Abstract
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated immunotherapy cannot be carried out on a large scale clinically due to its low universality. In recent years, cyclic guanosine monophosphate synthase/interferon gene stimulating factor (cGAS/STING)-mediated innate immune signaling pathway-mediated immunotherapy has attracted more and more attention. In addition, metabolic inhibitors also show good effects on tumor treatment, but their application is often limited because of their large first pass effect or difficult administration.
Methods
The particle size and potential parameters were measured by DLS. In order to determine the optimal ratio of the two drugs, we calculated the CI value of different nanoparticles through MTT experiment, and simulated their synergistic effect through Gaussian software. Then the morphology and crystal form of the best proportion of drugs were studied by TEM and XRD. The anti-tumor mechanism of composite nanoparticles was confirmed by the determination of metabolic related indexes, Q-PCR and WB. The antitumor effect and immune activation effect were comprehensively evaluated by in vivo and in vitro experiments.
Results
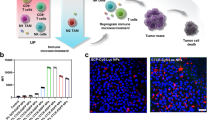
Here, we found and synthesized BCP nanoparticles ((BPA + CPI) @ PLGA NPs) which can effectively reduce the metabolism of tumor cells and inhibit cell proliferation. At the same time, the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) caused by mitochondrial metabolism disorder further activated the cGAS/STING signal pathway in Hepa1–6 cells. We found that the drug-treated Hepa1–6 cells had obvious TBK1 phosphorylation and STING dimerization. Combined with STING agonist, it could effectively promote the activation of CD8 T cells and enhanced the therapeutic effect on liver cancer.
Conclusion
Our results showed that PLGA nanocarrier can successfully improve the dosage forms of two metabolic inhibitors and show the effect of synergistic therapy. BCP nanoparticles can also activate the innate immunity of tumor cells and significantly enhance tumor inhibition after combined with STING agonists. This study has high reference and transformation value for the combined treatment of immunosuppression and metabolic inhibition.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Tumor growth needs massive ATP as energy supply. And the ability of tumor cells to absorb grapes is dozens of times higher than that of normal tissue cells, which called the "Warburg effect" [1,2,3]. Even under aerobic conditions, glucose produces lactic acid in tumor cells through glycolysis. It is a new treatment strategy for anti-tumor therapy by targeting tumor energy metabolism currently [4,5,6]. Among them, 3-bromopyruvate (3-BPA) and CPI-613 are widely studied as metabolic blockers [7,8,9,10]. 3-BPA has high affinity with GADPH and HK-II [11, 12]. It can completely interdict the activities of GADPH and HK-II under very low concentration [13, 14]. However, 3-BPA is instable in the liquid state and easy to decompose [15, 16]. CPI-613 is an inhibitor of mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism in tumor cells [17, 18]. It suppresses the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (KGDH) to restrain the glutamine replenishment pathway [19, 20]. Whereas CPI-613 is lipid-soluble which easily soluble in organic solvents, and difficult to dissolve in water [21, 22].
In recent years, with the rapid development of nanotechnology and wide application, nanomaterials have been widely used in biomedicine. Nanoparticles can protect drugs, reduce drug systemic toxicity, improve drug uptake, slow-release, and targeted drug delivery [23,24,25]. Hence, the above problem of drug solubility and stability in application could be well resolved by using nanomaterial.
Cancer immunotherapy is another new approach of anti-tumor therapy that apply the host immune system to fight against cancer [26]. Stimulator of interferon genes (STING), also known as transmembrane protein 173 (TMEM173) and MPYS/MITA/ERIS, which can induce the production of a variety of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, is shown great potential in enhancing anti-tumor immunity [27]. Many STING agonists have been developed or tested in preclinical and clinical trials for immunotherapy of diseases such as cancer and infectious diseases [28,29,30]. And yet, In terms of the current clinical attempts, it mainly focus on modified cyclic dinucleotide (CDN) to simulate the STING’s endogenous ligand (cGAMP) to treat solid tumors by intratumoral injection [29]. Using the symmetry of STING, GSK designed a connection strategy to cooperate with two symmetrically related amide benzimidazole (ABZI) based compounds to produce a high affinity ligand that interacts with STING in a cGAMP competitive manner. What’s more, ABZI was the first nonnucleotide intravenous STING agonist recently. ABZI not only overcomes the disadvantages of intratumoral injection but also has a strong anti-tumor effect [30].
In this study, 3-BPA and CPI-613 are applied conjunctively to block the energy metabolism of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) via a nano-drug delivery system for the first time. Meanwhile, we combine BCP NPs with anti-tumor immunotherapy innovatively. Our study sweeps the obstacle of poor solubility and easy decomposition in metabolic drugs combination. Moreover, paves a novel way to effectively restrict the growth and metastasis of HCC. We also provide a reliable basis for future research on the combined administration of metabolic and immune therapy.
Results
BCP NPs synthesis and characterizations
The BCP NPs synthesis procedure and its anti-tumor mechanism is illustrated in Scheme 1. The PLGA NPs were prepared by an emulsion solvent evaporation approach. Meanwhile, CPI-613 and 3-BPA were regarded as oil phase and water phase respectively, loaded in the PLGA NPs. A dynamic light scattering (DLS) was applied to measure the size and zeta potential of BCP NPs (Additional file 1: Table S1). The particle size and potential of different molar ratio BCP NPs were not much different. High performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC) and pyruvate assay kit were used to determine the drug load and encapsulation rate of the different BCP NPs (Additional file 1: Table S2).
As reported, the synergistic effect of two or more drugs largely depended on a series of factors, such as combination ratios, drug concentrations, and treatment time etc. [Mice samples All mice were purchased from Wuhan Institute of Biological Products Co. Ltd and Bei**g Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. 6–8 weeks female C57BL/6 mice were used for experiments. All studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Medical Research Institute, Wuhan University. To evaluate the biocompatibility and potential immunogenicity, Blood routine and liver and kidney function were analyzed. The whole blood samples were collected from BALB/c mice, detected by automatic blood cell analyzer (BC-2800vet, Mindray, China) and automatic biochemical analyser (Chemray 240, Shenzhen Redu Life Technology, China). The biocompatibility of BCP NPs was explored by hemolysis test. Briefly, to obtain the pure erythrocytes, the whole blood samples that obtained from healthy C57BL/6 mice were washed five times with PBS by centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min. The red blood cells were re-suspended in PBS for later use. BCP NPs dispersed in PBS at various concentrations (0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 µM), and incubated at 37 °C. 100% hemolysis was deemed as the erythrocytes mixed with DI water. The erythrocytes mixed with PBS was regarded as positive control. Finally, optical absorbance at 540 nm was recorded by a microplate reader. To establish the Hepa1–6 hepatocellular carcinoma tumor model, C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously with Hepa1–6 cells resuspended in DMEM (4 × 106 cells per mouse) on the right abdomen. CY7 was used to track the nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Briefly, tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were given the PLGA NPs which loaded Cy7 intravenously at a concentration of 5 mg/kg. Normal mice were used as negative control. The signal of Cy7 was measured at appropriate time points with the Caliper IVIS Lumina II (IVIS, Xenogen, Caliper Instruments). Tumor volume was measured in real time and calculated based on Eq. (1) [48] as follows: When the tumor size reached approximately 100 mm3. Mice were randomly divided into six groups, and were intravenously injected with 100 µL of (1) saline, (2) PLGA NPs, (3) free drugs (3-BPA + CPI-613), (4) BPA NPs, (5) CPI NPs, and (6) BCP NPs. The equivalent total drug dosages of 15 mg/kg were used for all the groups, respectively. An injection of medicine was given every 3 days. Simultaneously. The tumor volume was and body weight were recorded every other day. Finally, sacrificed the mice and excised the tumors and organs. The hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunofluorescent staining were all according to the standard protocols. When average tumor volume was 100 mm3, mice were randomly divided into four groups, 10 mice each group. Mice were intravenously injected with 100 µL of (1) saline, (2) BCP NPs, (3) ABZI (STING agonist), and (4) BCP NPs + ABZI. For all the groups, the total drug dosages were equivalent. The total drugs of BCP NPs were 15 mg/kg, and was given every 3 days. Meanwhile, the dose of ABZI was 1.5 mg/kg. The mice’s body weight and tumor volume were measured daily. The hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunofluorescent staining were all according to the standard protocols [52]. To explore whether ABZI activated the immune system in mice, the changes of CD8 molecules on the surface of mouse T cells after administration was examined. Briefly, all spleen samples were processed to cell suspension, re-suspended in the flow buffer, and incubated with mouse Fc blocker. Finally, before the flow cytometry analysis, cells were stained with CD45-PE, CD3-V421, and CD8-APC. All statistical analyses were completed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). A P-value smaller than 0.05 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) was regarded as statistically significant. All the data analyses were used Origin (OriginLab, MA, USA) and shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD).Routine hematology study in vivo
In vivo biocompatibility assay
Establishment of 4T1 tumor model
In vivo fluorescence imaging
Tumor inhibition in vivo
The combination of NPs and STING agonist
Statistical analysis
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Liberti MV, Locasale JW. The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci. 2016;41:211–8.
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324:1029–33.
Walz S, Lorenzin F, Morton J, Wiese KE, von Eyss B, Herold S, Rycak L, Dumay-Odelot H, Karim S, Bartkuhn M. Activation and repression by oncogenic MYC shape tumour-specific gene expression profiles. Nature. 2014;511:483–7.
Parks SK, Chiche J, Pouysségur J. Disrupting proton dynamics and energy metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:611–23.
Zhang Y, Yang J-M. Altered energy metabolism in cancer: a unique opportunity for therapeutic intervention. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14:81–9.
Cui H, Han W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Su X. Advances in the regulatory effects of bioactive peptides on metabolic signaling pathways in tumor cells. J Cancer. 2019;10:2425.
Sun Y, Liu Z, Zou X, Lan Y, Sun X, Wang X, Zhao S, Jiang C, Liu H. Mechanisms underlying 3-bromopyruvate-induced cell death in colon cancer. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2015;47:319–29.
Azevedo-Silva J, Queirós O, Baltazar F, Ułaszewski S, Goffeau A, Ko Y, Pedersen PL, Preto A, Casal M. The anticancer agent 3-bromopyruvate: a simple but powerful molecule taken from the lab to the bedside. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016;48:349–62.
Fan T, Sun G, Sun X, Zhao L, Zhong R, Peng Y. Tumor energy metabolism and potential of 3-bromopyruvate as an inhibitor of aerobic glycolysis: implications in tumor treatment. Cancers. 2019;11:317.
Dell’Antone P. Targets of 3-bromopyruvate, a new, energy depleting, anticancer agent. Med Chem. 2009;5:491–6.
Tang Z, Yuan S, Hu Y, Zhang H, Wu W, Zeng Z, Yang J, Yun J, Xu R, Huang P. Over-expression of GAPDH in human colorectal carcinoma as a preferred target of 3-bromopyruvate propyl ester. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2012;44:117–25.
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Vali M, Kunjithapatham R, Buijs M, Syed L, Rao P, Ota S, Kwak B, Loffroy R, Geschwind J. 3-bromopyruvate: a new targeted antiglycolytic agent and a promise for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;11:510–7.
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S, Kunjithapatham R, Geschwind J-F. Anticancer efficacy of the metabolic blocker 3-bromopyruvate: specific molecular targeting. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:13–20.
Fox JEM, Meredith D, Halestrap AP. Characterisation of human monocarboxylate transporter 4 substantiates its role in lactic acid efflux from skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2000;529:285–93.
Sadowska-Bartosz I, Bartosz G. Effect of 3-bromopyruvic acid on human erythrocyte antioxidant defense system. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37:1285–90.
Schaefer NG, Geschwind JF, Engles J, Buchanan JW, Wahl RL. Systemic administration of 3-bromopyruvate in treating disseminated aggressive lymphoma. Transl Res. 2012;159:51–7.
Noy A, Pardee TS, Nikolaenko L, Steiner RE, Abramson JS, Dunleavy K, Luther S. A phase II clinical trial of Cpi-613 (devimistat) in patients with relapsed or refractory Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia or high-grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2and/or BCL6. Blood. 2019;134:4087–4087.
Lee KC, Maturo C, Perera CN, Luddy J, Rodriguez R, Shorr R. Translational assessment of mitochondrial dysfunction of pancreatic cancer from in vitro gene microarray and animal efficacy studies, to early clinical studies, via the novel tumor-specific anti-mitochondrial agent, CPI-613. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2:91.
Stuart SD, Schauble A, Gupta S, Kennedy AD, Keppler BR, Bingham PM, Zachar Z. A strategically designed small molecule attacks alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in tumor cells through a redox process. Cancer Metab. 2014;2:1–15.
Zachar Z, Marecek J, Maturo C, Gupta S, Stuart SD, Howell K, Schauble A, Lem J, Piramzadian A, Karnik S. Non-redox-active lipoate derivates disrupt cancer cell mitochondrial metabolism and are potent anticancer agents in vivo. J Mol Med. 2011;89:1137–48.
Lee CK, Shorr R, Maturo C, Boteju WL, Sheldon A. Formation and anti-tumor activity of uncommon in vitro and in vivo metabolites of CPI-613, a novel anti-tumor compound that selectively alters tumor energy metabolism. Drug Metab Lett. 2011;5:163–82.
Zhang J, Lan CQ, Post M, Simard B, Deslandes Y, Hsieh TH. Design of nanoparticles as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Cancer Genom-Proteom. 2006;3:147–57.
Huang G, Huang H. Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018;25:766–72.
Kumari A, Yadav SK, Yadav SC. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf B. 2010;75:1–18.
Kim D-H, Li W, Chen J, Zhang Z, Green RM, Huang S, Larson AC. Multimodal imaging of nanocomposite microspheres for transcatheter intra-arterial drug delivery to liver tumors. Sci Rep. 2016;6:1–10.
Wang R-F. Innate immune regulation and cancer immunotherapy. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media; 2012.
Su T, Zhang Y, Valerie K, Wang X-Y, Lin S, Zhu G. STING activation in cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics. 2019;9:7759.
Barber GN. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:760–70.
Flood BA, Higgs EF, Li S, Luke JJ, Gajewski TF. STING pathway agonism as a cancer therapeutic. Immunol Rev. 2019;290:24–38.
Ramanjulu JM, Pesiridis GS, Yang J, Concha N, Singhaus R, Zhang S-Y, Tran J-L, Moore P, Lehmann S, Eberl HC. Design of amidobenzimidazole STING receptor agonists with systemic activity. Nature. 2018;564:439–43.
**ao B, Han MK, Viennois E, Wang L, Zhang M, Si X, Merlin D. Hyaluronic acid-functionalized polymeric nanoparticles for colon cancer-targeted combination chemotherapy. Nanoscale. 2015;7:17745–55.
Jaracz S, Chen J, Kuznetsova LV, Ojima I. Recent advances in tumor-targeting anticancer drug conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005;13:5043–54.
Plathow C, Weber WA. Tumor cell metabolism imaging. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:43S-63S.
Moreno-Sánchez R, Rodríguez-Enríquez S, Marín-Hernández A, Saavedra E. Energy metabolism in tumor cells. FEBS J. 2007;274:1393–418.
Laroui H, Theiss AL, Yan Y, Dalmasso G, Nguyen HT, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D. Functional TNFα gene silencing mediated by polyethyleneimine/TNFα siRNA nanocomplexes in inflamed colon. Biomaterials. 2011;32:1218–28.
Guo X, Wu Z, Li W, Wang Z, Li Q, Kong F, Zhang H, Zhu X, Du YP, ** Y. Appropriate size of magnetic nanoparticles for various bioapplications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:3092–106.
Ramasamy T, Kim JH, Choi JY, Tran TH, Choi H-G, Yong CS, Kim JO. pH sensitive polyelectrolyte complex micelles for highly effective combination chemotherapy. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2:6324–33.
Zolnik BS, Burgess DJ. Effect of acidic pH on PLGA microsphere degradation and release. J Control Release. 2007;122:338–44.
Wang J, Helder L, Shao J, Jansen JA, Yang M, Yang F. Encapsulation and release of doxycycline from electrospray-generated PLGA microspheres: effect of polymer end groups. Int J Pharm. 2019;564:1–9.
Chen Q, Gou S, Ma P, Song H, Zhou X, Huang Y, Han MK, Wan Y, Kang Y, **ao B. Oral administration of colitis tissue-accumulating porous nanoparticles for ulcerative colitis therapy. Int J Pharm. 2019;557:135–44.
Wu H, Wang S, Fang H, Zan X, Zhang J, Wan Y. Chitosan–polycaprolactone copolymer microspheres for transforming growth factor-β1 delivery. Colloids Surf B. 2011;82:602–8.
Mora-Huertas CE, Fessi H, Elaissari A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010;385:113–42.
Fedoryshin LL, Tavares AJ, Petryayeva E, Doughan S, Krull UJ. Near-infrared-triggered anticancer drug release from upconverting nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:13600–6.
Li X, Zhao Y, Yin J, Lin W. Organic fluorescent probes for detecting mitochondrial membrane potential. Coord Chem Rev. 2020;420:213419.
Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, Serganov AA, Liu Y, Jones RA, Hartmann G. Cyclic [G(2ʹ,5ʹ)pA(3ʹ,5ʹ)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. Cell. 2013;153:1094–107.
Ishikawa H, Zhe M, Barber GN. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature. 2009;461:788–92.
Xu Z, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, Chen Z. Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING. Mol Cell. 2013;51:226–35.
Chen Q, Sun L, Chen ZJ. Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:1142–9.
Ahn J, Barber GN. STING signaling and host defense against microbial infection. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1–10.
Abe T, Harashima A, **a T, Konno H, Konno K, Morales A, Ahn J, Gutman D, Barber GN. STING recognition of cytoplasmic DNA instigates cellular defense. Mol Cell. 2013;50:5–15.
Ishikawa H, Barber GN. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature. 2008;455:674–8.
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J, Zeller R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2008;2008:pdb.prot4986.
Acknowledgements
We thank Hao Yin and Ying Zhang from Medical Research Institute, Wuhan University for their assistance on the nanoparticle synthesis. We would like to thank Dr. Hongbin Shu for generous gift of anti-STING antibody. We would like to thank the staffs from the Core Facilities of Wuhan University for their assistance with data collections. This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31770183), the Non-Profit Central Research Institute Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2020-PT320-004), Medical Science Advancement Program (Basic Medical Sciences) of Wuhan University, Grant No. TFJC2018004 and Wuhan University Open Subsidy Funding Projects (LF20201347).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BF, SL, QL and QC conceived the project and designed the experiments. BF supervised the project. QL and BF wrote the manuscript. QL carried out and participated in the whole experiments. QC participated in the whole experiment and assisted in the preparation and characterization of materials, Q-PCR and animal experiments. XY supported the operation of the native PAGE. YZ, LL, ZZ, SZ and JL supported the operation and analysis of the western blot and Q-PCR. All the authors discussed the results and commentated manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures were performed in accordance with the Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on the Management of Laboratory Animals and approved by the ethics committee of Wuhan University, P. R. China.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1
: Table S1. Z-average and zeta potential of different CPI-613/3-BPA PLGA NPs. Table S2. Characteristics of the CPI-613/3-BPA-loaded nanoparticles. Table S3. Table 1 IC50 (μM, total drugs concentration) of nanoparticles against Hepa1–6 cells line. Figure S1. AML 12 cells treated with BCP NPs under gradient concentrations for 24 h and 48 h. Figure S2. 4T1 cells (a) and MCF-7 cells (b) treated with BCP NPs under gradient concentrations for 24 h and 48 h. Figure S3. Stability of nanoparticles under different conditions. Figure S4. Fluorescent images of Hepa1–6 cells after being treated with BCP NPs (equivalent Coumarin concentration: 10 µg/mL) for 1, 2, 4 and 6 h (scale bar: 100 µm). Figure S5. Fluorescence images of Hepa1–6 cells after various treatments analyzed by a LIVE/DEAD viability assay. The green and red dots denote live and dead cells, respectively (scale bar: 500 µm). Figure S6. Western blot analysis of phosphorylated TBK1 after the treatment of ABZI and BCP NPs of Hepa1–6 cells (a); The heat map for mRNA expression of metabolism-related genes of GAPDH, c-Myc, MCT1, HK-II, PKM, LDHA when the Hepa1–6 cells treated with different drugs (b). Figure S7. Hemolysis rate by incubating RBCs with DI water (positive control), PBS (negative control) or BCP NPs under various concentrations. (Inset: corresponding digital photos of centrifuge tube containing different samples). Figure S8. H&E stained tumor slices excised from major organs after the mice receiving various treatments (scale bar: 100 µm). Figure S9. H&E stained tumor slices excised from major organs after the mice receiving various treatments (scale bar: 100 µm).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Chen, Q., Yang, X. et al. Cocktail strategy based on a dual function nanoparticle and immune activator for effective tumor suppressive. J Nanobiotechnol 20, 84 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01241-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01241-y