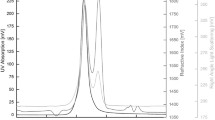
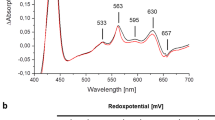
Abstract
Cytochrome bd-II is one of the three terminal quinol oxidases of the aerobic respiratory chain of Escherichia coli. Preparations of the detergent-solubilized untagged bd-II oxidase isolated from the bacterium were shown to scavenge hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with high rate producing molecular oxygen (O2). Addition of H2O2 to the same buffer that does not contain enzyme or contains thermally denatured cytochrome bd-II does not lead to any O2 production. The latter observation rules out involvement of adventitious transition metals bound to the protein. The H2O2-induced O2 production is not susceptible to inhibition by N-ethylmaleimide (the sulfhydryl binding compound), antimycin A (the compound that binds specifically to a quinol binding site), and CO (diatomic gas that binds specifically to the reduced heme d). However, O2 formation is inhibited by cyanide (IC50 = 4.5 ± 0.5 µM) and azide. Addition of H2O2 in the presence of dithiothreitol and ubiquinone-1 does not inactivate cytochrome bd-II and apparently does not affect the O2 reductase activity of the enzyme. The ability of cytochrome bd-II to detoxify H2O2 could play a role in bacterial physiology by conferring resistance to the peroxide-mediated stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- Q1 :
-
2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-1,4-benzoquinone
References
Gavrikova, E. V., Grivennikova, V. G., Borisov, V. B., Cecchini, G., and Vinogradov, A. D. (2009) Assembly of a chimeric respiratory chain from bovine heart submitochondrial particles and cytochrome bd terminal oxidase of Escherichia coli, FEBS Lett., 583, 1287-1291, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.03.022.
Poole, R. K., and Cook, G. M. (2000) Redundancy of aerobic respiratory chains in bacteria? Routes, reasons and regulation, Adv. Microb. Physiol., 43, 165-224, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2911(00)43005-5.
Murali, R., Gennis, R. B., and Hemp, J. (2021) Evolution of the cytochrome bd oxygen reductase superfamily and the function of CydAA’ in Archaea, ISME J., 15, 3534-3548, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01019-4.
Borisov, V. B. (2002) Defects in mitochondrial respiratory complexes III and IV, and human pathologies, Mol. Aspects Med., 23, 385-412, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0098-2997(02)00013-4.
Borisov, V. B. (2004) Mutations in respiratory chain complexes and human diseases, Ital. J. Biochem., 53, 34-40.
Azarkina, N., Borisov, V., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1997) Spontaneous spectral changes of the reduced cytochrome bd, FEBS Lett., 416, 171-174, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01196-4.
Borisov, V. B., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2015) Oxygen as acceptor, EcoSal Plus, 6, https://doi.org/10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2015.
Siletsky, S. A., Borisov, V. B., and Mamedov, M. D. (2017) Photosystem II and terminal respiratory oxidases: molecular machines operating in opposite directions, Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.), 22, 1379-1426, https://doi.org/10.2741/4550.
Borisov, V. B., and Siletsky, S. A. (2019) Features of organization and mechanism of catalysis of two families of terminal oxidases: Heme-copper and bd-type, Biochemistry (Moscow), 84, 1390-1402, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919110130.
Forte, E., Giuffre, A., Huang, L. S., Berry, E. A., and Borisov, V. B. (2020) Nitric oxide does not inhibit but is metabolized by the cytochrome bcc-aa3 supercomplex, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 21, 8521, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228521.
Borisov, V. B. (1996) Cytochrome bd: Structure and properties, Biochemistry (Moscow), 61, 565-574.
Borisov, V. B., Gennis, R. B., Hemp, J., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2011) The cytochrome bd respiratory oxygen reductases, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1807, 1398-1413, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.06.016.
Siletsky, S. A., and Borisov, V. B. (2021) Proton pum** and non-pum** terminal respiratory oxidases: Active sites intermediates of these molecular machines and their derivatives, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22, 10852, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910852.
Puustinen, A., Finel, M., Haltia, T., Gennis, R. B., and Wikstrom, M. (1991) Properties of the two terminal oxidases of Escherichia coli, Biochemistry, 30, 3936-3942, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00230a019.
Jasaitis, A., Borisov, V. B., Belevich, N. P., Morgan, J. E., Konstantinov, A. A., et al. (2000) Electrogenic reactions of cytochrome bd, Biochemistry, 39, 13800-13809, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi001165n.
Belevich, I., Borisov, V. B., Zhang, J., Yang, K., Konstantinov, A. A., et al. (2005) Time-resolved electrometric and optical studies on cytochrome bd suggest a mechanism of electron-proton coupling in the di-heme active site, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 3657-3662, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405683102.
Belevich, I., Borisov, V. B., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2007) Discovery of the true peroxy intermediate in the catalytic cycle of terminal oxidases by real-time measurement, J. Biol. Chem., 282, 28514-28519, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705562200.
Borisov, V. B., Belevich, I., Bloch, D. A., Mogi, T., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2008) Glutamate 107 in subunit I of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli is part of a transmembrane intraprotein pathway conducting protons from the cytoplasm to the heme b595/heme d active site, Biochemistry, 47, 7907-7914, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi800435a.
Borisov, V. B., Murali, R., Verkhovskaya, M. L., Bloch, D. A., Han, H., et al. (2011) Aerobic respiratory chain of Escherichia coli is not allowed to work in fully uncoupled mode, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 108, 17320-17324, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108217108.
Borisov, V. B., Siletsky, S. A., Paiardini, A., Hoogewijs, D., Forte, E., et al. (2021) Bacterial oxidases of the cytochrome bd family: Redox enzymes of unique structure, function and utility as drug targets, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 34, 1280-1318, https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2020.8039.
Forte, E., Borisov, V. B., Vicente, J. B., and Giuffre, A. (2017) Cytochrome bd and gaseous ligands in bacterial physiology, Adv. Microb. Physiol., 71, 171-234, https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ampbs.2017.05.002.
Borisov, V. B., Smirnova, I. A., Krasnosel’skaya, I. A., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1994) Oxygenated cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli can be converted into the oxidized form by lipophilic electron acceptors, Biochemistry (Moscow), 59, 437-443.
Azarkina, N., Siletsky, S., Borisov, V., von Wachenfeldt, C., Hederstedt, L., et al. (1999) A cytochrome bb′-type quinol oxidase in Bacillus subtilis strain 168, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 32810-32817, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.46.32810.
Forte, E., Borisov, V. B., Konstantinov, A. A., Brunori, M., Giuffre, A., et al. (2007) Cytochrome bd, a key oxidase in bacterial survival and tolerance to nitrosative stress, Ital. J. Biochem., 56, 265-269.
Giuffre, A., Borisov, V. B., Mastronicola, D., Sarti, P., and Forte, E. (2012) Cytochrome bd oxidase and nitric oxide: From reaction mechanisms to bacterial physiology, FEBS Lett., 586, 622-629, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.07.035.
Giuffre, A., Borisov, V. B., Arese, M., Sarti, P., and Forte, E. (2014) Cytochrome bd oxidase and bacterial tolerance to oxidative and nitrosative stress, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1837, 1178-1187, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.01.016.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Siletsky, S. A., Arese, M., Davletshin, A. I., et al. (2015) Cytochrome bd protects bacteria against oxidative and nitrosative stress: A potential target for next-generation antimicrobial agents, Biochemistry (Moscow), 80, 565-575, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915050077.
Poole, R. K., and Hill, S. (1997) Respiratory protection of nitrogenase activity in Azotobacter vinelandii – roles of the terminal oxidases, Biosci. Rep., 17, 307-317, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027336712748.
Bertsova, Y. V., Demin, O. V., and Bogachev, A. V. (2005) Respiratory protection of nitrogenase complex in Azotobacter vinelandii [in Russian], Usp. Biol. Khim., 45, 205-234.
Mobius, K., Arias-Cartin, R., Breckau, D., Hannig, A. L., Riedmann, K., et al. (2010) Heme biosynthesis is coupled to electron transport chains for energy generation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 10436-10441, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000956107.
Bader, M., Muse, W., Ballou, D. P., Gassner, C., and Bardwell, J. C. A. (1999) Oxidative protein folding is driven by the electron transport system, Cell, 98, 217-227, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81016-8.
Lu, P., Heineke, M. H., Koul, A., Andries, K., Cook, G. M., et al. (2015) The cytochrome bd-type quinol oxidase is important for survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis under peroxide and antibiotic-induced stress, Sci. Rep., 5, 10333, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10333.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Siletsky, S. A., Sarti, P., and Giuffre, A. (2015) Cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli catalyzes peroxynitrite decomposition, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1847, 182-188, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.10.006.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Konstantinov, A. A., Poole, R. K., Sarti, P., et al. (2004) Interaction of the bacterial terminal oxidase cytochrome bd with nitric oxide, FEBS Lett., 576, 201-204, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.013.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Sarti, P., Brunori, M., Konstantinov, A. A., et al. (2006) Nitric oxide reacts with the ferryl-oxo catalytic intermediate of the CuB-lacking cytochrome bd terminal oxidase, FEBS Lett., 580, 4823-4826, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.07.072.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Sarti, P., Brunori, M., Konstantinov, A. A., et al. (2007) Redox control of fast ligand dissociation from Escherichia coli cytochrome bd, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 355, 97-102, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.118.
Mason, M. G., Shepherd, M., Nicholls, P., Dobbin, P. S., Dodsworth, K. S., et al. (2009) Cytochrome bd confers nitric oxide resistance to Escherichia coli, Nat. Chem. Biol., 5, 94-96, https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.135.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Giuffre, A., Konstantinov, A., and Sarti, P. (2009) Reaction of nitric oxide with the oxidized di-heme and heme-copper oxygen-reducing centers of terminal oxidases: Different reaction pathways and end-products, J. Inorg. Biochem., 103, 1185-1187, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**orgbio.2009.06.002.
Shepherd, M., Achard, M. E., Idris, A., Totsika, M., Phan, M. D., et al. (2016) The cytochrome bd-I respiratory oxidase augments survival of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli during infection, Sci. Rep., 6, 35285, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35285.
Holyoake, L. V., Hunt, S., Sanguinetti, G., Cook, G. M., Howard, M. J., et al. (2016) CydDC-mediated reductant export in Escherichia coli controls the transcriptional wiring of energy metabolism and combats nitrosative stress, Biochem. J., 473, 693-701, https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20150536.
Jones-Carson, J., Husain, M., Liu, L., Orlicky, D. J., and Vazquez-Torres, A. (2016) Cytochrome bd-dependent bioenergetics and antinitrosative defenses in Salmonella pathogenesis, MBio, 7, e02052-02016, https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02052-16.
Meng, Q., Yin, J., **, M., and Gao, H. (2018) Distinct nitrite and nitric oxide physiologies in Escherichia coli and Shewanella oneidensis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 84, e00559-00518, https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00559-18.
Beebout, C. J., Eberly, A. R., Werby, S. H., Reasoner, S. A., Brannon, J. R., et al. (2019) Respiratory heterogeneity shapes biofilm formation and host colonization in uropathogenic Escherichia coli, MBio, 10, e02400-18, https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02400-18.
Forte, E., Borisov, V. B., Falabella, M., Colaco, H. G., Tinajero-Trejo, M., et al. (2016) The terminal oxidase cytochrome bd promotes sulfide-resistant bacterial respiration and growth, Sci. Rep., 6, 23788, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23788.
Korshunov, S., Imlay, K. R., and Imlay, J. A. (2016) The cytochrome bd oxidase of Escherichia coli prevents respiratory inhibition by endogenous and exogenous hydrogen sulfide, Mol. Microbiol., 101, 62-77, https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13372.
Forte, E., and Giuffre, A. (2016) How bacteria breathe in hydrogen sulphide-rich environments, The Biochemist, 38, 8-11, https://doi.org/10.1042/BIO03805008.
Borisov, V. B., and Forte, E. (2021) Terminal oxidase cytochrome bd protects bacteria against hydrogen sulfide toxicity, Biochemistry (Moscow), 86, 22-32, https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629792101003X.
Borisov, V. B., and Forte, E. (2021) Impact of hydrogen sulfide on mitochondrial and bacterial bioenergetics, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22, 12688, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312688.
Forte, E., Siletsky, S. A., and Borisov, V. B. (2021) In Escherichia coli ammonia inhibits cytochrome bo3 but activates cytochrome bd-I, Antioxidants (Basel), 10, 13, https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10010013.
Borisov, V., Gennis, R., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1995) Peroxide complex of cytochrome bd: kinetics of generation and stability, Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int., 37, 975-982.
Borisov, V. B., Gennis, R. B., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1995) Interaction of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli with hydrogen peroxide, Biochemistry (Moscow), 60, 231-239.
Lindqvist, A., Membrillo-Hernandez, J., Poole, R. K., and Cook, G. M. (2000) Roles of respiratory oxidases in protecting Escherichia coli K12 from oxidative stress, Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 78, 23-31, https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1002779201379.
Korshunov, S., and Imlay, J. A. (2010) Two sources of endogenous hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli, Mol. Microbiol., 75, 1389-1401, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07059.x.
Borisov, V. B., Davletshin, A. I., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2010) Peroxidase activity of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli, Biochemistry (Moscow), 75, 428-436, https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791004005X.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Davletshin, A., Mastronicola, D., Sarti, P., et al. (2013) Cytochrome bd oxidase from Escherichia coli displays high catalase activity: An additional defense against oxidative stress, FEBS Lett., 587, 2214-2218, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.047.
Forte, E., Borisov, V. B., Davletshin, A., Mastronicola, D., Sarti, P., et al. (2013) Cytochrome bd oxidase and hydrogen peroxide resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, MBio, 4, e01006-01013, https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01006-13.
Al-Attar, S., Yu, Y., Pinkse, M., Hoeser, J., Friedrich, T., et al. (2016) Cytochrome bd displays significant quinol peroxidase activity, Sci. Rep., 6, 27631, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27631.
Borisov, V. B., Siletsky, S. A., Nastasi, M. R., and Forte, E. (2021) ROS defense systems and terminal oxidases in bacteria, Antioxidants (Basel), 10, 839, https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060839.
Safarian, S., Rajendran, C., Muller, H., Preu, J., Langer, J. D., et al. (2016) Structure of a bd oxidase indicates similar mechanisms for membrane-integrated oxygen reductases, Science, 352, 583-586, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf2477.
Thesseling, A., Rasmussen, T., Burschel, S., Wohlwend, D., Kagi, J., et al. (2019) Homologous bd oxidases share the same architecture but differ in mechanism, Nat. Commun., 10, 5138, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13122-4.
Safarian, S., Hahn, A., Mills, D. J., Radloff, M., Eisinger, M. L., et al. (2019) Active site rearrangement and structural divergence in prokaryotic respiratory oxidases, Science, 366, 100-104, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay0967.
Wang, W., Gao, Y., Tang, Y., Zhou, X., Lai, Y., et al. (2021) Cryo-EM structure of mycobacterial cytochrome bd reveals two oxygen access channels, Nat. Commun., 12, 4621, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24924-w.
Safarian, S., Opel-Reading, H. K., Wu, D., Mehdipour, A. R., Hards, K., et al. (2021) The cryo-EM structure of the bd oxidase from M. tuberculosis reveals a unique structural framework and enables rational drug design to combat TB, Nat. Commun., 12, 5236, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25537-z.
Grauel, A., Kagi, J., Rasmussen, T., Makarchuk, I., Oppermann, S., et al. (2021) Structure of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd-II type oxidase with bound aurachin D, Nat. Commun., 12, 6498, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26835-2.
Grund, T. N., Radloff, M., Wu, D., Goojani, H. G., Witte, L. F., et al. (2021) Mechanistic and structural diversity between cytochrome bd isoforms of Escherichia coli, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 118, e2114013118, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2114013118.
Friedrich, T., Wohlwend, D., and Borisov, V. B. (2022) Recent advances in structural studies of cytochrome bd and its potential application as a drug target, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23, 3166, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063166.
Yang, K., Borisov, V. B., Konstantinov, A. A., and Gennis, R. B. (2008) The fully oxidized form of the cytochrome bd quinol oxidase from E. coli does not participate in the catalytic cycle: Direct evidence from rapid kinetics studies, FEBS Lett., 582, 3705-3709, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.09.038.
Borisov, V. B., Forte, E., Sarti, P., and Giuffre, A. (2011) Catalytic intermediates of cytochrome bd terminal oxidase at steady-state: Ferryl and oxy-ferrous species dominate, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1807, 503-509, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.02.007.
Paulus, A., Rossius, S. G., Dijk, M., and de Vries, S. (2012) Oxoferryl-porphyrin radical catalytic intermediate in cytochrome bd oxidases protects cells from formation of reactive oxygen species, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 8830-8838, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.333542.
D’mello, R., Hill, S., and Poole, R. K. (1996) The cytochrome bd quinol oxidase in Escherichia coli has an extremely high oxygen affinity and two-oxygen-binding haems: Implications for regulation of activity in vivo by oxygen inhibition, Microbiology, 142, 755-763, https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-142-4-755.
Belevich, I., Borisov, V. B., Konstantinov, A. A., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2005) Oxygenated complex of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli: Stability and photolability, FEBS Lett., 579, 4567-4570, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.011.
Belevich, I., Borisov, V. B., Bloch, D. A., Konstantinov, A. A., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2007) Cytochrome bd from Azotobacter vinelandii: evidence for high-affinity oxygen binding, Biochemistry, 46, 11177-11184, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi700862u.
Siletsky, S. A., Rappaport, F., Poole, R. K., and Borisov, V. B. (2016) Evidence for fast electron transfer between the high-spin haems in cytochrome bd-I from Escherichia coli, PLoS One, 11, e0155186, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155186.
Hill, J. J., Alben, J. O., and Gennis, R. B. (1993) Spectroscopic evidence for a heme-heme binuclear center in the cytochrome bd ubiquinol oxidase from Escherichia coli, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 5863-5867, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.12.5863.
Muntyan, M. S., Bloch, D. A., Drachev, L. A., and Skulachev, V. P. (1993) Kinetics of CO binding to putative Na+-motive oxidases of the o-type from Bacillus FTU and of the d-type from Escherichia coli, FEBS Lett., 327, 347-350, https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(93)81018-u.
Tsubaki, M., Hori, H., Mogi, T., and Anraku, Y. (1995) Cyanide-binding site of bd-type ubiquinol oxidase from Escherichia coli, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 28565-28569, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.48.28565.
Borisov, V., Arutyunyan, A. M., Osborne, J. P., Gennis, R. B., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1999) Magnetic circular dichroism used to examine the interaction of Escherichia coli cytochrome bd with ligands, Biochemistry, 38, 740-750, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi981908t.
Vos, M. H., Borisov, V. B., Liebl, U., Martin, J. L., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2000) Femtosecond resolution of ligand-heme interactions in the high-affinity quinol oxidase bd: A di-heme active site? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 1554-1559, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.030528197.
Borisov, V. B., Sedelnikova, S. E., Poole, R. K., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2001) Interaction of cytochrome bd with carbon monoxide at low and room temperatures: Evidence that only a small fraction of heme b595 reacts with CO, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 22095-22099, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M011542200.
Borisov, V. B., Liebl, U., Rappaport, F., Martin, J. L., Zhang, J., et al. (2002) Interactions between heme d and heme b595 in quinol oxidase bd from Escherichia coli: A photoselection study using femtosecond spectroscopy, Biochemistry, 41, 1654-1662, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0158019.
Arutyunyan, A. M., Borisov, V. B., Novoderezhkin, V. I., Ghaim, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2008) Strong excitonic interactions in the oxygen-reducing site of bd-type oxidase: The Fe-to-Fe distance between hemes d and b595 is 10 A, Biochemistry, 47, 1752-1759, https://doi.org/10.1021/bi701884g.
Borisov, V. B. (2008) Interaction of bd-type quinol oxidase from Escherichia coli and carbon monoxide: Heme d binds CO with high affinity, Biochemistry (Moscow), 73, 14-22, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297908010021.
Bloch, D. A., Borisov, V. B., Mogi, T., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2009) Heme/heme redox interaction and resolution of individual optical absorption spectra of the hemes in cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1787, 1246-1253, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.05.003.
Rappaport, F., Zhang, J., Vos, M. H., Gennis, R. B., and Borisov, V. B. (2010) Heme-heme and heme-ligand interactions in the di-heme oxygen-reducing site of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli revealed by nanosecond absorption spectroscopy, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1797, 1657-1664, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.05.010.
Arutyunyan, A. M., Sakamoto, J., Inadome, M., Kabashima, Y., and Borisov, V. B. (2012) Optical and magneto-optical activity of cytochrome bd from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1817, 2087-2094, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.06.009.
Borisov, V. B., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2013) Accommodation of CO in the di-heme active site of cytochrome bd terminal oxidase from Escherichia coli, J. Inorg. Biochem., 118, 65-67, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**orgbio.2012.09.016.
Siletsky, S. A., Zaspa, A. A., Poole, R. K., and Borisov, V. B. (2014) Microsecond time-resolved absorption spectroscopy used to study CO compounds of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli, PLoS One, 9, e95617, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095617.
Siletsky, S. A., Dyuba, A. V., Elkina, D. A., Monakhova, M. V., and Borisov, V. B. (2017) Spectral-kinetic analysis of recombination reaction of heme centers of bd-type quinol oxidase from Escherichia coli with carbon monoxide, Biochemistry-Moscow, 82, 1354-1366, https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791711013X.
Bekker, M., de Vries, S., Ter Beek, A., Hellingwerf, K. J., and de Mattos, M. J. (2009) Respiration of Escherichia coli can be fully uncoupled via the nonelectrogenic terminal cytochrome bd-II oxidase, J. Bacteriol., 191, 5510-5517, https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00562-09.
Shepherd, M., Sanguinetti, G., Cook, G. M., and Poole, R. K. (2010) Compensations for diminished terminal oxidase activity in Escherichia coli: cytochrome bd-II-mediated respiration and glutamate metabolism, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 18464-18472, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.118448.
Rivera-Chavez, F., Zhang, L. F., Faber, F., Lopez, C. A., Byndloss, M. X., et al. (2016) Depletion of butyrate-producing Clostridia from the gut microbiota drives an aerobic luminal expansion of Salmonella, Cell Host Microbe, 19, 443-454, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.03.004.
Chanin, R. B., Winter, M. G., Spiga, L., Hughes, E. R., Zhu, W., et al. (2020) Epithelial-derived reactive oxygen species enable AppBCX-mediated aerobic respiration of Escherichia coli during intestinal inflammation, Cell Host Microbe, 28, 780-788.e785, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2020.09.005.
Miller, M. J., and Gennis, R. B. (1986) Purification and reconstitution of the cytochrome d terminal oxidase complex from Escherichia coli, Methods Enzymol., 126, 87-94, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(86)26011-5.
Goutelle, S., Maurin, M., Rougier, F., Barbaut, X., Bourguignon, L., et al. (2008) The Hill equation: A review of its capabilities in pharmacological modelling, Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 22, 633-648, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00633.x.
Forte, E., Borisov, V. B., Siletsky, S. A., Petrosino, M., and Giuffre, A. (2019) In the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli cytochromes bd-I and bd-II are more sensitive to carbon monoxide inhibition than cytochrome bo3, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg., 1860, 148088, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2019.148088.
Sturr, M. G., Krulwich, T. A., and Hicks, D. B. (1996) Purification of a cytochrome bd terminal oxidase encoded by the Escherichia coli app locus from a Δcyo Δcyd strain complemented by genes from Bacillus firmus OF4, J. Bacteriol., 178, 1742-1749, https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.6.1742-1749.1996.
Borisov, V. B. (2020) Effect of membrane environment on ligand-binding properties of the terminal oxidase cytochrome bd-I from Escherichia coli, Biochemistry (Moscow), 85, 1603-1612, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920120123.
Deisseroth, A., and Dounce, A. L. (1970) Catalase: Physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role, Physiol. Rev., 50, 319-375, https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1970.50.3.319.
Su, S., Panmanee, W., Wilson, J. J., Mahtani, H. K., Li, Q., et al. (2014) Catalase (KatA) plays a role in protection against anaerobic nitric oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, PLoS One, 9, e91813, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091813.
Brown, G. C. (1995) Reversible binding and inhibition of catalase by nitric oxide, Eur. J. Biochem., 232, 188-191, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20798.x.
Lu, H., Li, Z., and Hu, N. (2003) Direct voltammetry and electrocatalytic properties of catalase incorporated in polyacrylamide hydrogel films, Biophys. Chem., 104, 623-632, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4622(03)00121-2.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to M. Bekker (University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for providing the strain of E. coli MB37 and to R. B. Gennis (University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois, USA) for the strain of E. coli GO105/pTK1. V. B. Borisov would also like to express his deepest gratitude to A. D. Vinogradov (untimely departed), the author’s teacher from the student bench to the defense of the doctoral dissertation.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 22-24-00045, https://rscf.ru/en/project/22-24-00045/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.F. and V.B.B. conceived the study, designed the experimental plan and wrote the paper. E.F., M.R.N., and V.B.B. performed and analyzed the experiments. All authors reviewed the results, contributed to data interpretation and critical revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interests in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forte, E., Nastasi, M.R. & Borisov, V.B. Preparations of Terminal Oxidase Cytochrome bd-II Isolated from Escherichia coli Reveal Significant Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity. Biochemistry Moscow 87, 720–730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922080041
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922080041