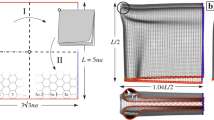
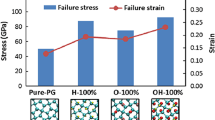
Abstract
Inspired by the origami architecture and the progress in the functionalization of carbon-based nanomaterials, we design a carbon nanotube origami (CNT-O) metamaterial with the assistance of hydrogenation and by utilizing molecular dynamics simulation. The mechanical properties, including stiffness, ultimate strength, failure strain, and Poisson’s ratio, are systematically studied. Our findings show that the mechanical properties of CNT-O can be tuned and programmed by altering the underlying topological parameters and adopting surface functionalization. We resort to computational simulation, theoretical analysis, and experimentation to demonstrate that an extremely broad range of strain-dependent and scale-independent negative Poisson’s ratio can be achieved for nanoarchitected metamaterials, mainly driven by the kinematics of the folding/unfolding in origamis. The proposed origami strategy imparts a platform for designing the next generation of low-dimensional nanomaterials (e.g., graphene and CNT) with highly tunable auxeticity.
Impact statement
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs), the classic one-dimensional material, were uncovered in 1991 and reported to be made out of a single graphene layer later in 1993. Since these discoveries, the carbon-based materials have attracted intensive research interest due to their outstanding thermo-electro-mechanical properties. To expand their range of applications and overcome their shortcomings such as brittleness and low-dimensional feature, many engineering strategies have been proposed to modify their properties. Inspired by the ancient art of paper folding, we first construct the CNT origami with a Miura-ori tessellation via surface functionalization using hydrogen atoms and then resort to molecular dynamics simulation, theoretical analysis, and experimental test to demonstrate that the origami strategy can provide a platform for designing CNTs with enhanced stretchability, high strength, and scale-independent strain-dependent negative Poisson’s ratio. More specifically, the mechanical properties of CNT origamis can be tuned and programmed by altering the folding width and topological parameters of Miura-ori patterns. Our findings provide new opportunities for the realization of low-dimensional architected nanomaterials capable of achieving tunable mechanical properties and auxeticity.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Y. Gogotsi, MRS Bull. 40(12), 1110 (2015)
S.Y. Kim, J.C. Lee, G. Seo, J.H. Woo, M. Lee, J. Nam, J.Y. Sim, H.R. Kim, E.C. Park, S. Park, Small Sci. 2, 2100111 (2022)
Z. Komeily-Nia, L.-T. Qu, J.-L. Li, Small Sci. 1(2), 2000026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/smsc.202000026
B. Ni, D. Steinbach, Z. Yang, A. Lew, B. Zhang, Q. Fang, M.J. Buehler, J. Lou, MRS Bull. 47(8), 848 (2022)
T. Cui, S. Mukherjee, P.M. Sudeep, G. Colas, F. Najafi, J. Tam, P.M. Ajayan, C.V. Singh, Y. Sun, T. Filleter, Nat. Mater. 19, 405 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-019-0586-y
A. Kis, G. Csanyi, J.P. Salvetat, T.N. Lee, E. Couteau, A.J. Kulik, W. Benoit, J. Brugger, L. Forro, Nat. Mater. 3, 153 (2004)
M. Guo, Y. Qian, H. Qi, K. Bi, Y. Chen, Carbon 157, 185 (2020)
T.W. Odom, J.-L. Huang, P. Kim, C.M. Lieber, Nature 391, 62 (1998)
N. Hamada, S. Sawada, A. Oshiyama, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 1579 (1992)
J. Wu, H. Ma, P. Yin, Y. Ge, Y. Zhang, L. Li, H. Zhang, H. Lin, Small Sci. 1(4), 2000053 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/smsc.202000053
A. Peigney, C. Laurent, E. Flahaut, R.R. Bacsa, A. Rousset, Carbon 39, 507 (2001)
C. Zhang, A. Akbarzadeh, W. Kang, J. Wang, A. Mirabolghasemi, Carbon 131, 38 (2018)
J. Cai, A. Akbarzadeh, Mater. Des. 206, 109811 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109811
J. Cai, H. Chen, Y. Li, A. Akbarzadeh, Small Sci. 2(12), 2270024 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/smsc.202270024
H. Zhan, G. Zhang, J.M. Bell, V.B.C. Tan, Y. Gu, Nat. Commun. 11, 1905 (2020)
E. Pop, V. Varshney, A.K. Roy, MRS Bull. 37(12), 1273 (2012)
G.S. Jung, M.J. Buehler, Nano Lett. 18, 4845 (2018)
Z. Yang, M.J. Buehler, Small Methods 6, 84 (2022)
A. Pedrielli, S. Taioli, G. Garberoglio, N.M. Pugno, Carbon 132, 766 (2018)
Y. Zhu, Y. Wang, B. Wu, Z. He, J. **a, H. Wu, Nano Lett. 21, 8401 (2021)
T.C. Shyu, P.F. Damasceno, P.M. Dodd, A. Lamoureux, L. Xu, M. Shlian, M. Shtein, S.C. Glotzer, N.A. Kotov, Nat. Mater. 14, 785 (2015)
M. Schenk, S.D. Guest, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 3276 (2013)
L. Yuan, H. Dai, J. Song, J. Ma, Y. Chen, Mater. Des. 189, 108494 (2020)
S. Li, H. Fang, S. Sadeghi, P. Bhovad, K.W. Wang, Adv. Mater. 31, e1805282 (2019)
S.J.P. Callens, A.A. Zadpoor, Mater. Today 21, 241 (2018)
P.M. Reis, F. Lopez Jimenez, J. Marthelot, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 12234 (2015)
J. Cai, E. Estakhrianhaghighi, A. Akbarzadeh, Carbon 191(5696), 610 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.02.008
Z.Y. Wei, Z.V. Guo, L. Dudte, H.Y. Liang, L. Mahadevan, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 215501 (2013)
E. Boatti, N. Vasios, K. Bertoldi, Adv. Mater. 29, 1700360 (2017)
D. Melancon, B. Gorissen, C.J. Garcia-Mora, C. Hoberman, K. Bertoldi, Nature 592, 545 (2021)
Z. Zhai, Y. Wang, K. Lin, L. Wu, H. Jiang, Sci. Adv. 6(47), eabe2000 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe2000
B. Treml, A. Gillman, P. Buskohl, R. Vaia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 6916 (2018)
B.N. Khare, M. Meyyappan, J. Kralj, P. Wilhite, M. Sisay, H. Imanaka, J. Koehne, C.W. Baushchlicher, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 5237 (2002)
D.C. Elias, R.R. Nair, T.M. Mohiuddin, S.V. Morozov, P. Blake, M.P. Halsall, A.C. Ferrari, D.W. Boukhvalov, M.I. Katsnelson, A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, Science 323, 610 (2009)
B.N. Khare, M. Meyyappan, A.M. Cassell, C.V. Nguyen, J. Han, Nano Lett. 2, 73 (2001)
S. Pekker, J.P. Salvetat, E. Jakab, J.M. Bonard, L. Forró, J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 7938 (2001)
G. Zhang, P. Qi, X. Wang, Y. Lu, D. Mann, X. Li, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6026 (2006)
A.V. Talyzin, S. Luzan, I.V. Anoshkin, A.G. Nasibulin, H. Jiang, E.I. Kauppinen, V.M. Mikoushkin, V.V. Shnitov, D.E. Marchenko, D. Noreus, ACS Nano 5, 5132 (2011)
Z. Sun, C.L. Pint, D.C. Marcano, C. Zhang, J. Yao, G. Ruan, Z. Yan, Y. Zhu, R.H. Hauge, J.M. Tour, Nat. Commun. 2, 559 (2011)
S. Plimpton, J. Comput. Phys. 117(1), 1 (1995)
A. Stukowski, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2010)
F. Müller-Plathe, J. Chem. Phys. 106, 6082 (1997)
S. Zhu, T. Li, ACS Nano 8, 2864 (2014)
D.T. Ho, V.H. Ho, V. Babar, S.Y. Kim, U. Schwingenschlogl, Nanoscale 12, 10172 (2020)
J. Mu, C. Hou, H. Wang, Y. Li, Q. Zhang, M. Zhu, Sci. Adv. 1, e1500533 (2015)
L. Liu, Y. Liu, X. Li, N. Liu, B. Cui, X. Huang, Phys. Status Solidi B 256, 1900095 (2019)
Q. Lu, M. Arroyo, R. Huang, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 42, 102002 (2009)
X. Shi, B. Peng, N.M. Pugno, H. Gao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 191913 (2012)
K. Liu, P.P. Pratapa, D. Misseroni, T. Tachi, G.H. Paulino, Adv. Mater. 34, e2107998 (2022)
M. Eidini, G.H. Paulino, Sci. Adv. 1, e1500224 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This research was undertaken, in part, thanks to funding from the Canada Research Chairs program to A.H.A. in Multifunctional Metamaterials. A.H.A. also acknowledges the financial support by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada through NSERC Discovery Grant (RGPIN-2022-04493) and the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) through the John R. Evans Leaders Fund. J.C. acknowledges the financial support provided by the China Scholarship Council (File No. 201909370077), Quebec Research Fund - Nature and Technologies (FRQNT) doctoral awards (B2X), and McGill University. This research was enabled by support from Calcul Québec and Compute Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Shahryari, B. & Akbarzadeh, A. Tunable auxeticity in hydrogenated carbon nanotube origami metamaterial. MRS Bulletin 49, 38–48 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-023-00545-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-023-00545-0