Selenium removal from mining and process wastewater: A systematic review of available technologies, J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.—Aqua, 2018, vol. 67, no. 8, pp. 903–918. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2018.109
Nancharaiah, Y.V., Sarvajith, M., and Lens, P.N.L., Selenite reduction and ammoniacal nitrogen removal in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor, Water Res., 2018, vol. 131, pp. 131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.watres.2017.12.028
Nurhayati, E., Bagastyo, A.Y., Hartatik, D.D., and Direstiyani, L.C., The enhancement of biodegradability index of mature landfill leachate by electrochemical oxidation process using boron-doped diamond and dimensionally stable anode, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2020, vol. 46, no. 11, pp. 4811–4822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04242-4
Gomes, J.A., Daida, P., Kesmez, M., Weir, M., Moreno, H., Parga, J.R., and Cocke, D.L., Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using combined Al–Fe electrode system and characterization of products, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, vol. 139. no. 2, pp. 220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjhazmat.2005.11.108
Smith, R.W. and Altman, K.A., Activated alumina for the removal of selenium oxyanions from heap leach detoxification solutions, Miner. Metall. Process., 2004, vol. 21, pp. 27–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403298
Meher, A. K., Jadhav, A., Labhsetwar, N., and Bansiwal, A., Simultaneous removal of selenite and selenate from drinking water using mesoporous activated alumina, Appl. Water Sci., 2020, vol. 10, pp. 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1090-x
Torres, J., Pintos, V., Gonzatto, L., Dommguez, S., Kremer, C., and Kremer, E., Selenium chemical speciation in natural waters: Protonation and complexation behaviour of selenite and selenate in the presence of environmentally relevant cations, Chem. Geol., 2011, vol. 8, no. 288, pp. 32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.06.015
Kazeem, T.S., Labaran, B.A., Ahmed, H.U.R., Mohammed, T., Essa, M.H., Al-Suwaiyan, M.S., and Vohra, M.S., Treatment of aqueous selenocyanate anions using electrocoagulation, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2019, vol. 14, pp. 10538–10564. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.11.51
Baek, K., Kasem, N., Ciblak, A., Vesper, D., Padilla, I., and Alshawabkeh, A.N., 2013, Electrochemical removal of selenate from aqueous solutions, Chem. Eng. J., 2013, vol. 215, pp. 678–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/jxej.2012.09.135
Kumar, A. and Prasad, K.S., Role of nano-selenium in health and environment, J. Biotechnol., 2021, vol. 325, pp. 152–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjbiotec.2020.11.004
Yetilmezsoy, K., Demirel, S., and Vanderbei, R.J., Response surface modelling of Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution by Pistacia vera L.: Box–Behnken experimental design, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, vol. 171, no. 1, pp. 551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjhazmat.2009.06.035
Okonji, S.O., Achari, G., and Pernitsky, D., Removal of organoselenium from aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron supported on granular activated carbon, Water, 2022, vol. 14, no. 6, p. 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14060987
Yamamura, S., Yamashita M, Fujimoto N, Kuroda M, Kashiwa, M., Sei, K., Fujita, M., and Ike, M., Bacillus selenatarsenatis sp. nov., a selenate- and arsenate-reducing bacterium isolated from the effluent drain of a glass-manufacturing plant, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 1060–1064. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64667-0
Ozyonar, F. and Karagozoglu, B., Operating cost analysis and treatment of domestic wastewater by electrocoagulation using aluminium electrodes, Pollut. J. Environ. Stud., 2011, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 173–179.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledges the financial support through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2024R354) in King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
The author R. Jothiramalingam acknowledges the financial support through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2024R354) in King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.P. Kavitha: Supervision, writing—original draft, preparation; N. Balasubramanian: writing—original draft, review and editing: R. Jothiramalingam: writing—original draft, review and editing, M. Karnan: writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Allerton Press remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kavitha, N.P., Balasubramanian, N., Jothiramalingam, R. et al. Mathematical Modelling and Response Surface Methodology Approach of Electrocoagulation Hybrid Activated Sludge Process for an Efficient Removal of Selenium from Mining Wastewater. J. Water Chem. Technol. 46, 279–291 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X24030056
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X24030056