Abstract
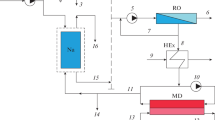
The article explores the possibility of increasing the efficiency of seawater desalination by membrane distillation using low-potential (80–85°C) waste heat of the diesel power plant cooling system and preventing the formation of calcium sulfate scale on membranes by nanofiltration softening of a part of the source water. A membrane module integrated into the cooling system by means of an intermediate circulation loop fed with a mixture of softened and raw seawater provides distillate production and coolant cooling. The study has been carried out by computer simulation of the system design model, transformed into a computer program, using the example of Caspian and Black Sea waters, using a direct-contact membrane distillation module having a plate-and-frame configuration. It has been found that Caspian water is characterized by a high potential of sulfate scale formation and the salinity of the membrane module feed water should not exceed 30 g/dm3 when the intermediate loop is fed with a mixture of softened and raw water in an equal ratio, whereas this parameter in the case of Black Sea water can be increased to 95 g/dm3 even without softening. In both cases, a high conversion of make-up water is achieved: 75–80%. The recovery rate of the membrane module feed water is 5.2–6.8%. The energy consumption is associated only with the operation of pumps. For each megawatt of generated electric power, 4.9–5.5 t/day of distillate (desalinated water) is produced. The study has been computational and analytical in nature and, as such, makes further experimental verification of the results necessary.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Peter G. Youssef, Mahmoud M. Saad, and Raya K. AL-Dadah, Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 4, 402 (2015).
D. González, et al., Renew. Sustainable Energy Rev. 80, 238 (2017).
Jantaporn Waritha, et al., Chem. Eng. Res. Design 128, 15 (2017).
Jiaze Ma, et al., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57, 31 (2018).
**anguo Yu, et al., Desalination 323, 134 (2013).
N. E. Koeman-Stein, et al., Water Res. Ind. 14, 11 (2016).
Rubina Bahar, et al., Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 42, 1 (2020).
R. Schwantes, et al., Desalination 323, 93 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.04.011
Elnaz Norouzi and Chanwoo Park, Desalin. Water Treat. 106, 40 (2018).
S. S. Kofi, et al., Environ. Int. 138, 105588 (2020).
A. Bassel, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 4413 (2018).
S. P. Rudobashta and S. Yu. Makhmud, Khim. Khim. Prom. 55, 100 (2012).
M. Khayt, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 164, 56 (2011).
A. E. Al-Rawajfeh, Thermal Sci. 15, 55 (2011).
A. Khalifa, et al., Desalination 404, 22 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by S. Zatonsky
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agamaliyev, M.M., Ahmadova, J.A. & Aliyeva, O.O. Waste Heat Utilization of Diesel Power Plant Cooling System for Seawater Desalination by Membrane Distillation. Membr. Membr. Technol. 4, 48–58 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751622010024
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751622010024