Abstract
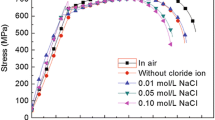
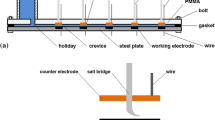
Assessment of anodic and cathodic potentials on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of API X52 pipeline steel through slow strain rate tests (SSRT) was studied. The SSRT were carried out in a NS4 solution to simulated dilute ground water that has been found to be associated with SCC of pipelines. SSRT were performed and evaluated in air and in the NS4 solution at room temperature at an extension rate of 1×10-6 in/sec. Tests were performed at controlled electrochemical polarization potentials, both anodic and cathodic (100, 200, 400 mV) versus the open circuit corrosion potential. The results of reduction in area ratio (RAR), time to failure ratio (TFR) and plastic elongation ratio (PER) of the specimens tested in the soil solution indicate that X52 pipeline steel was susceptible to SCC at cathodic potentials. These specimens showed a brittle type of fracture with transgranular appearance. The SCC proceess and mechanism of X52 steel in the NS4 solution is mixed-controlled by both anodic dissolution and the hydrogen involvement. At positive potentials the SCC is based mainly on the anodic dissolution mechanism. When the applied potentials shifted negatively, the SCC on the steel follows mainly hydrogen embrittlement mechanism. This mechanism was confirmed through the internal cracks observed in the specimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Κ. Krist and L. Leewis, Pipeline & Gas Journal, 49–52, (1998).
J. A. Beavers and B. A. Harle, Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Artic Engineering, 123,147–51,(2001).
ASTM G-129, Slow strain rate testing to evaluate the susceptibility of metallic materials to environmentally assisted cracking, 1–7, (2006).
R. D. Kane, C.J.B.M. Joia, A.L.L.T. Small and J.A.C. Ponciano, Materials Performance, 36, 71–74, (1997).
J. A. Beavers, J. T. Jhonson and R. L. Sutherby, International Pipeline Conference (IPC), ASME, 979–991 (2000).
R. N. Parkins, Stress Corrosion Cracking - The Slow Strain Rate Technique, ASTM STP 665, edited by G.M. Ugiansky and J.H. Payer, 5–25, (1979).
R. N. Parkins, J. A. Beavers, Corrosion. 59, 258–273, (2003).
W. Chen, F. King, E. Vokes, Corrosion. 58, 267–275, (2002).
M. Puiggali, S. Rousserie, M. Touzet, Corrosion. 58, 961–970, (2002).
X.C. Li, R.L. Eadie and J.L. Luo, Corrosion Engineering, Science and Technology, 43(4), 297–303, (2008).
A. Benmoussat and M. Hadjel, Journal of Corrosion Science and Engineering, 7, 1–14, (2005).
L. J. Qiao, J. L. Luo, Journal of Materials Science Letters, 16, 516–520, (1997).
NACE TM-0198 Slow Strain Rate Test Method for Screening Corrosion-Resistant Alloys (CRAs) for Stress Corrosion Cracking in Sour Oilfield Service, 1–21, (2004).
Z. Y. Liu, X.G. Li, C.W. Du, G.L. Zhai and Y. F. Cheng, Corrosion Science, 50, 2251–2257 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Téllez-Vázquez, J.O., Patiño-Carachure, C., Bedolla-Jacuinde, A. et al. Cathodic Protection Effect on the Assessment of SCC Susceptibility of X52 Pipeline Steel. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1242, 453 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1242-S4-53
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1242-S4-53