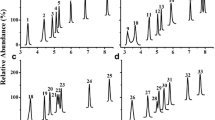
Abstract
Approaches to the highly sensitive determination of low-molecular-weight fatty acids and amino acids in blood serum samples of patients diagnosed with endometriosis by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection (GC–MS) and HPLC with a diode array detector were proposed. Conditions for the selective determination of 23 amino acids in the form of dansyl chloride derivatives by reversed-phase HPLC with spectrophotometric detection were found, and the main factors influencing the separation parameters (pH of the mobile phase, the solvent and the buffer solution, and the gradient profile) were identified. It was shown that the traditional GC determination of metabolites in the form of silyl derivatives did not provide the required sensitivity: the high volatility of derivatives already at the stage of sample preparation led to significant losses and, as a consequence, to irreproducible results. Conditions for the determination of organic acids without derivatization using GC–MS on a polar stationary phase were optimized. A procedure for preparing blood serum for analysis (precipitation of proteins and removal of lipids) and conditions for the selective separation of analytes (temperature gradient, 70−230°C) were proposed. The developed approaches made it possible to obtain characteristic profiles of organic acids in the blood serum samples of patients with endometriosis and uterine myoma (as a comparison reference group).







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Giudice, L.C., N. Engl. J. Med., 2010, vol. 362, p. 2389. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1000274
Govorov, I., Sitkin, S., Pervunina, T., Moskvin, A., Baranenko, D., and Komlichenko, E., Curr. Med. Chem., 2020, vol. 27, no. 22, p. 3611. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867326666190104124245
Kartsova, L.A., Bessonova, E.A., Deev, V.A., and Kolobova, E.A., Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2023, p. 1. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2022.2156770
Dutta, M., Singh, B., and Joshi, M., Sci. Rep., 2018, no. 8, p. 6466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23954-7
Dutta, M., Josh, M., Srivastava, S., Lodh, I., Chakravarty, B., and Chaudhury, K., Mol. Biosyst., 2012, vol. 8, p. 3281. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mb25353d
Jana, S.K., Dutta, M., Joshi, M., Srivastava, S., Chakravarty, B., and Chaudhury, K., BioMed Res. Int., 2013, vol. 2013, p. 329058. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/329058
Vicente-Munoz, S., Morcillo, I., Puchades-Carrasco, L., Paya, V., Pellicer, A., and Pineda-Lucena, A., Fertil. Steril., 2015, vol. 104, no. 5, p. 1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.07.1149
Vicente-Munoz, S., Morcillo, I., Puchades-Carrasco, L., Paya, V., Pellicer, A., and Pineda-Lucena, A., Fertil. Steril., 2016, vol. 106, no. 5, p. 1733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.014
Li, J., Guan, L., Zhang, H., Gao, Y., Sun, J., Gong, X., Li, D., Chen, P., Liang, X., and Huang, M., Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol., 2018, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0360-z
Wang, L.-L., Guo, H.-H., Huang, S., Feng, C.-L., Han, Y.-X., and Jiang, J.-D., J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2017, vol. 1057, p. 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.004
Chadchan, S.B., Popli, P., Ambati, C.R., Tycksen, E., Han, S.J., Bulun, S.E., Putluri, N., Biest, S.W., and Kommagani, R., Life Sci. Alliance, 2021, vol. 4, no. 12, p. e202101224. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202101224
Zeng, M. and Cao, H., J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, vol. 1083, p. 137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.02.040
Mulat, D.G. and Feilberg, A., Talanta, 2015, vol. 143, p. 56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.065
Amer, B., Nebel, C., Bertram, H.C., Mortensen, G., and Dalsgaard, T.K., Lipids, 2015, vol. 50, p. 681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4029-5
Zhang, H., Wang, Z., and Liu, O., J. Pharm. Anal., 2015, vol. 5, no. 4, p. 223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.01.005
Douny, C., Dufourny, S., Brose, F., Verachtert, P., Rondia, P., Lebrun, S., and Scippo, M.-L., J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2019, vol. 1124, p. 188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.06.01
Gao, H., Yu, X., Sun, R., Yang, N., He, J., Tao, M., and Wang, G., J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, vols. 1077–1078, p. 28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.12.021
Lu, X., Fang, M., Dai, Y., Yang, Y., Fan, A., Xu, J., and Li, N., J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, vol. 1089, p. 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.037
Covian, D., Ruas-Madiedo, P., Margolles, A., Gueimonde, M., de Los Reyes Gavilan, C.G., and Salazar, N., Front. Microbiol., 2016, vol. 7, p. 185. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00185
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the Resource Center “Methods of Analysis of the Composition of Matter” of the Science Park of St. Petersburg State University for the provided equipment.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 19-13-00370).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Makhlyarchuk
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bessonova, E.A., Araslanova, A.T., Lazaretova, A.I. et al. Metabolic Profiling of Carboxylic Acids and Amino Acids in the Biological Fluids of Patients Diagnosed with Endometriosis Using Liquid (HPLC-UV) and Gas (GC–MS) Chromatography. J Anal Chem 78, 1469–1479 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934823100040
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934823100040