Abstract
Objective
Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy has replaced axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) as the definitive nodal staging procedure for breast cancer. SLN biopsy has been proven to cause less morbidity and be more cost effective than complete ALND. Short-term follow-up has shown that lymphatic map** and SLN have a low false-negative rate, but there is limited data demonstrating long-term outcomes within a large consecutive series of patients.
Methods
Retrospective review of a prospective database of breast cancer patients at our institution was performed. The initial map** of 1,530 patients with invasive breast cancer who demonstrated a negative sentinel node biopsy and no axillary dissection between January 1995 and June 2003 were collated and reviewed to achieve a long-term follow-up. These 1,530 patients were reviewed for follow-up time, local recurrences, distant metastases, and survival.
Results
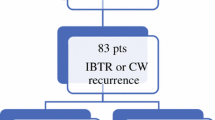
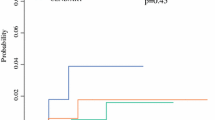
1,530 consecutively mapped invasive breast cancer patients had a negative SLN biopsy and no ALND. The mean invasive tumor size was 1.40 cm. Of 1,530 patients, 73% (1,121) underwent lumpectomy and 27% (409) underwent mastectomy. Mean follow-up was 4.92 years (range 0–12.0 years). There have been 4 (0.26%) patients presenting with local axillary recurrences, 54 (3.53%) patients presenting with local recurrences in the ipsilateral breast/chest wall, and 24 (1.57%) presenting with distant metastases.
Conclusion
These data confirm that SLN biopsy is an effective and safe alternative to ALND for detection of nodal metastases in patients with invasive breast cancer and should be used as the standard tool for nodal staging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher B, Slack NH. Number of lymph nodes examined and the prognosis of breast carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970;131(1):79–88.
Nemoto T, et al. Management and survival of female breast cancer: results of a national survey by the American College of Surgeons. Cancer. 1980;45(12):2917–24.
Petrek JA, Pressman PI, Smith RA. Lymphedema: current issues in research and management. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50(5):292–307.
Bass SS, et al. Lymphatic map** and sentinel lymph node biopsy. Breast J. 1999;5(5):288–95.
Fleissig A, et al. Post-operative arm morbidity and quality of life Results of the ALMANAC randomised trial comparing sentinel node biopsy with standard axillary treatment in the management of patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95(3):279–93.
Lucci A, et al. Surgical complications associated with sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) plus axillary lymph node dissection compared with SLND alone in the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Trial Z0011. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(24):3657–63.
Krag DN, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(10):881–8.
Liberman L. Pathologic analysis of sentinel lymph nodes in breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;88(5):971–7.
Veronesi U, et al. A randomized comparison of sentinel-node biopsy with routine axillary dissection in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(6):546–53.
Marrazzo A, et al. Is sentinel lymph node biopsy more accurate than axillary dissection for staging nodal involvement in breast cancer patients? Chir Ital. 2007;59(5):693–9.
Cox CE. Lymphatic map** in breast cancer: combination technique. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8(9 Suppl):67S–70S.
Bass SS, et al. The role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 1999;189(2):183–94.
van der Ploeg IMC, et al. Axillary recurrence after a tumour-negative sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34(12):1277–84.
Naik A, et al. The risk of axillary relapse after sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer is comparable with that of axillary lymph node dissection: a follow-up study of 4008 procedures. Ann Surg. 2004;240(3):468–71.
Bergkvist L, et al. Axillary recurrence rate after negative sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer: three-year follow-up of the Swedish Multicenter Cohort Study. Ann Surg. 2008;247(1):150–6 doi 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318153ff40.
Takei H, et al. Recurrence after sentinel lymph node biopsy with or without axillary lymph node dissection in patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2007;14(1):16–24.
Veronesi U, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer: early results in 953 patients with negative sentinel node biopsy and no axillary dissection. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41(2):231–7.
Poletti P, et al. Axillary recurrence in sentinel lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(11):1842–6.
Blanchard DK, et al. Relapse and morbidity in patients undergoing sentinel lymph node biopsy alone or with axillary dissection for breast cancer. Arch Surg. 2003;138(5):482–7 (discussion 487–8).
Jeruss JS, et al. Axillary recurrence after sentinel node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005;12(1):34–40.
Swenson KK, et al. Axillary disease recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection for breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;104(9):1834–9.
Carcoforo P, et al. Accuracy and reliability of sentinel node biopsy in patients with breast cancer Single centre study with long term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95(2):111–6.
de Kanter AY, et al. 5-Year follow-up of sentinel node negative breast cancer patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006;32(3):282–6.
Veronesi U, et al. Conservative treatment of early breast cancer Long-term results of 1232 cases treated with quadrantectomy, axillary dissection, and radiotherapy. Ann Surg. 1990;211(3):250–9.
Recht A, et al. Regional nodal failure after conservative surgery and radiotherapy for early-stage breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9(6):988–96.
Chua B, Ung O, Boyages J. Competing considerations in regional nodal treatment for early breast cancer. Breast J. 2002;8(1):15–22.
Louis-Sylvestre C, et al. Axillary treatment in conservative management of operable breast cancer: dissection or radiotherapy? Results of a randomized study with 15 years of follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(1):97–101.
Greco M, et al. Breast cancer patients treated without axillary surgery: clinical implications and biologic analysis. Ann Surg. 2000;232(1):1–7.
Acknowledgment
We thank Jeff King at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center Comprehensive Breast Cancer Program Database and Helen Lewis at the Cancer Registry for their assistance in data retrieval. We also thank Samira Y. Khera, MD, Danielle M. Hasson, Laura B. White, and Elisabeth L. Dupont, MD for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0800-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiluk, J.V., Ly, Q.P., Meade, T. et al. Axillary Recurrence Rate Following Negative Sentinel Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer: Long-Term Follow-Up. Ann Surg Oncol 18 (Suppl 3), 339–342 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0704-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0704-1