Abstract
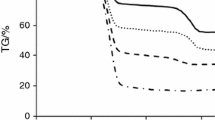
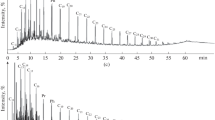
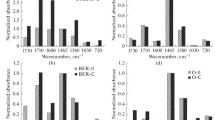
The composition of the products of cracking of oil shale (OS) from the Kashpirskoe deposit and kerogen isolated from it has been studied. The influence of OS mineral components on the material balance and qualitative composition of cracking products was shown. It was found that the amount of gaseous and solid products in kerogen cracking products decreased, and the yield of liquid products increased. The removal of mineral components from OS led to an increase in the oil content and a decrease in asphaltenes in liquid cracking products; the resin content changed slightly, and the yield of light fractions increased. The effects of mineral components on the structural-group characteristics of resins and asphaltenes in liquid cracking products were determined. The absence of mineral components led to an enlargement of resin molecules; on the contrary, asphaltene molecules became more compact.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
World Energy Council, World Energy Focus Annual 2017. https://www.worldenergy.org/publications/entry/world-energy-focus-2017.
Sun, Y., Bai, F., Liu, B., Liu, Y., Guo, M., Guo, W., Wang, Q., Lü, X., Yang, F., and Yang, Y., Fuel, 2014, vol. 115, pp. 338–346.
World Energy Council, World Energy Resources 2016. https://www.worldenergy.org/publications/2016/world-energy-resources-2016/.
Ishii, S., Seta, M., Nagasaki, T., Nakai, N., Nagai, M., Miyamoto, Y., Imada, H., Doihata, K., Saito, K., and Sekimoto, Y., Oil Shales of the World, Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1990, pp. 1285–1291.
Mozhaiskaya, M.V., Pevneva, G.S., and Surkov, V.G., Zh. Sib. Fed. Univ., Khim., 2021, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 234–241.
Patrakov, Yu.F. and Fedorova, N.I., Solid Fuel Chem., 2009, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 129–134. https://doi.org/10.3103/S036152190903001X
Goncharov, A.V. and Krivtsov, E.B., Pet. Chem., 2021, vol. 61, no. 9, pp. 1071–1078. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544121090061
Chernysheva, E.A., Mir Nefteprod., 2008, no. 1, pp. 6–9.
Mozhaiskaya, M.V., Pevneva, G.S., Krivtsov, E.B., and Pantilov, P.V., Solid Fuel Chem., 2023, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 16–20. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0361521923020106
Funding
This work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and carried out within the framework of a state contract of the Institute of Petroleum Chemistry, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (NIOKTR 121031200185-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Makhlyarchuk
Publisher’s Note.
Allerton Press remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Pantilov, P.V., Gorbunova, M.V. & Krivtsov, E.B. Influence of Mineral Components on the Composition of Oil Shale Organic Matter Cracking Products. Solid Fuel Chem. 58, 124–128 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0361521924020101
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0361521924020101