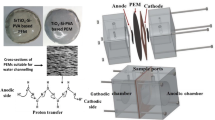
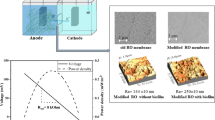
Abstract—
We studied the physicochemical and electrochemical characteristics of microbial fuel cells (MFCs) with a new proton-exchange membrane. It was synthesized on the basis of zeolite-doped polyvinyl alcohol cross-linked with sulfosuccinic acid (PVA-SSA-BEA). An MF-4SK industrial membrane (Plastpolymer, Russia) was used as a comparative sample. Various sugars were added as substrates (glucose, arabinose, galactose, xylose). The role of the bioagent was performed by the strain Micrococcus luteus 1-i. MFCs with PVA‑SSA-BEA and MF-4SK membranes showed rather close electrochemical characteristics. A higher electricity output was performed with the addition of glucose, galactose, the lowest—with the use of xylose. The data obtained indicate that the proposed PVA-SSA-BEA membrane is promising for use as an alternative to proton-exchange membranes widely used in fuel cell technology.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ramya, M. and Kumar, P.S., A review on recent advancements in bioenergy production using microbial fuel cells, Chemosphere, 2022, vol. 288, p. 132512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132512
Wilberforce, T., Abdelkareem, M.A., Elsaid, K., Olabi, A.G., and Sayed, E.T., Role of carbon-based nanomaterials in improving the performance of microbial fuel cells, Energy, 2022, vol. 240, p. 122478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.122478
Boas, J.V., Oliveira, V.B., Simões, M., and Pinto, A.M.F.R., Review on microbial fuel cells applications, developments and costs, J. Environ. Manag., 2022, vol. 307, p. 114525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114525
Mohyudin, S., Farooq, R., Jubeen, F., Rasheed, T., Fatima, M., and Sher, F., Microbial fuel cells a state-of-the-art technology for wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation, Environ. Res., 2022, vol. 204, p. 112387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112387
Liu, L., Zhou, X., Wang, Y., Li, S., Yin, R., Ji, X., Zhao, X., and Li, B., Study of high active and redox-stable La0.9Ca0.1Fe0.9Nb0.1O3 – δ/Sm0.1Ce0.9O2 − δ composite ceramic electrode for solid oxide reversible cells, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 236, p. 371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.195
Moon, J.M., Kondaveeti, S., and Min, B., Evaluation of low-cost separators for increased power generation in single chamber microbial fuel cells with membrane electrode assembly, Fuel Cells, 2015, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 230. https://doi.org/10.1002/fuce.201400036
Hendrana, S., Chaldun, E.R., Pudjiastuti, S., Rahayu, I., Natanael, C.L., Oktaverina, D., and Semboor, M.S., Heterogeneous sulphonation of polystyrene for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell application, Macromol. Symp., 2013, vol. 1, p. 80. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201350509
Bai, Z., Durstock, M.F., and Dang, T.D., Proton conductivity and properties of sulfonated polyarylenethioether sulfones as proton exchange membranes in fuel cells, J. Membr. Sci., 2006, vol. 281, nos. 1–2, p. 508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.04.021
Umar, M.F., Rafatullah, M., Abbas, S.Z., Mohamad, I.M.N., and Ismail, N., Advancement in benthic microbial fuel cells toward sustainable bioremediation and renewable energy production, Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health, 2021, vol. 18, no. 7, p. 3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073811
Wang, H., Chen, P., Zhang, Sh., Jiang, J., Hua, T., and Li, F., Degradation of pyrene using single-chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cells: electrochemical parameters and bacterial community changes, Sci. Total Environ., 2022, vol. 804, p. 150153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150153
Dai, Q., Zhang, S., Liu, H., Huang, J., and Li, L., Sulfide-mediated azo dye degradation and microbial community analysis in a single-chamber air cathode microbial fuel cell, Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, vol. 131, p. 107349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2019.107349
Chesnokova, A.N., Zhamsaranzhapova, T.D., Zakarchevskiy, S.A., Kulshrestha, V., Skornikova, S.A., Makarov, S.S., and Pozhidaev, Yu.N., Effect of zeolite content on proton conductivity and technical characteristics of the membranes based on crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol. Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Prikl. Khim. Biotekhnol., 2020, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 360. https://doi.org/10.21285/2227-2925-2020-10-2-360-367
Stom, D.I., Konovalova, E.Yu., Zhdanova, G.O., Tolstoy, M.Yu., and Vyatchina, O.F., Active sludge and strains isolated from it as bioagents in biofuel cells, Proc. 17th Int. Multidisciplinary Sci. Geoconf. SGEM 2017, Vienna, 2017, vol. 17, issue 42, p. 19. https://doi.org/10.5593/sgem2017/42/S17.003
Kuznetsov, A.V., Khorina, N.N., Konovalova, E.Yu., Amsheev, D.Yu., Ponamoreva, O.N., and Stom, D.I., Bioelectrochemical processes of oxidation of dicarboxylic amino acids by strain Micrococcus luteus 1-I in a biofuel cell, IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 2021, vol. 808, p. 012038. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/808/1/012038
Lebedeva, O.V., Pozhidaev, Yu.N., Malakhova, E.A., Raskulova, T.V., Chesnokova, A.N., Kulshrestha, V., et al., Sodium p-styrene sulfonate-1-vinylimidazole copolymers for acid-base proton-exchange membranes, Membr. Membr. Technol., 2020, vol. 2, p. 76. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751620020079
Volkov, V.I., Pavlov, A.A., and Sanginov, E.A., Ionic transport mechanism in cation-exchange membranes studied by NMR technique, Solid State Ionics, 2011, vol. 188, no. 1, p. 124.
Stenina, I.A. and Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Ionic mobility in ion-exchange membranes, Membranes, 2021, vol. 11, p. 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030198
Yaroslavtsev, A.B., Solid electrolytes: main prospects of research and development, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2016, vol. 85, p. 1255. https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4634
Peng, J., Tian, M., Cantillo, N.M., and Zawodzinski, T., The ion and water transport properties of K+ and Na+ form perfluorosulfonic acid polymer, Electrochim. Acta, 2018, vol. 282, p. 544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.035
Shi, S., Weber, A.Z., and Kusoglu, A., Structure-transport relationship of perfluorosulfonic-acid membranes in different cationic forms, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 220, p. 517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.10.096
Okada, T., **e, G., Gorseth, O., Kjelstrup, S., Nakamura, N., and Arimura, T., Ion and water transport characteristics of Nafion membranes as electrolytes, Electrochim. Acta, 1998, vol. 43, p. 3741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(98)00132-7
Heyrovska, R., Dependence of ion-water distances on covalent radii, ionic radii in water and distances of oxygen and hydrogen of water from ion/water boundaries, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2006, p. 600.
Konovalova, E.Yu., Barbora, L., Chizhik, K.I., and Stom, D.I., Micrococcus luteus and Serratia marcescens, as a new association of bio-agents for microbial fuel cells, IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci., 2020, vol. 408, p. 012080. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/408/1/012080
Choi, Y., Jung, E., Park, H., Jung, S., and Kim, S., Effect of initial carbon sources on the performance of a microbial fuel cell containing environmental microorganism Micrococcus luteus, Korean Chem. Soc., 2007, vol. 28, no. 9, p. 1591.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to S.A. Skornikova, Candidate of Chemistry, Associate Professor of INRTU—for providing of zeolites samples, to E.Yu. Konovalova—for providing of strain M. luteus 1-i.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of the Baikal Research and Education Center (grant no. FZZS-2021-0007) and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 21-54-12022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chesnokova, A.N., Zakarchevsky, S.A., Zhdanova, G.O. et al. Electrochemical Parameters of Microbial Fuel Cells Based on the Micrococcus luteus Strain, New Ion-Exchange Membranes and Various Sugars. Russ J Electrochem 59, 660–665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193523090057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193523090057