Abstract
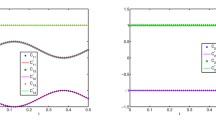
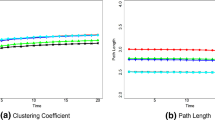
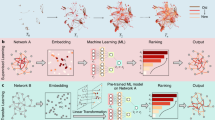
In a complex network, different groups of nodes may have existed for different amounts of time. To detect the evolutionary history of a network is of great importance. We present a spectral-analysis based method to address this fundamental question in network science. In particular, we find that there are complex networks in the real-world for which there is a positive correlation between the eigenvalue magnitude and node age. In situations where the network topology is unknown but short time series measured from nodes are available, we suggest to uncover the network topology at the present (or any given time of interest) by using compressive sensing and then perform the spectral analysis. Knowledge of ages of various groups of nodes can provide significant insights into the evolutionary process underpinning the network. It should be noted, however, that at the present the applicability of our method is limited to the networks for which information about the node age has been encoded gradually in the eigen-properties through evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.J. Newman, Networks, An Introduction (Oxford University Press, New York, 2010)
W.-X. Wang, R. Yang, Y.-C. Lai, V. Kovanis, M.A.F. Harrison, Europhys. Lett. 94, 48006 (2011)
W.-X. Wang, R. Yang, Y.-C. Lai, V. Kovanis, C. Grebogi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 154101 (2011)
A.-L. Barabási, R. Albert, Science 286, 509 (1999)
G.-M. Zhu, H.J. Yang, C.Y. Yin, B. Li, Phys. Rev. E 77, 066113 (2008)
H.J. Yang, F.C. Zhao, B.H. Wang, Chaos 16 (2006)
J. Ren, B. Li, Phys. Rev. E 79, 051922 (2009)
J. Ren, W.-X. Wang, B. Li, Y.-C. Lai, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 058701 (2010)
S. Jalan, G.-M. Zhu, B. Li, Phys. Rev. E 84, 046107 (2011)
D.J. Watts, S.H. Strogatz, Nature 393, 440 (1998)
J.G. Restrepo, E. Ott, B.R. Hunt, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 114101 (2004)
K. Park, L. Huang, Y.-C. Lai, Phys. Rev. E 75, 026211 (2007)
P. Erdös, A. Rényi, Publ. Math. Inst. Hung. Acad. Sci. 5, 17 (1960)
A.V. Vazquez, A. Flammini, A. Maritan, A. Vespignani, Complexus 1, 38 (2003)
A. Wagner, Mol. Biol. Evol. 18, 1283 (2001)
A. Wagner, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 270, 457 (2003)
C. von Mering, R. Krause, B. Snel, M. Cornell, S.G. Oliver, S. Fields, P. Bork, Nature 417, 399 (2002)
C.R. Woese, Microbiol. Rev. 51, 221 (1987)
E. Ravasz, A.L. Somera, D.A. Mongru, Z. Oltvai, A.-L. Barabási, Science 297, 1551 (2002)
E. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 489 (2006)
E. Candès, J. Romberg, T. Tao, Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 59, 1207 (2006)
E. Candès, in Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians (Madrid, Spain, 2006)
D. Donoho, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52, 1289 (2006)
R.G. Baraniuk, IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24, 118 (2007)
E. Candès, M. Wakin, IEEE Signal Processing Mag. 25, 21 (2008)
E. Candès, T. Tao, IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 51, 4203 (2005)
M. Girvan, M.E.J. Newman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7821 (2002)
O.E. Rössler, Phys. Lett. A 57, 397 (1976)
S. Hempel, A. Koseska, J. Kurths, Z. Nikoloski, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 054101 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G.M., Yang, H.J., Yang, R. et al. Uncovering evolutionary ages of nodes in complex networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 85, 106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-21019-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2012-21019-2