Abstract
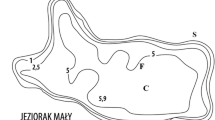
The study was conducted in Lake Długie located in Olsztyn, the Masurian Lake District. In the 1950s and in the 1960s, Lake Długie was used for 20 years as a collector of raw domestic and storm sewage. This has led to complete degradation of the lake. After preliminary protection measures implemented in the catchment, the lake was restored by artificial aeration and phosphorus inactivation methods. Long-term recultivation of the reservoir resulted in a significant and long-lasting improvement of the water quality. Before restoration, the average concentration of organic phosphorus in the surface water layer amounted to 0.166 mg Porg l−1 and of organic nitrogen — to 3.0 mg Norg l−1. After restoration, these values decreased to 0.058 mg Porg l−1 and 2.0 mg Norg l−1. The results obtained eight years after the recultivation of Lake Długie are extremely interesting. The amounts of chlorophyll a did not exceed 7 μg l−1, water transparency remained at a depth of 2.9 m, and BOD5 did not exceed 2 mg O2 l−1. These observations show that during implementation of recultivation treatments, only chemical parameters of the water significantly changed, while biological elements reacted to the treatments with some delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blindow, I., Hargeby, A., Mayercordt, J. & Schubert H. (2006). Primary production in two shallow lakes with contrasting plant form dominance: A paradox of enrichment? Limnology and Oceanography. 51(6): 2711–2721.
Brooks, A.S. & Zastrow, J.C. (2002). The potential influence of climate change on offsore primary production in Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research. 28(4): 597–607.
Brzozowska, R. & Gawrońska, H. (2005). Influence of a multi — year artificial aeration of a lake using destratification method on the sediment — water phosphorus exchange. Archive of Environmental Protection. 31(3): 71–88. doi.org/10.1016/SO380.
Cooke, G.D., Welch, E.B., Peterson, S.A. & Newroth, P.R. (2005). Restoration and management of lakes and reservoirs. Taylor & Francis, A CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida. pp. 591.
Dunalska, J.A. (2011). Impact of morphometric and catchment variables on summer organic carbon richness in deep temperate lakes. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems. 403(03): 1–11. doi:10.1051/kmae/2011043.
Dunalska, J.A., Górniak, D., Jaworska, B., Evelyn, E. & Gaiser E.E. (2012). Effect of temperature on organic matter transformation in a different ambient nutrient availability. Ecological Engineering. 49: 27–34. doi.org/10.1016/jecoleng.2012.08.023.
Dunst, R.C., Born, S.M., Uttomark, P.D., Smith, S.A., Nichols, S.A., Peterson, J.O., Knauer, R., Serns, S.L., Winter, D.R., & Wirth, T.L. (1974). Survey of lake rehabilitation techniques and experiences. Departament of Natural Resources, Madison Tech. Bull. 75: 1–177.
Finger, D., Wüest, A. & Bossard, P. (2013). Effects of oligotrophication on primary production in peri-alpine lakes. Water Resources Research. 49(8): 4700–4710. doi:10.1002/wrcr.20355.
Gawrońska, H. (1984). Wpływ ograniczenia dopływu ścieków na warunki fizyczno — chemiczne wód Jeziora Długiego w Olsztynie. Rocz. Nauk Rol. 100(4): 27–52.
Gawrońska, H., Lossow, K. & Grochowska, J. (2005). Rekultywacja Jeziora Długiego w Olsztynie. Wyd. Edycja pp. 52.
Grochowska, J. & Brzozowska, R. (2013). The influence of different recultivation methods on the water buffer capacity in degraded urban lake. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems. 410(01): 2–13.dx.doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2013056.
Grochowska, J., Brzozowska, R. & Łopata, M. (2013). Durability of changes in phosphorus compounds in water of an urban lake after application of two reclamation methods. Water Science and Technology. 68(1): 234–239.doi:10.2166/wst.2013.249.
Grochowska, J. & Gawrońska, H. (2004). Restoration effectiveness of a degraded lake using multi — year artificial aeration. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies. 13(6): 671–681.
Helmroos, H., Hietanen, S., Niemistö, J. & Horpilla, J. (2012). Sediment resuspension and denitrification affect the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio of shallow lake waters. Fundamental and Applied Limnology. 180(3): 193–205. doi:10.1127/1863-9135/2012/2013.
Hermanowicz, W., Dożańska, W., Dojlido, J., Koziorowski, B. & Zerbe, J. (1999). Fizyczno — chemiczne badanie wody i ścieków. Wyd. Arkady. pp 530.
Imboden, D.M. (1992). Possibilities and limitations of lake restoration: Conclusions for Lake Lugano. Aquatic Sciences. 54(3/4): 382–390.
Karlsson, J., Byström, P., Ask, J., Persson, L. & Jansson, M. (2009). Light limitation of nutrient poor lake ecosystems. Nature. 460: 506–509. doi:10.1038/nature08179.
Klapper, H. (1991). Control of eutrophication in inland waters. Ellis Horwood, New York. pp. 337.
Klapper, H. (2003). Technologies for lake restoration. Journal of Limnology. 62(1):73–90.
Lewis, W.M. (2011) Global primary production of lakes: 19 th Baldi Memorial Lecture. Inland Waters. 1: 1–28.
Mucha, A. & Rybak, M. (1979). Zawartość chlorofilu w fitoplanktonie Jeziora Długiego. Zesz. Nauk. ART. 9: 47–53.
Nara, F., Tani, Y., Soma, Y., Soma, M., Naraoka, H., Watanabe, T., Horiuchi, K., Kawai, T., Oda, T. & Nakamura, T. (2005). Response of phytoplankton productivity to climate change recorded by sedimentary photosynthetic pigments in Lake Hovsgol (Mongolia) for the last 23,000 years. Quaternary International. 136: 71–81. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2004.11.009.
OkSun, K., Imhoff, J.F., Witzel, K. & Junier, P. (2011). Distribution of denitrifying bacterial communities in the stratified water column and sediment — water interface in two freshwater lakes and the Baltic Sea. Aquatic Ecology. 45: 99–112. doi:10.1007/s10452-010-9335-7.
Peterson, B.J. (1980). Aquatic primary productivity and the 14C-CO2 method: A history of the productivity problem. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 11, 1359–1385.
Robarts, R.D. (1983). Factors controlling primary production in a hypertrophic lake (Hartbeespoort Dam, South Africa). Journal of Plankton Research. 6(1): 91–105.
Rodziewicz, H. & Rybak, M. (1979). Plankton roślinny Jeziora Długiego. Zesz. Nauk. ART. 9: 55–62.
Romero-Viana, L., Keely, B.J., Camacho, A. & Vicente, E. (2010). Primary production in Lake La Cruz (Spain) over the last four centuries: reconstruction based on sedimentary signal of photosynthetic pigments. Journal of Paleolimnology. 43: 771–786. doi:10.1007/s10933-009-9367-y.
Standard methods for examination water and wastewater (1980). American Public Health Association. AWWA, WPCF, Washington DC.
StatSoft Inc. (2010). STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 9.1. www.statsoft.com.
Tammeorg, O., Möls, T. & Kangur, K. (2014). Weather conditions influencing phosphorus concentration in the growing period in the large shallow lake Peipsi (Estonia/Russia). Journal of Limnology. 73(1): 11–19. doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2014.768.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., Lodge, D.M. & Carpenter, S.R. (2001). Whole — lake fertilization effects on distribution of primary production between benthic and pelagic habitats. Ecology. 82(4): 1065–1077.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Grochowska, J., Brzozowska, R. & Parszuto, K. The influence of different recultivation techniques on primary production processes in a degraded urban lake. Ocean and Hydro 43, 211–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-014-0135-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-014-0135-x