Abstract
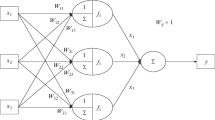
The potential use of artificial neural networks to describe liquid–liquid phase equilibria in ternary systems under polythermal conditions is considered. The study was carried out on the example of ten ternary systems, including binary splitting subsystems of water–esters of carboxylic acids, which determines the phase splitting in ternary systems (the third component is alcohol or carboxylic acid). The features of the selected network architecture are presented, and the results, with a critical assessment of the accuracy of the calculations, are given in the tables. Approximations based on artificial neural networks are compared with calculations based on the non-random two-liquid (NRTL) model.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Muravyev, N.V., Luciano, G., Ornaghi, H.L., Svoboda, R., and Vyazovkin, S., Artificial neural networks for pyrolysis, thermal analysis, and thermokinetic studies: The status quo, Molecules, 2021, vol. 26, no. 12, p. 1.
Li, F., Gu, Z., Ge, L., Sun, D., Deng, X., Wang, S., Hu, B., and Xu, J., Application of artificial neural networks to X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis, X-ray Spectrom., 2019, vol. 48, no. 2, p. 138.
Santos, I., Castro, L., Rodriguez-Fernandez, N., Torrente-Patiño, A., and Carballal, A., Artificial neural networks and deep learning in the visual arts: A review, Neural Comput. Appl., 2021, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 121.
Kumar, R., Aggarwal, R.K., and Sharma, J.D., Comparison of regression and artificial neural network models for estimation of global solar radiations, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2015, vol. 52, p. 1294.
Haglin, J.M., Jimenez, G., and Eltorai, A.E.M., Artificial neural networks in medicine, Health Technol., 2019, vol. 9, no. 1.
Wilson, G.M., Vapor–liquid equilibrium. XI: A new expression for the excess free energy of mixing, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, vol. 86, no. 2, p. 127.
Renon, H. and Prausnitz, J.M., Local compositions in thermodynamic excess functions for liquid mixtures, AIChE J., 1968, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 135.
Fredenslund, A., Jones, R.L., and Prausnitz, J.M., Group-contribution estimation of activity coefficients in nonideal liquid mixtures, AIChE J., 1975, vol. 21, no. 6, p. 1086.
Abrams, D.S. and Prausnitz, J.M., Statistical thermodynamics of liquid mixtures: A new expression for the excess Gibbs energy of partly or completely miscible systems, AIChE J., 1975, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 116.
Gross, J. and Sadowski, G., Reply to comment on “Perturbed-chain saft: An equation of state based on a perturbation theory for chain molecules,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, vol. 58, no. 14, p. 5744.
Nguyen, V.D., Tan, R.R., Brondial, Y., and Fuchino, T., Prediction of vapor–liquid equilibrium data for ternary systems using artificial neural networks, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2007, vol. 254, nos. 1–2, p. 188–197.
Roosta, A., Hekayati, J., and Javanmardi, J., Application of artificial neural networks and genetic programming in vapor–liquid equilibrium of C1 to C7 alkane binary mixtures, Neural Comput. Appl., 2019, vol. 31, no. 4, p. 1165.
Argatov, I. and Kocherbitov, V., A note on artificial neural network modeling of vapor–liquid equilibrium in multicomponent mixtures, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2019, vol. 502, Article 112282.
Toikka, A.M., Misikov, G.K., and Petrov, A.V., Analysis of data on vapor–liquid equilibrium in multicomponent systems using artificial neural networks, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng, 2021, vol. 55, no. 3, p. 403.
Farzaneh-Gord, M., Mohseni-Gharyehsafa, B., Ebrahimi-Moghadam, A., Jabari-Moghadam, A., Toikka, A., and Zvereva, I., Precise calculation of natural gas sound speed using neural networks: An application in flow meter calibration, Flow Meas. Instrum., 2018, vol. 64, p. 90.
Farzaneh-Gord, M., Rahbari, H.R., Mohseni-Gharesafa, B., Toikka, A., and Zvereva, I., Accurate determination of natural gas compressibility factor by measuring temperature, pressure and Joule–Thomson coefficient: Artificial neural network approach, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 2021, vol. 202, p. 108427.
Focke, W.W., Mixture models based on neural network averaging, Neural Comput., 2006, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 1.
Sarlak, F., Pirhoushyaran, T., Shaahmadi, F., Yaghoubi, Z., and Bazooyar, B., The development of intelligent models for liquid–liquid equilibria (LLE) phase behavior of thiophene/alkane/ionic liquid ternary system, Sep. Sci. Technol., 2018, vol. 53, no. 18, p. 2935.
Cavalcanti, R.N., Oliveira, M.B., and Meirelles, A.J.A., Liquid–liquid equilibria for systems containing fatty acid ethyl esters, ethanol and glycerol at 333.15 and 343.15 K: Experimental data, thermodynamic and artificial neural network modeling, Braz. J. Chem. Eng., 2018, vol. 35, no. 2, p. 819.
Reynel-Ávila, H.E., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., and Tapia-Picazo, J.C., An artificial neural network-based NRTL model for simulating liquid–liquid equilibria of systems present in biofuels production, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2019, vol. 483, p. 153–164.
Bekri, S., Özmen, D., Türkmenoğlu, A., and Özmen, A., Application of deep neural network (DNN) for experimental liquid–liquid equilibrium data of water + butyric acid + 5-methyl-2-hexanone ternary systems, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2021, vol. 544–545, Article 113094.
Haykin, S., Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1999.
Trofimova, M., Sadaev, A., Samarov, A., Golikova, A., Tsvetov, N., Toikka, M., and Toikka, A., Liquid–liquid equilibrium of acetic acid–ethanol–ethyl acetate–water quaternary system: Data review and new results at 323.15 K and 333.15 K, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2020, vol. 503, Article 112321.
Toikka, M., Vernadskaya, V., and Samarov, A., Solubility, liquid–liquid equilibrium and critical states for quaternary system acetic acid–n-amyl alcohol–n-amyl acetate–water at 303.15 K and atmospheric pressure, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2018, vol. 471, pp. 68–73.
Samarov, A.A., Toikka, M.A., Naumkin, P.V., and Toikka, A.M., Chemical equilibrium and liquid-phase splitting in acetic acid + n-propanol + n-propyl acetate + water system at 293.15 and 353.15 K, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng., 2016, vol. 50, no. 5, p. 739.
Toikka, M., Samarov, A., Trofimova, M., Golikova, A., Tsvetov, N., and Toikka, A., Solubility, liquid–liquid equilibrium and critical states for the quaternary system acetic acid–ethanol–ethyl acetate–water at 303.15 K and 313.15 K, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2014, vol. 373, pp. 72–79.
Trofimova, M., Toikka, M., and Toikka, A., Solubility, liquid–liquid equilibrium and critical states for the quaternary system acetic acid–ethanol–ethyl acetate–water at 293.15 K, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2012, vol. 313, pp. 46–51.
Toikka, M., Samarov, A., and Toikka, A., Solubility, liquid–liquid equilibrium and critical states for the system acetic acid + n-propanol + n-propyl acetate + water at 293.15 k and 303.15 k, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2014, vol. 375, pp. 66–72.
Toikka, M., Sadaev, A., Lobacheva, O., and Golikova, A., Experimental liquid–liquid equilibrium and solubility study of an acetic acid–n-propyl alcohol–n-propyl acetate–water system at 323.15 and 333.15 K, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2020, vol. 65, no. 11, pp. 5352–5359.
Toikka, M.A., Tsvetov, N.S., and Toikka, A.M., Splitting of the liquid solution and the compositions of liquid phases in the water–n-propanol–n-propyl acetate system at 293.15, 303.15, and 313.15 K, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng., 2011, vol. 45, no. 4, p. 429.
Samarov, A., Toikka, M., and Toikka, A., Liquid–liquid equilibrium and critical states for the system acetic acid + n-butanol + n-butyl acetate + water at 308.15 K, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2015, vol. 385, pp. 129–133.
Smirnov, A., Sadaeva, A., Podryadova, K., and Toikka, M., Quaternary liquid–liquid equilibrium, solubility and critical states: acetic acid–n-butanol–n-butyl acetate–water at 318.15 K and atmospheric pressure, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2019, vol. 493, pp. 102–108.
Toikka, M., Smirnov, A., and Samarov, A., Liquid–liquid equilibrium, solubility, and critical states in an acetic acid–n-butyl alcohol–n-butyl acetate–water system at 328.15 K and 101.3 K: Topology of phase diagrams and NRTL modeling, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2021, vol. 66, no. 3, p. 1466.
Ruiz Bevia, F., Prats Rico, D., Gomis Yagües, V., and Varo Galvañ, P., Quaternary liquid–liquid equilibrium: Water–acetic acid–1-butanol–n-butyl acetate at 25°C, Fluid Phase Equilib., 1984, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 171–183.
Ince, E. and Kirbaslar, S.I., Liquid–liquid equilibria of the water–acetic acid–butyl acetate system, Braz. J. Chem. Eng., 2002, vol. 19, no. 2, p. 243.
Wang, L., Cheng, Y., and Li, X., Liquid–liquid equilibria for the acetic acid + water + amyl acetate and acetic acid + water + 2-methyl ethyl acetate ternary systems, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2007, vol. 52, no. 6, p. 2171.
Trofimova, M., Misikov, G., Samarov, A., Prikhodko, I., and Toikka, M., Solubility in the system acetic acid–n-amyl alcohol–n-amyl acetate–water at 293.15 K, 303.15 K, 313.15 K and 323.15 K and atmospheric pressure, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2021, vol. 161, Article 106515.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to V. Kocherbitov (University of Malmö, Sweden) for useful consultations. The research was carried out on the computing resources of the Research Park of St. Petersburg State University, the Computing Centre of St. Petersburg State University.
Funding
The study was financed by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 21-13-00038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misikov, G.K., Petrov, A.V. & Toikka, A.M. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for the Analysis of Data on Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium in Three-Component Systems. Theor Found Chem Eng 56, 200–207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579522020129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579522020129