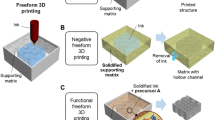
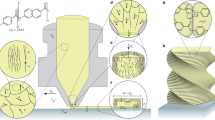
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) printing generates cellular architected metamaterials with complex geometries by introducing controlled porosity. Their ordered architecture, imitative from the hierarchical high-strength structure in nature, defines the mechanical properties that can be coupled with other properties such as the acoustic, thermal, or biologic response. Recent progress in the field of 3D architecture materials have advanced that enables for design of lightweight materials with high strength and stiffness at low densities. Applications of these materials have been identified in the fields of ultra-lightweight structures, thermal management, electrochemical devices, and high absorption capacity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Valdevit, A.J. Jacobsen, J.R. Greer, and W.B. Carter: Protocols for the optimal design of multi-functional cellular structures: from hypersonics to micro-architected materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 15 (2011).
K. Wang, Y. Zhao, Y.-H. Chang, Z. Qian, C. Zhang, B. Wang, M.A. Vannan, and M.J. Wang: Controlling the mechanical behavior of dual-material 3D printed meta-materials for patient-specific tissue-mimicking phantoms. Mater. Des. 90, 704 (2016).
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, F. Medina, H. Lopez, E. Martinez, B.I. Machado, D.H. Hernandez, L. Martinez, M.I. Lopez, R.B. Wicker, and J. Bracke: Next-generation biomedical implants using additive manufacturing of complex, cellular and functional mesh arrays. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 368, 1999 (2010).
C. Zhu, T. Liu, F. Qian, T.Y.J. Han, E.B. Duoss, J.D. Kuntz, C.M. Spadaccini, M.A. Worsley, and Y. Li: Supercapacitors based on three-dimensional hierarchical graphene aerogels with periodic macropores. Nano Lett. 16, 3448 (2016).
C. Xu, B.M. Gallant, P.U. Wunderlich, T. Lohmann, and J.R. Greer: Three-dimensional Au microlattices as positive electrodes for Li-O2 batteries. ACS Nano 9, 5876 (2015).
G. Von Freymann, A. Ledermann, M. Thiel, I. Staude, S. Essig, K. Busch, and M. Wegener: Three-dimensional nanostructures for photonics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 1038 (2010).
J. Christensen, M. Kadic, M. Wegener, O. Kraft, and M. Wegener: Vibrant times for mechanical metamaterials. MRS Commun. 5, 453 (2015).
L.J. Gibson, and M.F. Ashby: Cellular Solids Structure and Properties, 2nd ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001).
T.A. Schaedler, A.J. Jacobsen, A. Torrents, A.E. Sorensen, J. Lian, J.R. Greer, L. Valdevit, and W.B. Carter: Ultralight metallic microlattices. Science 334, 962 (2011).
M.F. Ashby: Cellular solids–scaling of properties. In Cellular Ceramics: Structure, Manufacturing, Properties and Applications, edited by M. Scheffler, and P. Colombo (WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2005), pp. 3.
L.C. Montemayor, and J.R. Greer: Mechanical response of hollow metallic nanolattices: combining structural and material size effects. J. Appl. Mech. 82, 071012 (2015).
J. Bauer, A. Schroer, R. Schwaiger, and O. Kraft: Approaching theoretical strength in glassy carbon nanolattices. Nat. Mater. 15, 438 (2016).
T. George, V.S. Deshpande, and H.N.G. Wadley: Mechanical response of carbon fiber composite sandwich panels with pyramidal truss cores. Compos. Part A, Appl. Sci. Manuf. 47, 31 (2013).
L. Dong, V. Deshpande, and H. Wadley: Mechanical response of Ti-6Al-4 V octet-truss lattice structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 60, 107 (2015).
N.A. Fleck, V.S. Deshpande, and M.F. Ashby: Micro-architectured materials: past, present and future. Proc. R. Soc. A 466, 2496 (2010).
V.S. Deshpande, M.F. Ashby, and N.A. Fleck: Foam topology: bending versus stretching dominated architectures. Acta Mater. 49, 1035 (2001).
L.R. Meza, A.J. Zelhofer, N. Clarke, A.J. Mateos, D.M. Kochmann, and J.R. Greer: Resilient 3D hierarchical architected metamaterials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 11502 (2015).
L. Valdevit, and J. Bauer: Fabrication of 3D micro-architected/nano-architected materials. In Three-Dimensional Microfabrication Using Two-photon Polymerization, edited by Tommaso Baldacchini (Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, 2016), pp. 345.
K.C. Cheung, and N. Gershenfeld: Reversibly assembled cellular composite materials. Science 341, 1219 (2013).
T. Zhu, J. Li, S. Ogata, and S. Yip: Mechanics of ultra-strength materials. MRS Bull. 34, 167 (2009).
B.G. Compton, and J.A. Lewis: 3D-printing of lightweight cellular composites. Adv. Mater. 26, 5930 (2014).
X. Zheng, H. Lee, T.H. Weisgraber, M. Shusteff, J. DeOtte, E.B. Duoss, J.D. Kuntz, M.M. Biener, Q. Ge, J. A. Jackson, S.O. Kucheyev, N.X. Fang, and C.M. Spadaccini: Ultralight, ultrastiff mechanical metamaterials. Science 344, 1373 (2014).
R.D. Farahani, K. Chizari, and D. Therriault: Three-dimensional printing of freeform helical microstructures: a review. Nanoscale 6, 10470 (2014).
L. Montemayor, V. Chernow, and Julia J.R. Greer: Materials by design: using architecture in material design to reach new property spaces. MRS Bull. 40, 1122 (2015).
T. Bückmann, N. Stenger, M. Kadic, J. Kaschke, A. Frölich, T. Kennerknecht, C. Eberl, M. Thiel, and M. Wegener: Tailored 3D mechanical metamaterials made by dip-in direct-laser-writing optical lithography. Adv. Mater. 24, 2710 (2012).
F. Brenne, T. Niendorf, and H.J. Maier: Additively manufactured cellular structures: impact of microstructure and local strains on the monotonic and cyclic behavior under uniaxial and bending load. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 213, 1558 (2013).
L.C. Montemayor, L.R. Meza, and J.R. Greer: Design and fabrication of hollow rigid nanolattices via two-photon lithography. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16, 184 (2014).
L.R. Meza, S. Das, and J.R. Greer: Strong, lightweight, and recoverable three-dimensional ceramic nanolattices. Science 345, 1322 (2014).
S. Naghieh, M.R. Karamooz Ravari, M. Badrossamay, E. Foroozmehr, and M. Kadkhodaei: Numerical investigation of the mechanical properties of the additive manufactured bone scaffolds fabricated by FDM: the effect of layer penetration and post-heating. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 59, 241 (2016).
R.D. Farahani, L.L. Lebel, and D. Therriault: Laboratory Processing parameters investigation for the fabrication of self-supported and free-form polymeric microstructures using ultraviolet-assisted three-dimensional printing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 055020 (2014).
M.F. Ashby: The properties of foams and lattices. Philos. Trans. A, Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 364, 15 (2006).
J. Bauer, S. Hengsbachb, I. Tesaria, R. Schwaigera, and O. Kraft: High-strength cellular ceramic composites with 3D microarchitecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 2453 (2014).
C. Zhu, T.Y.-J. Han, E.B. Duoss, A.M. Golobic, J.D. Kuntz, C.M. Spadaccini, and M.A. Worsley: Highly compressible 3D periodic gra-phene aerogel microlattices. Nat. Commun. 6, 6962 (2015).
D. Lin, S. **, F. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Zhou, and G.J. Cheng: 3D stereolithography printing of graphene oxide reinforced complex architectures. Nanotechnology 26, 434003 (2015).
J.R. Raney, and J.A. Lewis: Printing mesoscale architectures. MRS Bull. 40, 943 (2015).
T. Serra, J.A. Planell, and M. Navarro: High-resolution PLA-based composite scaffolds via 3-D printing technology. Acta Biomater. 9, 5521 (2013).
A. Szczurek, A. Ortona, L. Ferrari, E. Rezaei, G. Medjahdi, V. Fierro, D. Bychanok, P. Kuzhir, and A. Celzard: Carbon periodic cellular architectures. Carbon 88, 70 (2015).
J. **ong, R. Mines, R. Ghosh, A. Vaziri, L. Ma, A. Ohrndorf, H.J. Christ, and L. Wu: Advanced micro-lattice materials. Adv. Eng. Mater. 17, 1253 (2015).
J.P.P. Kruth, P. Mercelis, J. Van Vaerenbergh, L. Froyen, M. Rombouts, J. Van Vaerenbergh, L. Froyen, M. Rombouts, J. Van Vaerenbergh, L. Froyen, and M. Rombouts: Binding mechanisms in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 11, 26 (2005).
A.J. Jacobsen, W. Barvosa-Carter, and S. Nutt: Micro-scale truss structures formed from self-propagating photopolymer waveguides. Adv. Mater. 19, 3892 (2007).
A. Torrents, T.A. Schaedler, A.J. Jacobsen, W.B. Carter, and L. Valdevit: Characterization of nickel-based microlattice materials with structural hierarchy from the nanometer to the millimeter scale. Acta Mater. 60, 511 (2012).
A.T. Lausic, A.G. Bird, C.A. Steeves, and G.D. Hibbard: Scale-dependent failure of stereolithographic polymer microtrusses in three-point bending. J. Compos. Mater. 50, 1739 (2015).
J. Bauer, A. Schroer, R. Schwaiger, I. Tesari, C. Lange, L. Valdevit, and O. Kraft: Push-to-pull tensile testing of ultra-strong nanoscale ceramic–polymer composites made by additive manufacturing. Extreme Mech. Lett. 3, 105 (2015).
Z. Yang, C. Yan, J. Liu, S. Chabi, Y. **a, and Y. Zhu: Designing 3D gra-phene networks via a 3D-printed Ni template. RSC Adv. 5, 29397 (2015).
E. Taneva, B. Kusnoto, and C.A. Evans: 3D scanning, imaging and printing in orthodontics. In Issues in Contemporary Orthodontics, edited by Farid Bourzgui (INTECH, Rijeka, Croatia, 2015), pp. 148.
A. Clausen, F. Wang, J.S. Jensen, O. Sigmund, and J.A. Lewis: Topology optimized architectures with programmable Poisson’s Ratio over large Deformations. Adv. Mater. 27, 5523 (2015).
Z. Yang, S. Chabi, Y. **a, and Y. Zhu: Preparation of 3D graphene-based architectures and their applications in supercapacitors. Progr. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25, 554 (2015).
J.T. Kim, S.K. Seol, J. Pyo, J.S. Lee, J.H. Je, and G. Margaritondo: Three-dimensional writing of conducting polymer nanowire arrays by meniscus-guided polymerization. Adv. Mater. 23, 1968 (2011).
S.K. Seol, W.S. Chang, D. Kim, and S. Jung: Carbon nanotube-conducting polymer composite wires formed by fountain pen growth (FPG) route. RSC Adv. 2, 8926 (2012).
J.H. Kim, W.S. Chang, D. Kim, J.R. Yang, J.T. Han, G.W. Lee, J.T. Kim, and S.K. Seol: 3D printing of reduced graphene oxide nanowires. Adv. Mater. 27, 157 (2015).
M.R. Karamooz Ravari, M. Kadkhodaei, M. Badrossamay, and R. Rezaei: Numerical investigation on mechanical properties of cellular lattice structures fabricated by fused deposition modeling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 88, 154 (2014).
T.J. Ober, D. Foresti, and J.A. Lewis: Active mixing of complex fluids at the microscale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 12293 (2015).
K. Wang, Y.-H. Chang, Y. Chen, C. Zhang, and B. Wang: Designable dualmaterial auxetic metamaterials using three-dimensional printing. Mater. Des. 67, 159 (2015).
H. Gao, B. Ji, I.L. Jäger, E. Arzt, and P. Fratzl: Materials become insensitive to flaws at nanoscale: lessons from nature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5597 (2013).
Y. Ma, and Y. Chen: Three-dimensional graphene networks: synthesis, properties and applications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2, 40 (2015).
B. Román-Manso, F.M. Figueiredo, B. Achiaga, R. Barea, D. Pérez-Coll, A. Morelos-Gómez, M. Terrones, I. Osendi, M. Belmonte, and P. Miranzo: Electrically functional 3D-architectured graphene/SiC composites. Carbon 100, 318 (2016).
L. Dong, V. Deshpande, and H. Wadley: Mechanical properties of carbon fiber composite octet-truss lattice structures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 119, 26 (2015).
J. Liu, W. Qiao, J. Liu, D. **e, Z. Zhou, L. Wu, and L. Ma: High temperature indentation behaviors of carbon fiber composite pyramidal truss structures. Compos. Struct. 131, 266 (2015).
A.G. Mark, S. Palagi, T. Qiu, and P. Fischer: Auxetic metamaterial simplifies soft robot design (IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation Proc., Sweden, 2016), p. 4951.
C.S. Roper, R.C. Schubert, K.J. Maloney, D. Page, C.J. Ro, S.S. Yang, and A.J. Jacobsen: Scalable 3D bicontinuous fluid networks: polymer heat exchangers toward artificial organs. Adv. Mater. 27, 2479 (2015).
L.C. Mozdzen, R. Rodgers, J.M. Banks, R.C. Bailey, and B.A.C. Harley: Increasing the strength and bioactivity of collagen scaffolds using customizable arrays of 3D-printed polymer fibers. Acta Biomater. 33, 25 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work received financial support from Discovery Accelerator Supplement Grant 493028-2016, funded by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, M., Han, S.M. & Kim, W.S. Three-dimensionally printed cellular architecture materials: perspectives on fabrication, material advances, and applications. MRS Communications 7, 8–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2016.62
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2016.62