Abstract
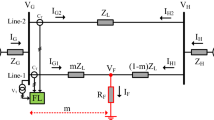
An accurate algorithm for fault location of double phase-to-earth fault on transmission line of direct ground neutral system is presented. The algorithm, which employs the faulted phase network and zero-sequence network as fault-location model in which the source impedance at the remote end is not involved, effectively eliminates the effect of load flow and fault resistance on the accuracy of fault location. The algorithm achieves accurate location by measuring only one local end data and is used in a procedure that provides automatic determination of faulted types and phases, and does not require the engineer to specify them. Simulation results showed the effectiveness of the algorithm under the condition of double phase-to-earth fault.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bo, Z.Q., 2002. Daptive non-communication protection for power lines BO scheme. II. The instant operation approach.IEEE Trans on Power Delivery,17(1): 92–96.
Djuric, M. B., Radojevic, Z. M. and Terzija, V. V., 1998. Distance protection and fault location utilizing only phase current phasors.IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery,13(4): 1020–1025.
Eriksson, L., Saha, M. M. and Rockfeller, G. D., 1985. An accurate fault locator with compensation for apparent reactance in the fault resistance resulting from remote-end feed.IEEE Trans. PAS,104(2): 424–436.
Kezunovic, M. and Perunicic, B., 1995. Synchronized sampling improves fault location.IEEE Computer Applications in Power,10(1): 30–33.
Kezunovic, M. and Perunicic, B., 1996. Automated transmission line fault analysis using synchronized sampling at two end.IEEE Trans on Power System,11(1): 441–447.
Novosel, D., Hart, D. G. and Udren, E., 1996. Unsynchronized two—terminal fault location estimation.IEEE Trans on Power Delivery,11(1): 130–136.
Thomas, D. W. P, Christopoulos, C. and Tang, Y. G., 2001. A Single Ended Fault Location Scheme. IEE Developments in Power System Protection Seventh International Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, p. 414–417.
Zamore, A. and Minambres, L. F., 1996. Fault location on two-terminal transmission lines based on voltages.IEEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib.,143(1): 1–5.
Zhang, Q. C., Zhang, Y. and Song, W. N., 1998. Transmission line fault location for single-phase-to-earth fault on non-direct-ground neutral system.IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery,10(3): 1086–1093.
Zhang, Q. C., Zhang, Y. and Song, W. N., 1999. Fault location of two-parallel transmission line for non-earth fault using one-terminal data.IEEE PES Transaction on Power Delivery,14(3): 863–866.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project (No. 023801211) supported by the Key Science Foundation of Tian**, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qing-chao, Z., Hui, D., Chao, G. et al. Fault location of two-parallel transmission line for double phase-to-earth fault using one-terminal data. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 4, 520–525 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0520
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2003.0520