Abstract
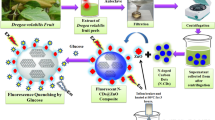
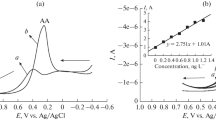
Fluorescent chemical sensors have been proposed to detect drugs by increasing or shutting down the fluorescence emission and absorption. These sensors have been used because they are non-destructive, able to show concentrations, have fast response time and high accuracy. In this research, a chemical sensor based on PbS functionalized with gelatin quantum dots was utilized for sulfacetamide detection. The calibration curve was linear in the range of 0.02 to 10 µg/L. The standard deviation was less than 2.0%, and the method detection limit (3s/m) was 0.022 nM; the response for PbS quantum dot–gelatin nanocomposite sensor was obtained in 50 s at 330 nm at a 95% confidence level. The artificial neural network model was used as a tool for determining the mean square error (MSE of 0.031) for sulfacetamide by PbS quantum dot–gelatin nanocomposite sensor. The observed outcomes confirmed suitable recovery and very low detection limit for sulfacetamide determination. The fluorometric method was applied to quantify sulfacetamide in real samples such as urine and blood and could be used for other drugs and hospital samples. The chemical PbS quantum dot–gelatin nanocomposite sensor is an excellent sensor with good reproducibility.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tanreh, S., Shameli, A., and Balali, E., J. Appl. Chem. Res., 2018, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 79.
Darweesh, S.A., Al-Haidari, I.M.A., Mohammed, A.K., and Dikran, S.B., J. Pure Appl. Sci., 2017, vol. 26, no. 3, p. 281.
Hull, C.A. and Johnson, S.M., Crit. Care Med., 2004, vol. 73, no. 6, p. 425.
Yadav, S.K., Choubey, P.K., Agrawal, B., and Goyal, R.N., Talanta, 2014, vol. 118, p. 96.
Byrom, L., Zappala, T., and Muir, J., Australas. J. Dermatol., 2013, vol. 54, no. 2, p. 144.
Nagaraja, P., Yathirajan, H., sunitha, K., and Vasantha, R., J. AOAC Int., 2002, vol. 85, no. 4, p. 869.
Baran, W., Sochacka, J., and Wardas, W., Chemosphere, 2006, vol. 65, no. 8, p. 1295.
El-Ragehy Maha, N., Hegazy, A., Abd El Hamid Samia, G., and Tawfik, S.A., Bull. Fac. Pharm. Cairo Univ., 2018, vol. 56, no. 2, p. 207.
Hajian, R., Fadaeian, M., and Ghanbari, F., Asian J. Chem., 2010, vol. 22, p. 6840.
Zheng, H. and Wang, P., Se Pu, 2007, vol. 25, no. 2, p. 238.
El-Ragehy Maha, N., Hegazy, A., Abd El Hamid, G., and Tawfik, S.A., J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2017, vol. 55, no. 10, p. 1000.
Borras, S., Companyo, R., and Guiteras, J., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2011, vol. 59, no. 10, p. 5240.
Gallego, J.L. and Arroyo, J.P., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2003, vol. 31, p. 873.
Pargari, M., Marahel, F., and Mombini Godajdar, B., J. Phys. Theor. Chem., 2020, vol. 17, nos. 1–2, p. 1.
Al-Uzri, W.A. and Fadil, G., Asian. J. Chem., 2017, vol. 29, no. 4, p. 782.
Samadi, N. and Narimani, S., J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci., 2016, vol. 6, p. 387.
Hatamie, A., Marahel, F., and Sharifat, A., Talanta, 2018, vol. 176, p. 518.
Huang, W.B., Gu, W., Huang, H.X., Wang, J.B., Shen, W.X., Lv, Y.Y., and Shen, J., Dyes Pigm., 2017, vol. 143, p. 427.
Brahim, N.B., Mohamed, N.B.H., Echabaane, M., Haouari, M., Chaabane, R.B., Negrerie, M., and Ouada, H.B., Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 220, p. 1346.
Dai, Y., Yao, K., Fu, J., Xue, K., Yang, L., and Xu, K., Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, vol. 251, p. 877.
Knoblauch, C., Griep, M., and Friedrich, C., Sensors, 2014, vol. 14, p. 19731.
Mirsalari, M. and Elhami, S., Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2020, vol. 240, Article 118617.
Yang, X., Liu, M., Yin, Y., Tang, F., Xu, H., and Liao, X., Sensors, 2018, vol. 18, no. 4, p. 964.
Coester, C., Langer, K., Brisen, H., and Kruter, J., J. Microencapsulation, 2000, vol. 17, p. 187.
Zypan, J., Acta. Chim. Slov., 1994, vol. 41, no. 3, p. 327.
Marahel, F., Mombeni Goodajdar, B., Niknam, L., Faridnia, M., Pournamdari, E., and Mohammad Doost, S., Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem., 2021, vol. 101, no. 5. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1901895
Samadi, N. and Narimani, S., Sens. Lett. J., 2016, vol. 14, p. 530.
Zhao, Y., Zou, J., and Shi, W., J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2005, vol. 121, p. 20.
Shyju, T.S., Anandhi, S., Sivakumar, R., and Gopalakrishnan, R., Int. J. Nanosci., 2014, vol. 13, p. 1450001.
Zohreh, M., Ghoreishi, S.M., Behpour, M., and Mohammadhassan, M., Arab. J. Chem., 2017, vol. 10, p. 657.
Adel, R., Ebrahim, S., Shokry, A., Soliman, M., and Khalil, M., ACS Omega, 2021, vol. 6, p. 2167.
Al-Nuri, I., Israa, A., and Al-Obaydi, A., J. Raf. Sci., 2009, vol. 20, no. 4, p. 17.
Liang, S.S., Qi, L., Zhang, R.L., **, M., and Zhang, Z.Q., Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, vol. 244, p. 585.
Dutta, P., Saikia, D., Adhikary, N.C., and Sarma, N.S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, vol. 7, p. 24778.
Ahmed, S., Anwar, N., Sheraz, M.A., and Ahmad, I., J. Pharm. BioAllied Sci., 2017, vol. 9, no. 2, p. 126.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge partial support of this work by the Islamic Azad University, Branch of Omidiyeh Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davoudi, S., Marahel, F. Determination of Sulfacetamide in Blood and Urine Using PBS Quantum Dots Sensor and Artificial Neural Networks. J Anal Chem 77, 1448–1457 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934822110041
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934822110041