Abstract
Nitrate ester plasticized polyether (NEPE) is a kind of high-energy solid propellant that has both good mechanical properties and high specific impulse. However, its unique composition makes its combustion mechanism different from both double-base propellants and composite propellants. In order to study the combustion mechanism of NEPE propellants, we improved the free radical cracking model of previous research to make it capable of predicting the burning rate of NEPE propellants. To study the combustion characteristics and provide data support for the model, an experimental system was built and four kinds of NEPE propellants with different compositions and grain size distributions were tested. The results show that our modified model can reflect the combustion characteristics of NEPE propellants with an acceptable accuracy. The difference between the model and the experimental data is mainly caused by uncertain environmental factors and the ignorance of interactions between components. Both the experimental data and the results predicted by the model show that increasing the backpressure helps to increase the burning rate of NEPE propellants. Furthermore, the grain size of the oxidizer inside the NEPE propellant has a more severe impact on the burning rate but a lighter impact on the burning rate pressure exponent in comparison with the grain size of aluminum. For aluminum-free NEPE propellants, the reaction in the gas phase is dominant in the combustion process while adding aluminum into the propellant makes the solid phase dominant in the final stage. The combustion of fine aluminum particles near the burning surface generates heat feedback to the burning surface which evidently influences the surface temperature. However, the agglomeration of coarse aluminum particles has little effect on the burning surface temperature.
目的
因NEPE 推进剂具有独特的燃烧性能和燃烧机理, 现有模型无法直接用于其燃烧相关研究。本文希 望对现有模型进行改进, 并基于自由基裂解模型 建立一个计算NEPE 推进剂燃速的模型, 然后对 NEPE 推进剂燃烧进行观察和测量, 研究其燃烧 特性, 以期为所建模型提供数据支持。
创新点
1. 基于自由基裂解模型, 计算每种成分同时存在 多种粒径分布的NEPE 推进剂的燃速; 2. 建立试 验系统, 观察NEPE 推进剂燃烧火焰形态。
方法
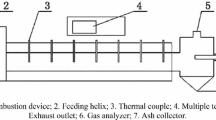
1. 通过理论推导, 构建燃速与推进剂成分的粒径和含量以及燃烧室压**之间的关系, 得到燃速计 算公式(公式(1)–(10)); 2. 利用建立的模型, 计算四种不同粒径分布的NEPE 推进剂在不同压 **下的燃速, 并与试验结果进行比较,验证模型 的可行性(图7); 3. 建立试验系统,测量NEPE 推进剂的燃速和燃面温度, 并观察其燃烧火焰 (图5 和6), 分析不同成分对燃烧的影响。
结论
1. 基于自由基裂解模型建立的燃烧模型可用于预 测NEPE 推进剂的燃速; ;2. 铝颗粒的添加对NEPE 推进剂的燃烧火焰形态和气相反应都有较大影 响; 3. 氧化剂(高氯酸铵和奥克托今)颗粒的粒 径对燃速的影响比铝颗粒的粒径对燃速的影响 大, 但对燃速压**指数的影响相对较小。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benreuven M, 1980. Nitramine Monopropellant Deflagration and General Nonsteady Reacting Rocket Chamber Flows. PhD Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, USA.
Benreuven M, Caveny LH, Vichnevetsky RJ, et al., 1977. Flame zone and sub-surface reaction model for deflagrating RDX. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 16(1):1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0082-0784(77)80410-4
Davenas A, 1997. Solid Rocket Propulsion Technology. Zhang DX, translator. Astronautic Publishing House, Bei**g, China (in Chinese).
Ermolin NE, Korobeinichev OP, Kuibida LV, et al., 1987. Study of the kinetics and mechanism of chemical reactions in hexogen flames. Combustion, Explosion and Shock Waves, 22(5):544–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00755523
Fang YZ, Li SF, 2001. Experimental studies on effects of AP content and particle size in NEPE propellant. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 24(3):47–53 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2001.03.011
Fry RS, DeLuca L, Frederick R, et al., 2002. Evaluation of Methods for Solid Propellant Burning Rate Measurements. Technical Report, NATO RTO Advisory Report, AVT Working Group 016.
Khichar M, Patidar L, Thynell ST, 2018. Improvement and validation of a detailed reaction mechanism for thermal decomposition of RDX in liquid phase. Combustion and Flame, 198:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.10.005
Khichar M, Patidar L, Thynell ST, 2019. Comparative analysis of vaporization and thermal decomposition of cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine (RDX). Journal of Propulsion and Power, 35(6):1098–1107. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B37643
Li MM, Song HC, Wang Y, et al., 2008a. Modeling effects of aluminum content and particle size on NEPE combustion performance. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 16(3):319–322 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2008.03.020
Li MM, Song HC, Wang Y, et al., 2008b. Predicting effects of oxidizer content and particle size on NEPE combustion characteristics. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 29(4): 502–507 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2008.04.022
Li MM, Wang Y, Guo XD, et al., 2009. Numerical simulation for burning rate of GAP high-energy propellant. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 32(5):535–538 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2009.05.016
Li SF, Fang C, 2002. “Linkage-mutualism” mechanism for interactions between AP and HMX. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 23(1):79–83 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2002.01.021
Li SF, Niu HL, Zhang GC, et al., 2002. Laser ignition of NEPE propellant. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 23(2): 172–175 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2002.02.022
Li XM, Liu YF, Yao WS, et al., 2001. Study on low burning rate NEPE propellant. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 24(3):1–3 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2001.03.001
Liu YF, Yao WS, Li XM, et al., 2003. Combustion property of NEPE propellant. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 26(4):30–32 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2003.04.010
Luo YJ, Liu JR, 2007. Research progress of high energy solid propellant. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 15(4):407–410 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2007.04.029
Palopoli SF, Brill TB, 1991. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials 52. On the foam zone and surface chemistry of rapidly decomposing HMX. Combustion and Flame, 87(1):45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(91)90026-8
Pang AM, Wang BH, Tian DY, 2003. Combustion modeling of NEPE propellant. Modern Defence Technology, 31(2):29–32 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-086X.2003.02.006
Pang WQ, Fan XZ, Yi JH, et al., 2010. Thermal behavior and non-isothermal decomposition reaction kinetics of NEPE propellant with ammonium dinitramide. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 28(5):687–692. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.201090132
Patidar L, Thynell ST, 2017. Quantum mechanics investigation of initial reaction pathways and early ring-opening reactions in thermal decomposition of liquid-phase RDX. Combustion and Flame, 178:7–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.12.024
Patidar L, Khichar M, Thynell ST, 2018. Identification of initial decomposition reactions in liquid-phase HMX using quantum mechanics calculations. Combustion and Flame, 188:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.09.042
Patidar L, Khichar M, Thynell ST, 2019. Modeling of HMX monopropellant combustion with detailed condensedphase kinetics. AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2019 Forum. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2019-4210
Patidar L, Khichar M, Thynell ST, 2020. A comprehensive mechanism for liquid-phase decomposition of 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane (HMX): thermolysis experiments and detailed kinetic modeling. Combustion and Flame, 212:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.10.025
Peng PG, Liu DH, 1990. Ammonium perchlorate/nitramine propellant combustion simulation. Journal of Propulsion Technology, (4):63–70 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.1990.04.011
Prasad K, Yetter RA, Smooke MD, 1997. An eigenvalue method for computing the burning rates of RDX propellants. Combustion Science and Technology, 124(1–6): 35–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102209708935640
Prasad K, Yetter RA, Smooke MD, 1998. An eigenvalue method for computing the burning rates of HMX propellants. Combustion and Flame, 115(3):406–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-2180(98)00009-1
Song HC, 1986. Gunpowder Combustion Model and Burning Rate Estimation Method. PhD Thesis, Nan**g University of Science and Technology, Nan**g, China (in Chinese).
Sun YL, Ren H, Jiao QJ, 2018. Comparison of thermal behaviors and decomposition kinetics of NEPE propellant before and after storage. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 131(1):101–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6525-8
Wang F, Zhang XP, Hu RZ, et al., 2004. Study on combustion properties of nitrate ester plasticized polyether propellants at high pressure. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 25(5):469–472 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2004.05.019
Wang HM, Chen X, Zhao C, et al., 2015. Study on ignition and combustion characteristics of NEPE propellant under laser irradiation. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 36(8): 1262–1267 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.2015.08.021
Wang SP, 2007. Combustion Mechanism and Burning Rate Estimation Program of Composite Solid Propellant. MS Thesis, Nan**g University of Science and Technology, Nan**g, China (in Chinese).
**ang HS, Chen X, Zhou CS, et al., 2016. Effect of oxygen content in environment gas on the laser ignition process of NEPE propellant. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 39(3):75–79 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2016.03.0015
Yang D, Zhao BC, Song HC, et al., 1997. Modeling for nitramine (RDX, HMX) propellant burning characteristics. Journal of Nan**g University of Science and Technology, 21(5):415–418 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.1997.05.009
Yetter RA, Dryer FL, Allen MT, et al., 1995. Development of gas-phase reaction mechanisms for nitramine combustion. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 11(4):683–697. https://doi.org/10.2514/3.23894
Zhang XP, Dai ZL, 2007. Calculation for high-pressure combustion properties of high-energy solid propellant based on GA-BP neural network. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 30(3):229–232 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2007.03.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xu-dong NA designed the research. **ao-ting YAN and Xu-dong NA processed the corresponding data. **ao-ting YAN wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Zhi-xun XIA and Li-ya HUANG helped to organize the manuscript. **ao-ting YAN and Xu-dong NA revised and edited the final version.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
**ao-ting YAN, Zhi-xun XIA, Li-ya HUANG, and Xu-dong NA declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11572349) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2018JJ3606), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Xt., **a, Zx., Huang, Ly. et al. Combustion of nitrate ester plasticized polyether propellants. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 21, 834–847 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1900668
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1900668