Abstract
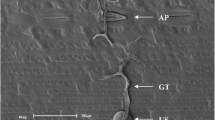
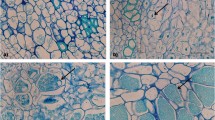
Pleiochaeta root rot caused by Pleiochaeta setosa is a major threat to the Australian lupin industry. Although Pleiochaeta root rot-resistant Lupinus albus varieties have been bred, there is no information on the likely mechanism of this resistance. Susceptible (Kiev mutant) and resistant (P25758) albus lupin cultivars were inoculated with spores of P. setosa strain PS6-1 and the infection process studied microscopically. No specialised penetration structures were observed on the roots, and infecting hyphae entered roots of both cultivars by growing directly between root surface cells. Lengths of conidial germ tubes on resistant hosts was significantly longer than on susceptible hosts, suggesting that a component of the resistance is via reduced host recognition by the pathogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JP, Thatcher LF, Singh KB (2005) Plant defence responses: conservation between models and crops. Functional Plant Biology 32, 21–34. doi: 10.1071/FP04136
Coombes NE (2002) The Reactive Tabu Search for efficient correlated experimental designs. PhD Thesis, Liverpool John Moores University. Concept implemented in DiGGer software. NSWDPI, Wagga Wagga, Australia.
Cullis BR, Smith AB, Coombes NE (2006) On the design of early generation variety trials with correlated data. Journal of Agricultural Biological & Environmental Statistics 11, 381–393. doi: 10.1198/ 108571106X154443
Dita MA, Rispai ON, Prats E, Rubiales D, Singh KB (2006) Biotechnology approaches to overcome biotic and abiotic stress constraints in legumes. Euphytica 147, 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s10681-006-6156-9
Harvey IC (1977) Studies of the infection of lupin leaves by Pleiochaeta setosa. Canadian Journal of Botany 55, 1261–1275.
Heath MC (2000) Non-host resistance and non-specific plant defences. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 3, 315–319. doi: 10.1016/ S1369-5266(00)00087-X
Hill GD (1998) Diseases of lupins. In ‘The pathology of food and pasture legumes’. (Eds DJ Allen, JM Lenn’e) pp. 559–589. (CAB International: Wallingford, UK)
Landers K, Sutherland S, Sykes J (2000) ‘Lupin, best practice management for sustainable production.’ (NSW Agriculture: Orange)
Niks R (1990) Effect of germ tube length on the fate of sporelings of Puccinia hordei in susceptible and resistant barley. Phytopathology 80, 57–60. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-80-57
Rohringer R, Kim WK, Samborski DJ, Howes NK (1977) Calcofluor: an optical brightener for fluorescence microscopy of fungal plant parasites in leaves. Phytopathology 67, 808–810.
Sator C (1990) Lupins (Lupinus spp.). Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry 10, 288–311.
Sweetingham MW (1984) Pleiochaeta setosa — a root pathogen of lupins. Australasian Plant Pathology 13, 21–22. doi: 10.1071/APP9840021
Sweetingham M, Yang H (1998) New sources of resistance to Pleiochaeta and Eradu patch disease in Lupinus spp. CLIMA final report to GRDC, project UWA 166. GRDC, Canberra, ACT.
Thatcher LF, Anderson JP, Singh KB (2005) Plant defence responses: what have we learnt from Arabidopsis? Functional Plant Biology 32, 1–19. doi: 10.1071/FP04135
Tivoli B, Baranger A, Avila CM, Banniza S, Barbetti M, et al. (2006) Screening techniques and sources of resistance to foliar diseases caused by major necrotrophic fungi in grain legumes. Euphytica 147, 223–253. doi: 10.1007/s10681-006-3131-4
Toyoda K, Collins NC, Takaashi A, Shirasu K (2002) Resistance and susceptibility of plants to fungal pathogens. Transgenic Research 11, 567–582. doi: 10.1023/A:1021182111770
Yang HA, Sweetingham MW, Cowling WA (1996) The leaf infection process and resistance to Pleiochaeta setosa in three lupin species. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 47, 787–799. doi: 10.1071/AR9960787
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wunderlich, N., Ash, G.J., Harper, J.D.I. et al. Penetration and symptom development of Pleiochaeta root rot in susceptible and resistant Lupinus albus cultivars. Australasian Plant Pathology 37, 387–391 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1071/AP08014
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AP08014