Abstract
Because dopamine (DA) is one of the most critical neurotransmitters that influence a wide variety of motivated human behaviors, it is necessary to develop a facile diagnostic tool that can quantify the physiological level. In this study, core–shell magnetic silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2) were prepared using a modified sol–gel reaction. The Fe3O4@SiO2 were functionalized using 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) via a facile and rapid synthetic route, hereafter referred to as Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA The resultant Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA not only adsorbed DA molecules, but also were easily separated from solution using a simple magnetic manipulation. The adsorbed amounts of DA by the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA were quantified by measuring the changes in fluorescence intensity of polydopamine (at 463 nm) originated from the self-polymerized DA remained in the supernatant before and after the adsorption process. The Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA exhibited two-stage adsorption behavior for DA, and the maximal adsorption capacity was 108.46 μg/g at pH 8.5. Our particle system demonstrated the potential application for extracting compounds with cis-diols (including catechol amines) from the biological fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Dopamine (DA) is one of the most important catecholamine neurotransmitters, which plays major roles in central nervous system processes, such as rewarding-motivated behavior in the brain, regulating exercise, and controlling the release of various hormones [1,2,3,4]. Since the DA system plays a key role in several medical conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, Segawa disease, schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, DA concentration in biological fluids is used as important indicator for early disease diagnosis [5, 6]. Several analytical methods have been used to detect DA molecules in bio-fluids, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay, fluorescence measurements, electrochemical analysis, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) [7,8,9,10,11,12]. However, it is very difficult to determine physiological levels of DA owing to its low concentration and the presence of interfering components, which can decrease the effectiveness of common analytical tools [13, 14]. Therefore, it is essential to separate target molecules from co-existing interfering components for accurate analysis.
Currently, solid-phase extraction (SPE) is the preferred method for concentrating and purifying small amounts of analytes from biological fluids [15, 16]. In particular, magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) is a new process for pre-concentrating target analytes using magnetic adsorbents [17]. The MSPE process has been applied in a wide range of fields for the separation of various materials because the adsorbent material does not need to be packed into any type of device, unlike traditional SPE [18, 19]. Therefore, there has been a great interest for develo** adsorbent materials consisting of a magnetite core and silica (or polymer) shell. In particular, the silica surface is easily activated and can anchor various functional groups because of its abundant Si–OH groups [19, 20]. Boronic acid is also known as a typical adsorbent for catecholamine extraction because it can form cyclic esters with cis-diol compounds under alkaline conditions [21,22,23,24]. Thus, boronic acid-functionalized materials exhibit strong affinity toward cis-diol-containing compounds, which leads to their applications for various functional materials and tasks, such as diagnostic sensing, magnetic separation, and targeted drug delivery [25, 26]. When preparing boronic acid-functionalized materials, however, amine-terminated matrices should be conjugated with 4-formylphenylboronic acid via reductive amination, which typically requires very long reaction times (more than 3 days) [27,28,29,30].
In this study, core–shell magnetic silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2) featuring surface amine groups were facilely prepared via sol–gel reactions, and the amine-terminated Fe3O4@SiO2 (Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2) were subsequently modified into carboxylic acid-terminated Fe3O4@SiO2 (Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH) via a linker elongation reaction with succinic anhydride (SA). Furthermore, the Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH was conjugated with 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) for 5 h. Boronic acid-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 (Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA) were not only magnetically separable, but also form cyclic esters with the cis-diol groups of DA. The Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA exhibited two-stage adsorption behavior, and the maximal adsorption capacity of DA was 108.46 μg/g at pH 8.5.
2 Experimental methods
2.1 Chemicals
All solvents were of analytical grade and were used as received. Iron(III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl2·4H2O), sodium citrate tribasic dehydrate, 3-aminopropyl trimethoxysilane (APTMS, 97%), tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), ammonia hydroxide (NH4OH, 29 wt%), APBA, SA, N,N-dimethyl formamide (DMF), N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-Nʹ-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt (NHS) and tris–HCl buffer (pH 8.0) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Deionized (DI) water (HPLC grade) was obtained from Daejung Co.
2.2 Amine-terminated magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2)
The core–shell magnetic silica nanoparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2) were synthesized by first mixing FeCl3·6H2O and FeCl2·4H2O (3:2 mol ratio) with DI water. Next, 20 mL NH4OH (29 wt%) was added quickly to the iron chloride mixture under vigorous stirring at room temperature (RT), and black magnetite precipitates were formed immediately after the addition of NH4OH. The precipitates were then mixed with citrate solution (1.0 M) for 3 h at RT, and the solution was refluxed for 2 h at 70 °C to obtain citrate-capped magnetite (C-Fe3O4) [31,32,33,34]. Afterward, APTMS-complexed magnetite (A-Fe3O4) particles were prepared by adding APTMS to the C-Fe3O4 solution at RT, which formed magnetite clusters featuring terminal alkoxy groups [35]. Then, 1.0 mL A-Fe3O4 was added to 80 mL ethanol that contained 5 mL NH4OH (29 wt%), followed by the rapid injection of 0.2 mL TEOS under vigorous stirring for 18 h at 30 °C. Next, 0.2 mL APTMS was added to the mixture under vigorous stirring for 2 h at 30 °C, followed by refluxing for 2 h at 70 °C to strongly anchor the surface amine groups. After the reaction product was centrifuged three times using ethanol and was subsequently dispersed in 30 mL ethanol, the Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 were obtained.
2.3 Boronic acid-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 (Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA)
First, 500 μL Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 was added dropwise to 30 mL DMF that contained 10% SA and the mixture was stirred continuously for 5 h by continuously purging N2 gas through it [36,37,38]. Afterward, the obtained Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH were washed with acetone several times. The purified Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH were dispersed in 30 mL DI water. Then, 30 mL Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH dispersion was mixed with 24 mg EDC and 27 mg NHS, followed by the addition of 8 mg APBA under continuous stirring for 5 h [39, 40]. After the reaction product was centrifuged and washed with DI three times, Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA were finally obtained. The product sample was subsequently dispersed in tris–HCl buffer prior to further characterization.
2.4 Measurement of DA concentration
The concentration of DA was determined by measuring the changes in fluorescence intensity of polydopamine (PDA) [41, 42]. Under alkaline pH condition, DA is transformed into the oxidized form of quinone, which self-polymerizes into polydopamine (PDA). Fluorescence spectra of PDA were recorded in the visible wavelength ranged of 400–600 nm at the excitation wavelength of 370 nm. Then, the DA concentration was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of PDA at 463 nm, using photoluminescence spectroscopy, based on the linearly regressed standard curve between the fluorescence intensity of PDA and the corresponding DA concentration [43].
2.5 Instrumental analysis
The sizes and morphologies of the samples were analyzed using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM, 15 kV, S-4700; Hitachi, Japan) instrument and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, 200 kV, H-7600; Hitachi, Japan) device, and the magnetic properties of the samples were measured using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM, model 7404; Lake Shore, USA). The surface functional groups and zeta potentials of the particles were analyzed using a Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (Vertex 70; Bruker, Germany) and zeta potential meter (Otsuka Electronics, Japan), respectively.
3 Results and discussion
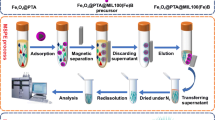
Scheme 1 depicts the synthetic procedure of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA, adsorption of DA on Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA, and final detection of residual DA in the supernatant. First, C-Fe3O4 was complexed with APTMS ligands to form A-Fe3O4. Additional file 1: Fig. S1 presents the clustered morphology of A-Fe3O4. Subsequently, A-Fe3O4 was coated with a silica layer via a sol–gel reaction with TEOS to obtain the Fe3O4@SiO2, followed by functionalization with surface amine groups. The Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 was converted into the Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH via a linker elongation reaction with SA. Lastly, APBA was conjugated with the Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH and formed the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA. Then, the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA was used to extract DA in tris–HCl buffer solution (at pH 8.5). Afterward,, the supernatant was separated from the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA using an external magnet. The residual DA in the supernatant was quantified based on the fluorescence intensity of PDA, which formed from the self-polymerized DA under alkaline conditions. Our chemical strategy combined a facile and rapid synthetic route with simple fluorescence analysis, which could compensate the drawbacks of conventional methods that typically require long preparation times and complex analysis procedures for trace DA detection.
Synthetic scheme of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic silica (Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA) nanoparticles, simple magnetic separation, and fluorescence detection of dopamine in supernatant. Here, TEOS, APTMS, DMF, SA, APBA, EDC, and NHS are tetraethyl orthosilicate, aminopropyl trimethoxysilane, N,N-dimethyl formamide, succinic anhydride, 3-aminophenylboronic acid, N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-Nʹ-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt, respectively
In the fabrication of core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2, more addition of silica precursor relative to Fe3O4 leads to the size increase of particles with more uniformity and lower magnetism. On the other hand, less addition of silica precursor leads to the size decrease of particles with less uniformity and larger magnetism, which can make it more difficult to control the binding process between DA and the particles. Thus, a certain size of particles with an appropriate magnetism needs to be prepared to enhance the binding process and produce uniform particle size.
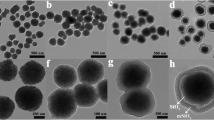
The size and morphology of the core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2 were studied using SEM and TEM, respectively. According to the SEM image in Fig. 1a, the Fe3O4@SiO2 exhibited uniform and spherical shapes. The average particle size was estimated to be 190 ± 9 nm using dynamic light scattering (Additional file 1: Fig. S2). The TEM image of Fe3O4@SiO2 illustrated the distinct embedding of Fe3O4 clusters into the silica matrix (Fig. 1b). The thickness of the silica shell was estimated to be ~ 30 nm by analyzing the TEM image.
Figure 2 illustrates the FTIR spectra of the as-prepared samples for each step of the synthesis process. The Fe3O4@SiO2 presented FTIR bands that corresponded to the stretching vibrations of Si–O–Si (1085 cm−1) and Fe–O (570 cm−1). On the other hand, Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 exhibited new peaks at 1550 and 1450 cm−1, which were attributed to the amine groups of APTMS. In addition, the peaks at 2923 and 2851 cm−1 were assigned to the asymmetric and symmetric C–H stretching vibrations of aliphatic –CH2−, respectively. Moreover, Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH, which formed during the coupling reaction of Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 with SA in DMF, exhibited additional peaks at 1640 and 1600 cm−1, which corresponded to the carbonyl and carboxylic acid groups of conjugated SA, respectively. The zeta potentials, ζ, of the samples presented alternating changes in surface charge depending on the surface functional groups, which indicated the successful modification of the particles: the ζ values of Fe3O4@SiO2, Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2, and Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH were − 18.78 ± 2.13, 14.25 ± 2.27, and − 41.38 ± 2.08, respectively (see Additional file 1: Fig. S3). In addition, Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA exhibited peaks at 1650 and 3000 cm−1, which were ascribed to the amide groups (CONH) and indicated the successful coupling reaction between the carboxyl groups of Fe3O4@SiO2-COOH and amine groups of APBA. Furthermore, Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA also exhibited peaks at 1380 cm−1 (B–O stretching) and 1450 cm−1 (benzene ring), which indicated the presence of boronic acid functional groups, as illustrated in the magnified images in the right column of Fig. 2.
The saturated magnetization curves of the samples were obtained using a VSM. As presented in Fig. 3, the functionalized particles exhibited lower magnetization values than the pristine Fe3O4@SiO2 and the magnetization values of the samples decreased as follows: Fe3O4@SiO2 (7.2 emu/g) > Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 (7.1 emu/g) > Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH (6.6 emu/g) > Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA (5.3 emu/g). All samples exhibited superparamagnetic characteristics of negligible remanence and coercivity, i.e., no hysteresis was observed in the magnetization curves. The saturated magnetisms of as-prepared particles were decreased with the increase of surface modification steps, due to the addition of nonmagnetic organic materials. After the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA were dispersed in solution, an external magnet was placed near the bottle containing the particles. As expected, the particles were attracted toward a spot near the external magnet. The complete separation of the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA using the external magnet was achieved within 2 min. The pictorial demonstration of the magnetic separation of the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA is illustrated in the inset of Fig. 3.
The XRD patterns of A-Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@SiO2 are shown in Additional file 1: Figure S4. All the XRD peaks of A-Fe3O4 are corresponding to (220), (311), (400), (422), (511) and (440) planes of Fe3O4 phase (JCPSD Card No. 76-0956). In contrast, Fe3O4@SiO2 exhibited the broad peak at ~ 22.5° that revealed the distinct amorphous silica phase, but did not show the distinct XRD peaks of Fe3O4 phase, indicative of the successful synthesis of core–shell nanostructure consisting of silica layer and clustered Fe3O4 core.
The colloidal stability of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA is important for their adsorption capacity for DA. The Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA were dispersed in five different media (DI water, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (pH 7.4), tris–HCl buffer (pH 8), tris–HCl buffer (pH 9), and ethanol) at RT. The dispersion degree of the particles was monitored after maintaining them in each media for 3 h, and then the mixtures were re-dispersed to check for the formation of precipitates in each bottle. According to the pictorial diagrams presented in Additional file 1: Fig. S5(a), (b), and (c), the dispersion degree of the particles increased as follows: ethanol < DI water < PBS (pH 7.4) ≅ tris–HCl (pH 9) < tris–HCl (pH 8). The lowest degree of particle dispersion was obtained for the ethanol mixture, whereas the highest degree of particle dispersion was obtained for the tris–HCl (pH 8.0) mixture. For the tris–HCl (pH 9.0) and PBS (pH 7.4) dispersions, some aggregation was observed at the bottom of the bottle after repeated dispersion/re-dispersion steps. Because the pKa value of APBA is ~ 8.6, the decrease in particle dispersion in the tris–HCl buffer (pH 9.0) mixture was probably due to the higher surface reactivity of APBA at pH 9.0 than that at pH 8.0.
Figure 4a illustrates the fluorescence intensity of converted PDA at 463 nm as a function of DA concentration. The standard curve was calibrated over the concentration range of 0.02–20 μM, but the standard curve deviated from linearity at the lowest concentration, below 50 nM, according to the inset of Fig. 4a. Afterwards, the adsorption process was carried out by adding 4 mg of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA to 2 mL DA solution. The supernatant contained the residual DA that was not adsorbed by the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA.
a Standard curve of dopamine (DA) concentration vs. fluorescence intensity of polydopamine (PDA) at 463 nm. b Comparative fluorescence spectra of PDA obtained from DA that remained in supernatant before and after adsorption using 3-aminophenylboronic acid-functionalized magnetic silica (Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA) nanoparticles at pH 8.5
DA is converted into the oxidized form of quinone product in the alkaline condition (at ~ pH 12), which is rapidly polymerized to polydopamine (PDA). Thus, the fluorescent intensity of PDA at 463 nm can be quantitatively related to the DA concentration of the sample using the linearly regressed standard curve between the fluorescent intensity of PDA, Y, and the corresponding DA concentration, X: X = (Y-2812.67)/1588.46 (R2 = 0.998), where the unit of X is μg of DA/mg of particles. Finally, the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA was calculated by converting the difference of fluorescent intensity before and after the adsorption of DA by the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA, as shown in Fig. 4b.
Additional file 1: Fig. S6 illustrates the effect of pH on the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA for DA (2.0 μM) in tris–HCl buffer solution (pH 7.0–9.5). Even though the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA turned out be maximal at pH 9.0, the adsorption process was carried out at pH 8.5 owing to the sensitive reactivity of DA under strong alkaline conditions (pH 9.0–9.5). According to the data in Fig. 5a, the adsorption capacity increased during the first 30 min and gradually reached saturation within 60 min. Thus, the equilibrium capacity of DA was achieved after 60 min of adsorption time. During the adsorption process, the borate groups were transformed into tetrahedral anionic forms which could form cyclic esters with DA molecules.
To evaluate their adsorption performance, the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA (4 mg) were added to 2 mL tris–HCl buffer solution (pH 8.5) containing different DA concentrations (0.5–20 nmol/mL). The mixed solution was gently shaken for 60 min and the supernatant was separated from the magnetic particles using an external magnetic field. Then, the adsorption capacity was calculated based on the changes in the fluorescence intensity of PDA before and after the adsorption process. As depicted in Fig. 5b, the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA exhibited two stage adsorption behavior for DA, and presented a distinct inflection point at ~ 5 μM, which was followed by the gradual increase to the saturated adsorption capacity value of 108.46 μg/g [27, 44,45,46].
According to Additional file 1: Fig. S7(a), the chemical state of DA changed depending on the solution pH [47]. At pH 8.5, the chemical structure of DA is H3DA− and H2DA. Thus, the exposed amine groups of DA anchored onto the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA could interact with the negative hydroxyl groups of the free DA in solution, which consequently lead to the additional adsorption of DA (see Additional file 1: Fig. S7(b)). It is plausible to assume that the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA is attributed to the monolayer adsorption of DA via cyclic ester formation and additional adsorption via electrostatic interactions between DA molecules.
4 Conclusions
In this study, the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA were facilely prepared for the efficient adsorption of DA molecules. First, core–shell Fe3O4@SiO2 were synthesized according to the modified sol–gel reaction between C-Fe3O4 and TEOS, and the surface of Fe3O4@SiO2 was functionalized using APTMS with primary amine groups. The Fe3O4@SiO2–NH2 was further modified into the Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH via a linker elongation reaction with succinic amide. The boronic acid-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 were finally prepared by conjugating APBA with the Fe3O4@SiO2–COOH using a EDC/NHS coupling agent. The Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA exhibited two-stage adsorption behavior for DA, and the maximal adsorption capacity was 108.46 μg/g at pH 8.5. Moreover, the Fe3O4@SiO2@APBA was rapidly separated using a simple magnetic manipulation process. Our particle systems demonstrated high affinity for DA molecules, which would make them suitable for extracting compounds (including catecholamine neurotransmitters) with cis-diols from the biological fluid.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
K.C. Berridge, T.E. Robinson, J.W. Aldridge, Dissecting components of reward: ‘liking’, ‘wanting’, and learning. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 9, 65–73 (2009)
Y. Bu, S.W. Lee, The characteristic Ag(core)Au(shell) nanoparticles as SERS substrates in detecting dopamine molecules at various pH ranges. Int. J. Nanomed. 10, 47–54 (2015)
A.P. Silwal, R. Yadav, J.E. Sprague, H.P. Lu, Raman spectroscopic signature markers of dopamine-human dopamine transporter interaction in living cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 8, 1510–1518 (2017)
Y.J. Kang, E.G. Cutler, H. Cho, Therapeutic nanoplatforms and delivery strategies for neurological disorders. Nano Converg. 5, 35 (2018)
J.H. An, D.K. Choi, K.J. Lee, J.W. Choi, Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of dopamine by DNA Targeting amplification assay in Parkisons’s model. Biosens. Bioelectron. 67, 739–746 (2015)
N. Yusoff, A. Pandikumar, R. Ramaraj, H.N. Lim, N.M. Huang, Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim. Acta 182, 2091–2114 (2015)
J. Kim, M. Jeon, K.J. Paeng, I.R. Paeng, Competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of catecholamine, dopamine in serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 619, 87–93 (2008)
Y. Zhang, B. Li, X. Chen, Simple and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Microchim. Acta 168, 107–113 (2009)
Y. Bu, S.W. Lee, Flower-like gold nanostructures electrodeposited on indium tin oxide (ITO) glass as a SERS-active substrate for sensing dopamine. Microchim. Acta 182, 1313–1321 (2015)
A.J. Stewart, J. Hendry, L. Dennany, Whole Blood Electrochemiluminescent Detection of Dopamine. Anal. Chem. 87, 11847–11853 (2015)
M. Meyyappan, Nano biosensors for neurochemical monitoring. Nano Converg. 2, 18 (2015)
V.D. Phung, W.S. Jung, T.A. Nguyen, J.H. Kim, S.W. Lee, Reliable and quantitative SERS detection of dopamine levels in human blood plasma using a plasmonic Au/Ag nanocluster substrate. Nanoscale. 10, 22493–22503 (2018)
K. Syslova, L. Rambousek, M. Kuzma, V. Najmanova, V. Bubenikova-Valesova, R. Slamberova, P. Kacer, Monitoring of dopamine and its metabolites in brain microdialysates: method combining freeze-drying with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1218, 3382–3391 (2011)
M. Kaya, M. Volkan, New approach for the surface enhanced resonance Raman scattering (SERRS) detection of dopamine at picomolar (pM) levels in the presence of ascorbic acid. Anal. Chem. 84, 7729–7735 (2012)
M.-C. Hennion, Solid-phase extraction: method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 856, 3–54 (1999)
F. Augusto, L.W. Hantao, N.G.S. Mogollón, S.C.G.N. Braga, New materials and trends in sorbents for solid-phase extraction. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 43, 14–23 (2013)
M. Šafařı́ková, I. Šafařı́k, Magnetic solid-phase extraction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 194, 108–112 (1999)
Q. Gao, C.Y. Lin, D. Luo, L.L. Suo, J.L. Chen, Y.Q. Feng, Magnetic solid-phase extraction using magnetic hypercrosslinked polymer for rapid determination of illegal drugs in urine. J. Sep. Sci. 34, 3083–3091 (2011)
Q. Gao, D. Luo, J. Ding, Y.Q. Feng, Rapid magnetic solid-phase extraction based on magnetite/silica/poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) composite microspheres for the determination of sulfonamide in milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 5602–5609 (2010)
Z. Li, J.C. Barnes, A. Bosoy, J.F. Stoddart, J.I. Zink, Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2590–2605 (2012)
Y. Wang, L. Sun, B. Yu, S. Li, S. Zhong, One-pot preparation of boronic acid and PEG bi-functionalized silica particles for separation and purification of catecholamine from rat serum. New J. Chem. 39, 8848–8854 (2015)
T. Soga, Y. Inoue, Determination of catecholamines in urine and plasma by on-line sample pretreatment using an internal surface boronic acid gel. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 620, 175–181 (1993)
H.S. Mader, O.S. Wolfbeis, Boronic acid based probes for microdetermination of saccharides and glycosylated biomolecules. Microchim. Acta 162, 1–34 (2008)
C. Lu, H. Li, H. Wang, Z. Liu, Probing the interactions between boronic acids and cis-diol-containing biomolecules by affinity capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 85, 2361–2369 (2013)
Y. Liu, L. Ren, Z. Liu, A unique boronic acid functionalized monolithic capillary for specific capture, separation and immobilization of cis-diol biomolecules. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47, 5067–5069 (2011)
C. Lü, and Z. Liu, Characterization of the Binding Strengths Between Boronic Acids and cis-Diol-Containing Biomolecules by Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis (Chap. 23), in Affinity chromatography: methods and protocols, Edited S. Reichelt, Springer New York, New York, NY (2015), pp. 297–307
H. Fan, C. Wang, Y. Wei, Synthesis and application of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic adsorbent for sensitive analysis of salbutamol residues in pig tissues. Biomed. Chromatogr. 29, 1834–1841 (2015)
X.-Y. Sun, R.-T. Ma, J. Chen, Y.-P. Shi, Boronate-affinity based magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the efficient extraction of the model glycoprotein horseradish peroxidase. Microchim. Acta 184, 3729–3737 (2017)
J. K. Kook, D. Koh, A. V. Tran, and S.-W. Lee, Boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanocomposites for an efficient extraction of dopamine molecules and their detection using fluorescent polydopamine. in Proceedings of the 22nd Microoptics Conference (MOC), pp. 362–363 (2017)
J.K. Kook, S.W. Lee, Facile synthesis of boronic acid-conjugated magnetic particles for an efficient extraction of dopamine neurotransmitter molecules. Jpn J Appl Phys. 57, 08PF03 (2018)
K.-W. Kim, S.-W. Lee, Facile synthesis of chitosan-mediated hematite clusters as an efficient photocatalyst. Sci. Adv. Mater. 8, 180–184 (2016)
T.-A. Nguyen, I.T. Kim, S.-W. Lee, B. Vyas, Chitosan-tethered iron oxide composites as an antisintering porous structure for high-performance Li-ion battery anodes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2720–2728 (2016)
S. Lim, D. Yang, S.-W. Lee, Fabrication of magnetite-hydrogel nanocomposites with clustered magnetite cores and poly(< I>N </I > -isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) Shells for drug delivery application. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10, 7295–7299 (2010)
K.W. Kim, J.S. Kim, S.W. Lee, J.K. Lee, Employment of Chitosan–linked Iron Oxides as Mesoporous Anode Materials for Improved Lithium–ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 170, 146–153 (2015)
H.-D. Oh, S.-W. Lee, Facile synthesis of QD-anchored composite particles with magnetite cluster cores (nFe3O4@SiO2@QDs). Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2191–2195 (2013)
Y. An, M. Chen, Q. Xue, W. Liu, Preparation and self-assembly of carboxylic acid-functionalized silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 311, 507–513 (2007)
S. Kralj, M. Drofenik, D. Makovec, Controlled surface functionalization of silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles with terminal amino and carboxyl groups. J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 2829–2841 (2010)
Y. Liang, J.L. Gong, Y. Huang, Y. Zheng, J.H. Jiang, G.L. Shen, R.Q. Yu, Biocompatible core-shell nanoparticle-based surface-enhanced Raman scattering probes for detection of DNA related to HIV gene using silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles as separation tools. Talanta 72, 443–449 (2007)
S. Liu, F. Shi, X. Zhao, L. Chen, X. Su, 3-Aminophenyl boronic acid-functionalized CuInS2 quantum dots as a near-infrared fluorescence probe for the determination of dopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 47, 379–384 (2013)
X. Zhong, H.-J. Bai, J.-J. Xu, H.-Y. Chen, Y.-H. Zhu, A reusable interface constructed by 3-aminophenylboronic acid-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes for cell capture, release, and cytosensing. Adv. Func. Mater. 20, 992–999 (2010)
J.H. Lin, C.J. Yu, Y.C. Yang, W.L. Tseng, Formation of fluorescent polydopamine dots from hydroxyl radical-induced degradation of polydopamine nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 15124–15130 (2015)
X. Zhang, S. Wang, L. Xu, L. Feng, Y. Ji, L. Tao, S. Li, Y. Wei, Biocompatible polydopamine fluorescent organic nanoparticles: facile preparation and cell imaging. Nanoscale. 4, 5581–5584 (2012)
A. Yildirim, M. Bayindir, Turn-on fluorescent dopamine sensing based on in situ formation of visible light emitting polydopamine nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 86, 5508–5512 (2014)
Z. Lin, L. Sun, W. Liu, Z. **a, H. Yang, G. Chen, Synthesis of boronic acid-functionalized molecularly imprinted silica nanoparticles for glycoprotein recognition and enrichment. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2, 637–643 (2014)
J. Ma, C. Wang, Y. Wei, Polyethyleneimine-facilitated high-capacity boronate affinity membrane and its application for the adsorption and enrichment of cis-diol-containing molecules. RSC Adv. 6, 43648–43655 (2016)
D. Sebők, E. Csapó, T. Preočanin, G. Bohus, N. Kallay, I. Dékány, Adsorption of ibuprofen and dopamine on functionalized gold using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy at solid-liquid interface. Croat. Chem. Acta 86, 287–295 (2013)
C.A. Martínez-Huitle, M. Cerro-Lopez, M.A. Quiroz, Electrochemical behaviour of dopamine at covalent modified glassy carbon electrode with l-cysteine: preliminary results. Mater. Res. 12, 375–384 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (Grant No. 20174030201530). We thank the Smart Materials Research center for IoT at Gachon University for its instrumental support (PL, FTIR, and SEM).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (Grant No. 20174030201530).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JKK, DYK, PVD and SWL reviewed literature, outlined, wrote, edited the manuscript and prepared figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Completing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1.
Additional figures.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Kook, J.K., Phung, VD., Koh, DY. et al. Facile synthesis of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for efficient dopamine extraction. Nano Convergence 6, 30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-019-0200-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-019-0200-7