Abstract
The concentrations of cadmium and other metal ions in selected organs, urine, and blood of female rats were measured after exposure to cadmium chloride through their diet or by oral or intravenous administration. The hematological and urinary variations were followed for 4 wk.
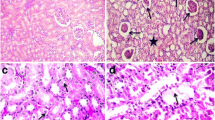
Body weight gain and the weights of livers and kidneys from all treated groups were not significantly different from the controls. No gross morphological changes were observed in any of the tissues studied at necropsy.
The accumulation of cadmium occurred in the liver and kidney. The zinc levels in these organs were elevated relative to controls, in all treated groups regardless of dose and exposure route. Copper was elevated in the liver, kidney, bone, and blood of animals subject to intravenous administration of cadmium. Hepatic iron was decreased in the dietary and orally treated groups, but was not affected in the intravenous study group. The level of magnesium in kidney was increased for all exposure routes, but that of liver was increased only in the intravenously injected groups. The changes in the concentrations of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus did not follow a specific pattern and varied from organ to organ, depending on the exposure route.
The discussion includes a relationship between tissue injury and the alteration of tissue essential element concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization, Cadmium, Environ. Health Criteria 134, 67–130 (1992).
H. Andersson, K. Petersson-Grawe, E. Lindqvist, J. Luthman, A. Oskarsson, and L. Olson, Low-level cadmium exposure of lactating rats causes alterations in brain serotonin levels in the offspring, Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 19, 105–115 (1997).
M. Webb, Cadmium, Br. Med. Bull. 31, 246–250 (1975).
M. Abdulla and J. Chmielnicka, New aspects on the distribution and metabolism of essential trace elements after dietary exposure to toxic metals, Biol. Trace Element Res. 23, 25–53 (1990).
L. Thijs, J. Staessen, A. Amery, P. Bruaux, J. P. Buchet, F. Claeys, et al., Determination of serum zinc in a random population sample of four Belgian towns with different degrees of environmental exposure to cadmium, Environ. Health Perspect. 98, 251–258 (1992).
S. Telisman, Interactions of essential and/or toxic metals and metalloids regarding interindividual differences in susceptibility to various toxicants and chronic diseases in man, Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 46, 459–476 1995.
S. C. Gad and C. S. Wei, Statistics for toxicologists, in Principles and Methods of Toxicology, 3rd ed., A. W. Hayes, ed., Raven, New York, pp. 221–274 (1994).
S. A. Gunn and T. C. Gould, Selective accumulation of 115Cd by cortex of rat kidney, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 96, 820–823 (1957).
L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg, and V. D. Vouk (eds.), Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam (1986).
N. Sugawara, Influence of cadmium on zinc distribution in the mouse liver and kidney: role of metallothionein, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmcol. 42, 377–386 (1977).
S. Hirano, N. Tsukamoto, E. Kobayashi, and K. T. Suzuki, Toxicity of cadmium oxide instilled into rat lung. I. Metabolism of cadmium oxide in the lung and its effects on essential elements, Toxicology 55, 15–24 (1989).
H. J. Weigel, H. J. Jager, and I. Elmadfa, Cadmium accumulation in rat organs after extended oral administration with low concentrations of cadmium oxide, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13, 279–287 (1984).
M. D. Stonard and M. Webb, Influence of dietary cadmium on the distribution of the essential metals copper, zinc and iron in tissues of the rat, Chem.-Biol. Interact. 15, 349–363 (1976).
W. Moore, Jr., J. F. Stara, W. C. Crocker, M. Malanchuk, and R. Iltis, Comparison of 115mcadmium retention in rats following different routes of administration, Environ. Res. 6, 819–829 (1973).
C. F. Decker, R. U. Byerrum, and C. A. Hoppert, A study of the distribution and retention of Cd-115 in the albino rat, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 66, 140–145 (1957).
F. N. Kotsonis and C. D. Klaassen, Toxicity and distribution of cadmium administered to rats at sublethal doses, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmcol. 41, 667–680 (1977).
Y. Lind, J. Engman, L. Jorhem, and A. W. Glynn, Cadmium accumulation in liver and kidney of mice exposed to the same weekly cadmium dose continuously or once a week, Fundam. Chem. Toxicol. 35, 891–895 (1997).
K. Nomiyama, Y. Sugata, H. Nomiyama, and A. Yamamoto, Dose-response relationship for cadmium, in Effects and Dose-Response Relationships of Toxic Metals, G. F. Nordberg, ed., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp. 380–385 (1976).
B. Elsenhaus, K. Kolb, K. Schumann, and W. Forth, The longitudal-distribution of cadmium, zinc, copper, iron, and metallothionein in the small-intestinal mucosa of rats after administration of cadmium chloride, Biol. Trace Element Res. 41, 31–46 (1994).
B. D. Whelton, D. P. Peterson, E. S. Moretti, R. W. Mauser, and M. H. Bhattacharyys, Hepatic levels of cadmium, zinc and copper in multiparous, nulliparous and ovariectomized mice fed either a nutrient-sufficient or -deficient diet containing cadmium, Toxicology 119, 141–153 (1997).
D. Bhattacharjee, T. K. Shetty, and K. Sandaram, Studies on the distribution of 115mCd in mice tissue, Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 7, 74–76 (1979).
K. L. Wong, R. Chachia, and D. C. Klaassen, Comparison of the toxicity and tissue distribution of cadmium in new born and adult rats after repeated administration, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 56, 317–325 (1980).
R. E. Dudley, L. M. Gammal, and C. D. Klaassen, Cadmium-induced hepatic and renal injury in chronically exposed rats: likely role of hepatic cadmium-metallothionein in nephrotoxicity, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 77, 414–426 (1985).
A. V. Colucci, D. Winge, and M. D. Kranso, Cadmium accumulation in rat liver, Arch. Environ. Health. 30, 153–157 (1975).
K. Kawai, K. Fukada, and M. Kimura, Morphological alterations in ezperimental cadmium exposure with special reference to the onset of renal lesion, in Effects and Dose-Response Relationships of Toxic Metals, G. F. Nordberg, ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 343–370 (1976).
J. A. Bonnell, J. H. Ross, and E. King, Renal lesions in experimental cadmium poisoning, Br. J. Ind. Med. 17, 69–80 (1960).
F. W. Bonner, L. J. King, and D. V. Parke, The tissue distribution and urinary excretion of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron, following repeated parenteral administration of cadmium to rats, Chem.-Biol. Interact. 27, 343–351 (1979).
L. Friberg, M. Piscator, G. F. Nordberg, and T. Kjellstrom, Cadmium in the Environment, 2nd ed. CRC, Cleveland, OH (1974).
R. Swiergrosz, M. Zakrezewska, K. Sawicka-Kapusta, K. Bacia, and I. Janowska, Accumulation of cadmium in and its effect on bank vole tissues after chronic exposure, Ectoxicol. Environ. Safety 41, 130–136 (1998).
O. Wada, A. Miyahara, S. Manabe, H. Matsui, and T. Ono. Effect of acute administration of cadmium on distribution of zinc in the hamster, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 9, 509–513 (1982).
M. Torra, J. To-Figueras, M. Rodamilans, M. Brunet, and J. Corbella, Cadmium and zinc relationships in the liver and kidney of humans exposed to environmental cadmium, Sci. Total Environ. 170, 53–57 (1995).
R. Honda and K. Nogawa, Cadmium, zinc and copper relationships in kidneys and liver of humans exposed to environmental cadmium, Arch. Toxicol. 59, 437–442 (1987).
R. Nimoyama, N. Koizumi, and T. Tsukamoto, Change of metal distribution in organs of cadmium-administration and copper-deficient rats, Jpn. J. Hyg. 48, 920–931 (1993) (in Japanese).
T. Maitani and K. T. Suzuki, Essential metal contents and metallothionein-like protein in testis of mice after cadmium administration, Toxicology 40, 1–12 (1986).
C. V. Nolan and Z. A. Shaikh, Determination of metallothionein in tissues by radioimmunoassay and by cadmium saturation method, Anal. Biochem. 154, 213–223 (1986).
H. E. Heilmaier, G. A. Drasch, E. Kretscmer, and K. H. Summer, Metallothionein, cadmium, copper and zinc levels of human and rat tissues, Toxicol. Lett. 38, 205–211 (1987).
M. Webb and R. D. Verschoyle, An investigation of the role of metallo-thioneins in protection against the acute toxicity of cadmium ion, Biochem. Pharmacol. 25, 673–679 (1976).
F. W. Bonner, L. J. King, and D. V. Parke, The effect of dietary cadmium on zinc, copper and iron levels in the bone of rats, Toxicol. Lett. 5, 105–108 (1980).
H. Yoshikawa, Accumulation of cadmium organs of mice by a long-term injection of cadmium and interactives of cadmium with copper, manganese and zinc already present in the animals, Jpn. J. Ind. Health 21, 171–177 (1979) (in Japanese).
K. Nomiyama and H. Nomiyama, Modified trace element metabolism in cadmium-induced renal dysfunctions, Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 59, 427–430 (1986).
S. L. Ashby, L. J. King, and D. V. W. Parke, Effect of acute administration of cadmium on the disposition of copper, zinc and iron in the rat, Environ. Res. 21, 177–185 (1980).
Y. Suzuki, Cadmium, copper, and zinc distribution in blood of rat after long-term cadmium administration, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 7, 215–262 (1981).
K. T. Suzuki, K. Yaguchi, R. Ohnuki, M. Nishikawa, and Y. K. Yamada, Extent of cadmium accumulation and its effect on essential metals in liver, kidney and body fluid, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 11, 713–726 (1983).
K. Nogawa, R. Honda, Y. Yamada, T. Kido, I. Tsuritani, and M. Ishizaki, Iron concentrations in liver and kidney of cadmium-exposed human subjects, Toxicol. Lett. 21, 209–212 (1984).
S. Kawano, T. Omura, H. Nakagawa, H. Toga, M. Nishi, and Y. Matsuo, Relationship between renal tubular damage and urinary excretion of heavy metals, Kankyo Hoken Report 46, 248–255. (1980) (in Japanese).
R. H. Wilson, F. De Eds, and A. J. Cox, Jr., Effects of continued cadmium feeding, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 71, 222–235 (1941).
L. Friberg, Health hazards in the manufacture of alkaline accumulators with special reference to chronic cadmium poisoning, Acta Med. Scand. 130(Suppl. 240), 1–124 (1950).
L. Friberg, Iron and liver administration in chronic cadmium poisoning and studies on the distribution and excretion of cadmium. Experimental investigations in rabbits, Acta Pharmacol. 11, 168–178 (1955).
N. Sugawara, C. Sugawara, and H. Miyake, Effect of subcutaneous and oral cadmium on iron metabolism: role of ceruloplasmin and metallothionein, Arch. Toxicol. 56, 25–28 (1984).
E. Prigge, Early signs of oral and inhalative cadmium uptake in rats, Arch. Toxicol. 40, 231–247 (1978).
E. Prigge, H. P. Baumert, and H. Muhle, Effects of dietary and inhalative cadmium on haemoglobin and haemocrit in rats, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17, 585–590 (1977).
M. Berlin and L. Friberg, Bone marrow activity and erythrocyte destruction in chronic cadmium poisoning, Arch. Environ. Health 1, 478–486 (1960).
B. Axelsson and M. Piscator, Serum proteins in cadmium-poisoned rabbits with special reference to haemolytic anaemia, Arch. Environ. Health 12, 374–381 (1966).
K. Zierold, Effects of cadmium on electrolyte ions in cultured rat hepatocytes studied by X-ray microanalysis of cryosections, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 144, 70–76 (1997).
S. K. El-Mofty, M. C. Scrutton, C. Nicolini, and J. L. Farber, Early, responsible plasma membrane injury in galactosamine-induced liver cell death, Am. J. Pathol. 79, 579 (1975).
R. J. Ingersell and R. H. Wassermann, Vitamin D3-induced calcium-binding protein, J. Biol. Chem. 246, 2802–2814 (1971).
N. Sugawara, Inhibitory effect of cadmium on calcium absorption from rat duodenum, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 5, 167–175 (1977).
M. Ando, Y. Sayato, M. Tonomura, and T. Osawa, Studies on excretion and uptake of cadmium by rats after continuous oral administration of cadmium, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 39, 321–327 (1977).
P. Massanyi, R. Toman, M. Valent, and O. Jones, Serum mineral profile of rabbits after an experimental administration of cadmium, J. Environ. Sci. Health A30, 2221–2227 (1995).
Z. Z. Wahba and M. P. Waalkes, Cadmium-induced route-specific alterations in essential trace element homeostasis, Toxicol. Lett. 54, 77–81 (1990).
K. Tuchiya, Y. Seki, and M. Sugita, Cadmium concentrations in the organs and tissues of cadavers from accidental deaths, Keio J. Med. 25, 83–90 (1976).
M. Yoshimura, S. Sugiyama, S. Doi, H. Noda, M. Yamaguchi, and S. Tatsumi, Secular changes of cadmium concentration accumulated in organs of Japanese from 1976 to 1986, Rep. Environ. Sci. Inst. Kinki Univ. 17, 211–214 (1989) (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshi, S., Nakagawa, Ji. & Ando, M. Effects of cadmium administration on the endogenous metal balance in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 76, 257–278 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:76:3:256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:76:3:256