Abstract
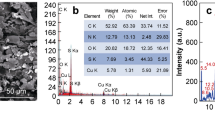
A piezoelectric immunosensor with a recognition layer based on magnetic carbon nanocomposites is developed for the determination of ciprofloxacin. The receptor coating of the sensor is formed by the action of a magnetic field on magnetic particles located on the surface of carbon nanotubes modified with a ciprofloxacin conjugate. The sizes of magnetic particles in the composition of the nanocomposite are determined by scanning electron microscopy. A dependence of the mass of the recognition coating on the size of magnetic particles on the surface of carbon nanotubes is shown. A detection cell with a sensor located above a neodymium magnet is proposed. The analytical characteristics of the immunosensor are determined, the limit of detection for ciprofloxacin is 2 ng/mL, and the linear range of determined concentrations is 5–400 ng/mL. The use of magnetic carbon nanocomposites in the creation of a recognition layer ensures the reduction of the time of sensor preparation to analysis from 24 to 1.5 h and extends its service life. The sensor is tested in the detection of antibiotics in milk and meat.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Skládal, P., TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2016, vol. 79, no. 5, p. 127.
Ermolaeva, T.N., Kalmykova, E.N., and Shashkanova, O.Yu., Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2008, vol. 78, no. 12, p. 2430.
Chauhan, R., Singh, J., Solanki, P.R., Basu, T., O’Kennedy, R., and Malhotrae, B.D., Biochem. Eng. J., 2015, vol. 103, no. 15, p. 103.
Vaughan, R.D. and Guilbault, G.G., Piezoelectric Sensor. Piezoelectric Immunosensor, Springer Series in Chemical Sensors and Biosensors, 2007, vol. 5, p. 237.
Ermolaeva, T.N. and Kalmykova, E.N., Russ. Chem. Rev., 2006, vol. 75, no. 5, p. 397.
Yanga, N., Chena, X., Renb, T., Zhanga, P., and Yang, D., Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 207, p. 690.
Jithesh, V.V. and Kaiming, Y., Biotechnol. Prog., 2007, vol. 23, p. 517.
Fama, D.W.H., Palaniappana, Al., Toka, A.I.Y., Liedberga, B., and Moochhalaa, S.M., Sens. Actuators, B, 2011, vol. 157, p. 1.
Wang, J. and Lin, Y., TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2008, vol. 27, no. 7, p. 619.
Le, J. and Ju, H., Adv. Rev., 2010, vol. 2, p. 496.
Hampitak, P., Jowitt, T.A., Melendrez, D., Fresquet, M., Hamilton, P., Iliut, M., Nie, K., Spencer, B., Lennon, R., and Vijayaraghavan, A., ACS Sens., 2020, vol. 5, no. 11, p. 3520.
Sassolas, A., Prieto-Simon, B., and Marty, J.-L., Am. J. Anal. Chem., 2012, vol. 3, p. 210.
Medyantseva, E.P., Brusnitsyn, D.V., Varlamova, R.M., Maksimov, A.A., Konovalova, O.A., and Budnikov, H.C., J. Anal. Chem., 2017, vol. 72, no. 4, p. 362.
Zhou, J., Gan, N., Li, T., Zhou, H., Li, X., Cao, Y., Wang, L., Sang, W., and Hu, F., Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, vol. 178, p. 494.
Zhou, L., Cai, P., Feng, Y., Cheng, J., **ang, H., Liu, J., Wu, D., and Zhou, X., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2012, vol. 735, p. 96.
Xu, Q., Wei, X., and Hao, Z., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2013, vol. 61, p. 1435.
Gao, L. and Chen, L., Microchim. Acta, 2013, vol. 180, p. 423.
Zarei, H., Ghourchian, H., Eskandari, K., and Zeinali, M., Anal. Biochem., 2012, vol. 421, p. 446.
Sánchez-Tirado, E., González-Cortés, A., Yáñez-Sedeño, P., and **arrón, J.M., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, vol. 113, p. 88.
Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Yan, B., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Shen, G., and Yu, R., J. Immunol. Methods, 2008, vol. 332, p. 103.
Zhou, J., Gan, N., Li, T., Zhou, H., Li, X., Cao, Y., Wang, L., Sang, W., and Hu, F., Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, vol. 178, p. 494.
Shanin, I.A., Thuy, N.T.D., and Eremin, S.A., Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. (Engl. Transl.), 2014, vol. 69, p. 136.
Grazhulene, S.S., Zolotareva, N.I., Red’kin, A.N., Shilkina, N.N., Mitina, A.A., and Khodos, I.I., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2020, vol. 93, no. 1, p. 57.
Sauerbrey, G., Z. Phys., 1959, vol. 55, p. 206.
Grazhulene, S.S., Zolotareva, N.I., Red’kin, A.N., Shilkina, N.N., Mitina, A.A., and Kolesnikova, A.M., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2018, vol. 91, no. 11, p. 1849.
Yu, F., Chen, J., Chen, L., Huai, J., Gong, W., Yuan, Z., Wang, J., and Ma, J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2012, vol. 378, p. 175.
Netto, C.G.C.M., Toma, H.E., and Andrade, L.H., J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym., 2013, vol. 85, p. 71.
Verges, A., Costo, R., Roca, G., Marco, J., Goya, G., Serna, C., and Morales, M., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 41, p. 1.
Resolution of the Board of the Eurasian Economic Commision no. 28 on February 13, 2018, On the maximum permissible levels of residues of veterinary medicinal products (pharmacologically active substances) that may be contained in unprocessed food products of animal origin, including raw materials, and methods for their determination. https://docs.cntd.ru/document/556522984. Accessed June 20, 2021.
Shukshina, E.I., Farafonova, O.V., Shanin, I.A., Grazhulene, S.S., Eremin, S.A., and Ermolaeva, T.N., Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2018, vol. 18, no. 3, p. 394. refs 14 and 21
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the Lipetsk Region, project no. 20-43-480001. At the Institute for Problems of Microelectronics Technology and High-Purity Materials of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the work was carried out within the framework of State Assignment no. 075-00355-21-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Kudrinskaya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bizina, E.V., Farafonova, O.V., Zolotareva, N.I. et al. A Piezoelectric Immunosensor Based on Magnetic Carbon Nanocomposites for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin. J Anal Chem 77, 458–465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934822040049
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934822040049