Abstract
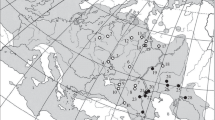
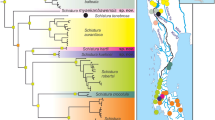
A comparative analysis of data on the morphological, genetic and ecological features of Russian, Persian and Colchic sturgeons was carried out in order to assess their taxonomic relations, diagnostic characteristics and distribution patterns in the Ponto-Caspian basin. The results confirmed the presence of two close related and morphologically similar species in the Caspian basin—Acipenser gueldenstaedtii and A. persicus, the reproductive isolation of which was proved by genetic data. The complex of diagnostic characters of these species includes, in addition to the traditionally accepted body color and the shape of the snout, several craniological indices: Pds/Ri and W/Ri. The Colchic sturgeon remains virtually unstudied from a genetic point of view. The results obtained allow us to consider it an independent subspecies – A. persicus colchicus. It differs from the Caspian Persian sturgeon, as well as from the Russian sturgeon with a longer snout and larger values of the craniological index B/Ri. The distribution of the Colchic sturgeon in the Black Sea basin requires further research.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abbasi, K., Mehdi Moradi, M., Alireza Mirzajani, A., et al., Ichthyodiversity in the Anzali Wetland and its related rivers in the southern Caspian Sea basin, Iran, J. Anim. Diversity, 2019, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 90–135. https://doi.org/10.29252/JAD.2019.1.2.6
Abdurakhmanov, Yu.A., Ryby presnykh vod Azerbaidzhana (Freshwater Fishes of Azerbaijan), Baku: Akad. Nauk AzSSR, 1962.
Ambroz, A.I., Sturgeons from the northwestern part of the Black Sea, Tr. VNIRO, 1964, vol. 52, pp. 287–347.
Antipa, G., Fauna Ihtiologică a Romăniei, Bucuresti: Acad. Rom. Publ. Fond. Adamachi, 1909.
Arefjev, V.A. and Nikolaev, A.I., Cytological analysis of the reciprocal hybrids between low- and high-chromosome acipenserids, the great sturgeon, Huso huso (L.), and the Russian sturgeons Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Brandt, Cytologia, 1991, vol. 56, pp. 495–502.
Artyukhin, E.N., The Persian sturgeon in the rivers of the North Caspian Sea and the prospects of its use in the sturgeon fishery, in Biologicheskie osnovy osetrovogo khozyaistva v vodakh SSSR (Biological Principles of the Sturgeon Fishery in Waters of the USSR), Moscow: Nauka, 1979, pp. 105–115.
Artyukhin, E.N. and Zarkua, Z.G., The taxonomic rank of sturgeon from the Rioni River (the Black Sea basin), Vopr. Ikhtiol., 1986, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 61–67.
Babushkin, N.Ya. and Borzenko, M.P., Osetrovye ryby Kaspiya (Sturgeon Fishes of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: Pischepromizdat, 1951.
Bănărescu, P., Pisces–Osteichthyes (peşti ganoizi şi osoşi), in Fauna Republicii Populare Romîne, Bucureşti: Acad. Rep. Pop. Rom., 1964, vol. 13.
Barmintseva, A.E. and Mugue, N.S., The applying of the data on genoty** on five tetraploid microsatellite loci for population identification in sturgeons, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi konferentsii “Osetrovye ryby i ikh budushchee” (Proc. Int. Conf. “Sturgeon Fishes and Their Future”), Berdyansk, 2011, pp. 95–98.
Belyaev, V.N., Sturgeon (Acipenser güldenstädti Br.), Byull. Vsekasp. Nauchn. Rybokhoz. Eksp., 1932, nos. 5–6, pp. 66–77.
Berg, L.S., Fauna Rossii i sopredel’nykh stran. Ryby (Marsipobranchii i Pisces) (Fauna of Russia and Adjacent Countries: Fishes (Marsipobranchii and Pisces)), St. Petersburg: Imper. Acad. Nauk, 1911, vol. 1.
Berg, L.S., Ryby presnykh vod Rossiiskoi imperii (Freshwater Fishes of Russian Empire), Moscow: Dep. Zemledeliya, 1916.
Berg, L.S., Ryby presnykh vod SSSR i sopredel’nykh stran (Freshwater Fishes of the USSR and Adjacent Countries), 3 ed., Leningrad: Gos. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Ozern. Rechn. Rybn. Khoz., 1933, part 3.
Berg, L.S., Acipenser guldenstadti persicus, a sturgeon from the South Caspian Sea, Ann. Mag. Hist. Lond., Ser. 10, 1934, vol. 13, pp. 317–318.
Berg, L.S., Ryby presnykh vod SSSR i sopredel’nykh stran (Freshwater Fishes of the USSR and Adjacent Countries), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1948, part 1.
Birstein, V.J. and DeSalle, R., Molecular phylogeny of Acipenserinae, Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 1998, vol. 9, pp. 141–155.
Birstein, V.J. and Doukakis, P., Molecular identification of sturgeon species: science, bureaucracy, and the impact of environmental agreements, in Monitoring Migratory Animals, Bonn: Fed. Agency Nat. Conserv., 2001, pp. 47–63.
Birstein, V.J., Doukakis, P., Sorkin, B., and DeSalle, R., Population aggregation analysis of three caviar–producing species of sturgeons and implications for the species identification of black caviar, Conserv. Biol., 1998, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 766–775. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.1998.97081.x
Birstein, V.J., Doukakis, P., and DeSalle, R., Polyphyly of mtDNA lineages in the Russian sturgeon, Acipenser gueldenstaedtii: forensic and evolutionary implications, Conserv. Genet., 2000, vol. 1, pp. 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010141906100
Birstein, V.J., Ruban, G., Ludwig, A., et al., The enigmatic Caspian Sea Russia sturgeon: how many cryptic forms does it contain, Syst. Biodiversity, 2005, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 203–218. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1477200005001647
Bogutskaya, N.G., Kiyashko, P.V., Naseka, A.M., and Orlova, M.I., Opredelitel’ ryb i bespozvonochnykh Kaspiiskogo morya. Tom 1. Ryby i mollyuski (Guide for Identification of Fishes and Invertebrates of the Caspian Sea, Vol. 1: Fishes and Mollusks), Moscow: KMK, 2013.
Borodin, N.A., Acipenser persicus, a sturgeon from the Caspian Sea, Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., Ser. 9, 1926, vol. 20, pp. 26–28.
Brandt, J.F. and Ratzeburg, J.T., Medizinische Zoologie oder getreue Darstellung und Beschreibung der Thiere, die in der Arzneimittellehre in Betracht kommen, in Systematischer Folge Herausgegeben, Berlin: Hirschwald, 1833, vol. 2.
Chebanov, M.S. and Galich, E.V., Sturgeon Hatchery Manual, FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. no. 558, Rome: UN Food Agric. Org., 2013.
Chebanov, M., Rosenthal, H., Gessner, J., et al., Sturgeon Hatchery Practices and Management for Release: Guidelines, FAO Fish. Aquacult. Techn. Pap. no. 570, Rome: UN Food Agric. Org., 2011.
Chugunov, N.L. and Chugunova, N.I., Comparative fishing–biological characteristics of sturgeons from the Sea of Azov, Tr. VNIRO, 1964, vol. 52, pp. 87–182.
Çiftci, Y., Eroğlu, O., and Firidin, Ş., Mitochondrial cytochrome b sequence variation in three sturgeon species (A. stellatus Pallas, 1771, A. gueldenstaedtii Brandt, 1883, H. huso Linnaeus, 1758) from the Black Sea coasts of Turkey, Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 2013, vol. 13, pp. 291–303. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v13_2_11
Detlaf, T.A., Ginzburg, A.S., and Shmal’gauzen, O.I., Razvitie osetrovykh ryb (The Development of Sturgeon Fishes), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1981.
Dillman, C.B., Wood, R.M., Kuhajda, B.R. et al., Molecular systematics of Scaphirhynchinae: an assessment of North American and Central Asian freshwater sturgeon species, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2007, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 290–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2007.00919.x
Elanidze, R.F., Ikhtiofauna rek i ozer Gruzii (Ichthyofauna of the Rivers and Lakes of Georgia), Tbilisi: Metsniereba, 1983.
Esmaeili, H.R., Coad, B.W., Mehraban, H.R. et al., An updated checklist of fishes of the Caspian Sea basin of Iran with a note on their zoogeography, Iran. J. Ichthyol., 2014, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 152–184.
Fontana, F., Chromosomal nucleolar organizer regions in four sturgeon species as markers of karyotype evolution in Acipenseriformes (Pisces), Genome, 1994, vol. 37, pp. 888–892.
Fontana, F. and Colombo, G., The chromosomes of Italian sturgeons, Experientia, 1974, vol. 30, pp. 739–742.
Fontana, F., Lanfredi, M., Rossi, R. et al., Karyotypic characterization of Acipenser gueldenstaedtii with C-, AgNO3, and fluorescence banding techniques, Ital. J. Zool., 1996, vol. 63, pp. 113–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250009609356117
Fontana, F., Lanfredi, M., Chicca, M. et al., Fluorescent in situ hybridization with rDNA probes on chromosomes of Acipenser ruthenus and Acipenser naccarii (Osteichthyes, Acipenseriformes), Genome, 1999, vol. 42, pp. 1008–1012. https://doi.org/10.1139/g99-030
Fontana, F., Tagliavini, J., and Congiu, C., Sturgeon genetics and cytogenetics: recent advancements and perspectives, Genetica, 2001, vol. 111, pp. 359–373. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1013711919443
Fontana, F., Congiu, L., Mudrak, V.A. et al., Evidence of hexaploid karyotype in shortnose sturgeon, Genome, 2008, vol. 51, pp. 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1139/g07-112
Jenneckens, I., Meyer, J.-N., Debus, L. et al., Evidence of mitochondrial DNA clones of Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baerii, within Russian sturgeon, Acipenser gueldenstaedtii, caught in the River Volga, Ecol. Lett., 2000, vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 503–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2000.00179.x
Kazancheev, E.N., Ryby Kaspiiskogo morya (Fishes of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: Rybnoe Khozyaistvo, 1963.
Kazancheev, E.N., Ryby Kaspiiskogo morya (Fishes of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: Legkaya Pishchevaya Prom-st’, 1981.
eivany, Y., Nasri, M., Abbasi, K., Abdoli, A., Atlas of Inland Water Fishes of Iran, Tehran: Iran Dep. Environ., 2016
Kottelat, M. and Freyhof, J., Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes, Berlin: Kottelat and Freyhof, 2007.
Krieger, J., Hett, A.K., Fuerst, P.A. et al., The molecular phylogeny of the order Acipenseriformes revisited, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 24, suppl. 1, pp. 36–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2008.01088.x
Kuljanishvili, T., Epitashvili, G., Freyhof, J. et al., Checklist of the freshwater fishes of Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2020, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.14038
Leonte, V., Contribuţii la cunoasterea raspindirii hranei si ritmului de crestere la puietul de sturioni marioni in Dunăre, Bull. Inst. Cerc. Piscicole, 1959, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 9–18.
Lönnberg, E., Contribution to the ichthyology of the Caspian Sea, K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl., 1900, vol. 26, no. 4 (8), pp. 3–38.
Ludwig, A., Identification of Acipenseriformes species in trade, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 24, suppl. 1, pp. 2–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2008.01085.x
Ludwig, A., Belfiore, N.M., Pitra, C. et al., Genome duplication events and functional reduction of ploidy levels in sturgeon (Acipenser, Huso and Scaphirhynchus), Genetics, 2001, vol. 158, no. 3, pp. 1203–1215.
Luk’yanenko, V.I., Umerov, Zh.G., and Karataeva, B.B., South Caspian sturgeon as a distinct species of genus Acipenser, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol., 1974, no. 5, pp. 736–738.
Mageramov, Ch.M., The appearance of the Volga’ sturgeon in the Kura River, in Osetrovye i problemy osetrovogo khozyaistva (Sturgeons and Sturgeon Farming), Moscow: Pishchevaya Prom-st’, 1972, pp. 289–293.
Marti, V.J., The taxonomy and biology of the Russian sturgeon of the Caucasian coast of the Black Sea, Zool. Zh., 1940, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 865–872.
Maiorova, A.A., The systematic of shads of the genus Caspialosa from the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov, Tr. Rybokhoz. Stn. Gruz., 1939, vol. 2, pp. 1–49.
Movchan, Yu.V., Russian sturgeon from the northeastern part of the Black Sea and the Kuban River, Vestn. Zool., 1967, vol. 6, pp. 26–32.
Mugue, N.S., Barmintseva, A.E., Rastorguev, S.M. et al., Polymorphism of the mitochondrial DNA control region in eight sturgeon species and development of a system for DNA–based species identification, Russ. J. Genet., 2008, vol. 44, no. 7, pp. 793–798. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795408070065
Ninua, N.Sh. and Japoshvili, B.O., Check list of fishes of Georgia, Proc. Inst. Zool., Tbilisi, 2008, vol. 23, pp. 163–176.
Nowruzfashkhami, M.R., Pourkazemi, M. and Baradarannoveiri, S., Chromosome study of Persian sturgeon Acipenser persicus B, Cytologia, 2000, vol. 65, pp. 197–202. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.65.197
Ogden, R., Mcewing, R., Gharbi, K., et al., Sturgeon conservation genomics: SNP discovery and validation using RAD sequencing, Mol. Ecol., 2013, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 3112–3123. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12234
Parin, N.V., An annotated catalog of fishlike vertebrates and fishes of the seas of Russia and adjacent countries, Part 1. Orders Myxiniformes–Gasterosteiformes, J. Ichthyol., 2001, vol. 41, suppl 1, pp. S51–S131.
Parin, N.V., Evseenko, S.A. and Vasil’eva, E.D., Ryby morei Rossii: annotirovannyi katalog (Fishes of Russian Seas: Annotated Catalogue), Moscow: KMK, 2014.
Perevaryukha, E.N., Sudakova, N.B., Geraskin, P.P., et al., Possible identification of Persian (Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897) by body color, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii “Problemy izucheniya, sokhraneniya i vosstanovleniya vodnykh biologicheskikh resursov v XXI veke,” Astrakhan’, 16–18 oktyabrya 2007g. (Proc. Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Study, Conservation, and Recovery of Aquatic Biological Resources in 21st Century,” Astrakhan, October 16–18, 2007), Astrakhan: Kasp. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Rybn. Khoz., 2007a, pp. 82–84.
Perevaryukha, E.N., Sudakova, N.B., Geraskin, P.P. et al., Morphological identification of the Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897), Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii “Problemy izucheniya, sokhraneniya i vosstanovleniya vodnykh biologicheskikh resursov v XXI veke,” Astrakhan’, 16–18 oktyabrya 2007g. (Proc. Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Study, Conservation, and Recovery of Aquatic Biological Resources in 21st Century,” Astrakhan, October 16–18, 2007), Astrakhan: Kasp. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Rybn. Khoz., 2007b, pp. 80–82.
Peseridi, N.E. Acipenser güldenstädti güldenstädti Brandt—the Russian sturgeon, in Ryby Kazakhstana (Fishes of Kazakhstan), Gvozdev, E.V. and Mitrofanov, V.P., Eds., Alma-Ata: Nauka, 1986, pp. 71–99.
Rapp, D., Ice Ages and Interglacials: Measurements, Interpretation and Models, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2009.
Rastorguev, S., Mugue, N., Volkov, A. and Barmintsev, V. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis of Ponto–Caspian sturgeon species, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 24, suppl. 1, pp. 46–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2008.01089.x
Rastorguev, S.M., Nedoluzhko, A.V., Mazur, A.M. et al., High-throughput SNP-genoty** analysis of the relationships among Ponto-Caspian sturgeon species, Ecol. Evol., 2013, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 2612–2618. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.659
Ruban, G.I. and Khodorevskaya, R.P., Caspian Sea sturgeon fishery: a historic overview, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 199–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2011.01725.x
Ruban, G.I., Kholodova, M.V., Kalmykov, V.A. and Sorokin, P.A. Morphological and molecular genetic study of the Persian sturgeon Acipenser persicus Borodin (Acipenseridae) taxonomic status, J. Ichthyol., 2008, vol. 48, no. 10, pp. 891–903. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945208100068
Ruban, G.I., Kholodova, M.V., Kalmykov, V.A. and Sorokin, P.A., A review of the taxonomic status of the Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus Borodin), J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2011, vol. 27, pp. 470–476. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2011.01668.x
Safaraliev, I.A., Meristic features as the key characters for identification of the Russian (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii) and Persian (Acipenser persicus) sturgeons from the Caspian Sea, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi nauchno-prakticheskoi konferentsii “Kompleksnyi podkhod k probleme sokhraneniya i vosstanovleniya bioresursov Kaspiiskogo morya v sovremennyy period” (Proc. Int. Sci.-Pract. Conf. “Modern Complex Approach to Conservation and Recovery of Biological Resources of the Caspian Sea”) Astrakhan: Kasp. Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Rybn. Khoz., 2008, pp. 134–137.
Salnikov, N.I. and Malyatsky, S.M., For the systematic of the Great sturgeon from the Black Sea–Sea of Azov basin, Trudy nauchn. rybokhoz. biolog. stantsii Gruzii, 1934, vol. 1, pp. 31–50.
Sergeev, A.A., The evaluation of genetic distances between populations of the Russian sturgeon from the Sea of Azov and the Caspian Sea, as well as between the Persian and Siberian sturgeons, by AFLP method, Materialy Mezhdunarodnoi konferentsii “Osetrovye ryby i ikh budushchee” (Proc. Int. Conf. “Sturgeon Fishes and Their Future”), Berdyansk, 2011, pp. 184–187.
Sergeev, A.A., Evolutionary relations and population differentiation of Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Brandt, Acipenser persicus Borodin, and Acipenser baerii Brandt, F1000Research, 2016, vol. 5, p. 2807. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10237.2
Sergeev, A.A., Population-genetic structure and phylogenetic relations of the Russian sturgeon Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Brandt, 1833, Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow: VNIRO, 2020.
Sokolov, L.I., Acipenser Linnaeus, 1758, in The Freshwater Fishes of Europe, Vol. 1, Part 2: General Introduction to Fishes. Acipenseriformes, Holčik, J., Ed., Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1989, pp. 201–205.
Sokolov, L.I., Fam. 2. Acipenseridae Bonapate, 1832—sturgeons, in Annotirovannyi katalog kruglorotykh i ryb kontinental’nykh vod Rossii (Annotated Checklist of Cyclostomata and Fishes of the Continental Waters of Russia), Moscow: Nauka, 1998, pp. 19–23.
The Freshwater Fishes of Europe, Vol. 1, Part 2: General Introduction to Fishes. Acipenseriformes, Holčik, J., Ed., Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1989.
Timoshkina, N.N., Barmintseva, A.E., Usatov, A.V. and Mugue, N.S., Intraspecific genetic polymorphism of Russian sturgeon Acipenser gueldenstaedtii, Russ. J. Genet., 2009, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795409090117
Vasil’ev, V.P., Evolyutsionnaya kariologiya ryb (Evolutionary Karyology of Fishes), Moscow: Nauka, 1985.
Vasil’ev, V.P., Mechanisms of polyploid evolution in fish: polyploidy in sturgeons, in Biology, Conservation and Sustainable Development of Sturgeons, Fish Fish. Ser. vol. 29, Carmona, R., Domezain, A., Garcia-Gallego, M., et al., Eds., New York: Springer-Verlag, 2009, pp. 97–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8437-9_6
Vasil’eva, E.D., Some morphological characteristics of Acipenserid fishes: considerations of their variability and utility in taxonomy, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 1999, vol. 15, nos. 4–5, pp. 32–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.1999.tb00201.x
Vasil’eva, E.D., Morphological data corroborating the assumption of independent origins within octoploid sturgeon species, J. Ichthyol., 2004, vol. 44, suppl. 1, pp. 63–72.
Vasil’eva, E.D., Ryby Chernogo morya. Opredelitel’ morskikh, solonovatovodnykh, evrigalinnykh i prokhodnykh vidov s tsvetnymi illyustratsiyami, sobrannymi S.V. Bogorodskim (Fish of the Black Sea. Guide for Identification of Marine, Saline, Euryhaline, and Anadromous Species with Color Illustrations Collected by S.V. Bogorodskii), Moscow: VNIRO, 2007.
Vasil’eva, E.D., Morphological and morphometric characters in sturgeon taxonomy and phylogeny, in Biology, Conservation and Sustainable Development of Sturgeons, Fish Fish. Ser. vol. 29, Carmona, R., Domezain, A., Garcia-Gallego, M., et al., Eds., New York: Springer-Verlag, 2009, pp. 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8437-9_3
Vasil’eva, E. and Vasil’ev, V., The problems of the evaluation of taxonomic relations in the species group Acipenser gueldenstaedtii (Acipenseridae): a modern approach, Proc. Konf. Naukowa “Aktualny Stan i Ochrona Naturalnych Populacji Ryb Jesiotrowatych Acipenseridae,” Kolman, R., Ed., Olsztyn: Inst. Ryb. Śródlądowego, 2014, pp. 167–187.
Vasil’eva, E.D., Grunina, A.S. and Recoubratsky, A.V., The pattern of manifestation of some morphological characters in androgenetic nucleo-cytoplasmatic hybrids of the Persian Acipenser persicus and Russian A. gueldenstaedtii sturgeons in the postlarval period, J. Ichthyol., 2001, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 454–460.
Vlasenko, A.D., Pavlov, A.V., Sokolov, L.I. and Vasil’ev, V.P., Acipenser gueldenstaedti Brandt, 1883, in The Freshwater Fishes of Europe, Vol. 1, Part 2: General Introduction to Fishes. Acipenseriformes, Holčik, J., Ed., Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1989a, pp. 294–344.
Vlasenko, A.D., Pavlov, A.V. and Vasil’ev, V.P., Acipenser persicus Borodin, 1897, in The Freshwater Fishes of Europe, Vol. 1, Part 2: General Introduction to Fishes. Acipenseriformes, Holčik, J., Ed., Wiesbaden: Aula-Verlag, 1989b, pp. 343–366.
Yanina, T.A., Neopleistotsen Ponto–Kaspiya: biostratigrafiya, paleogeografiya, korrelyatsiya (Neopleistocene of the Ponto–Caspian Region: Biostratigraphy, Paleogeography, and Correlation), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 2012.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are deeply grateful to Profs. R. Billard and J.-C. Hureau (MNHN) and Drs. A. Balushkin and A. Neelov (ZIN) for the possibility to study museum collections and to Dr. M. Chebanov (the Southern Branch of the Federal Center for Fish Breeding and Genetics (Kransnodar sturgeon hatchery)) for obtaining fresh sturgeon materials.
Funding
Scientific investigations of EV are supported by the State Project of ZMMU АААА–А16–116021660077–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
The article translated by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasil’eva, E.D., Vasil’ev, V.P. Taxonomic Relations of Russian and Persian Sturgeons (genus Acipenser, Acipenseridae): an Updated Synthesis. J. Ichthyol. 61, 17–32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945221010173
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945221010173