Abstract
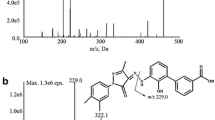
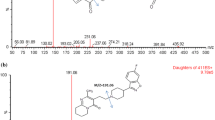
Batifiban is a new platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor antagonist. In this work, an analytical method based on liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry has been firstly developed and validated for the quantitative measurement of batifiban in human plasma to support the investigation of this compound. Separation of analyte and the internal standard eptifibatide was performed on a Thermo HyPURITY C18 column (150 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm) with a mobile phase consisting of formic acid 0.1% (v/v)–acetonitrile (40:60, v/v) at a flow rate of 0.25 mL min−1. The Waters QuattroMicro API triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was operated in multiple reaction monitoring mode via positive electrospray ionization interface using the transition m/z 819.2 → m/z (623.9 + 159.4) for batifiban and m/z 833.4 → m/z (645.7 + 159.3) for IS. The method was linear over the concentration range of 2.45–5,000 μg L−1. The intra- and inter- day precisions were less than 15% in terms of relative standard deviation, and the accuracy was within 8.5% in terms of relative error (RE). The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was identifiable and reproducible at 2.45 μg L−1 with acceptable precision and accuracy. The validated method offered sensitivity and wide linear concentration range. This method was successfully applied for the evaluation of pharmacokinetics of batifiban afer single oral doses of 55, 110 and 220 μg kg−1 batifiban to 36 Chinese healthy volunteers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Qiao J, Li Q, Deng J, Tan Z, Guo T, Li W (2009) J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 29(1):12–18
Madan M, Berkowitz SD, Tcheng JE (1998) Circulation 98(23):2629–2635
Kong DF, Califf RM, Miller DP (1998) Circulation 98(25):2829–2835
Seitz RJ, Siebler M (2008) Curr Vasc Pharmacol 6(1):29–36
Tricoci P, Newby LK, DE Kandzari, Harrington RA (2007) Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 5(3):401–412. doi:10.1586/14779072.5.3.401
Moser M, bertram U, Peter K, Bode C, Ruef J (2003) J Cardiovas Pharmacol 41(4):586–592
Harrington RA, Kleiman NS, Kottke-Marchant K, Lincoff AM, Tcheng JE, Sigmon KN et al (1995) Am J Cardiol 76(7):1222–1227. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(99)80345-2
Scarborough RM, Naughton MA, Teng W, Rose JW, Phillips, Nannizzi L et al (1993) J Biol Chem 268(2):1066–1073
Gibbins M (2004) J Cell Sci 117(16):3415–3425. doi:10.1242/jcs.01325
Mousa SA, Bozarth JM, Forsythe MS, Jackson SM, Leamy A, Diemer MM, Kapil RP, Knabb RM, Mayo MC, Pierce SK (1994) Circulation 89(1):3–12
Huck CW, Bonn GK (2000) J Chromatogr A 885(1-2):51–72. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00333-2
Shah VP, Midha KK, Findlay JWA, Hill HM, Hulse JD, McGilveray IJ, McKay G, Miller KJ, Patnaik RN, Powell ML, Tonelli A, Viswanathan CT, Yacobi A (2000) Pharm Res 17(12):1551–1557. doi:10.1023/A:1007669411738
Karnes HT, March C (1993) Pharm Res 10(10):1420–1426. doi:10.1023/A:1018958805795
Taylor PJ (2005) Clin Biochem 38(4):328–334. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.11.007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China 30528026, 30300428, 30672497 and 30500623, and by the China Medical Board of New York grants 01-755.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, ZR., Ou-Yang, DS., Zhou, G. et al. Validated LC–MS–MS Method for Quantitative Determination of Batifiban in Human Plasma and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Chroma 70, 415–421 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1195-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1195-8