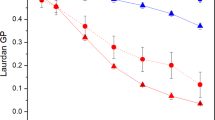
Abstract
Deinococcus radiodurans is well known for its unusual resistance to different environmental stresses. Recently, we have described a novel complex composed of the surface (S)-layer protein DR_2577 and the carotenoid deinoxanthin. We also showed a role of this complex in the UV resistance under desiccation. Both these properties, UV and desiccation resistance, suggest a selective pressure generated by Sun irradiation. In order to confirm this hypothesis we checked whether this S-layer Deinoxanthin Binding Complex (SDBC) has features of thermo-resistance, a property also expected in proteins evolved under solar irradiative pressure. We performed the spectroscopic characterization of the SDBC by means of thermal shift assay, circular dichroism and related in silico analysis. Our findings identify a stability typical of thermo-adapted proteins and provide a new insight into the origin of specific S-layer types. The results are discussed in terms of co-evolutionary mechanisms related to Sun-induced desiccation and heat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Baumeister, F. Karrenberg, R. Rachel, A. Engel, B. Heggeler and W. O. Saxton, The major cell envelope protein of Micrococcus radiodurans (R1). Structural and chemical characterization, Eur. J. Biochem., 1982, 125, 535–544.
D. Farci, C. Slavov, E. Tramontano and D. Piano, The S-layer protein DR_2577 binds the carotenoid deinoxanthin and under desiccation conditions protect against UV- radiation in Deinococcus radiodurans, Front. Microbiol., 2016, 7, 155.
D. Farci, M. W. Bowler, F. Esposito, S. McSweeney, E. Tramontano and D. Piano, Purification and characteriz- ation of DR_2577 (SlpA) a major S-layer protein from Deinococcus radiodurans, Front. Microbiol., 2015, 6, 414.
V. Mattimore and J. R. Battista, Radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans: functions necessary to survive ionizing radiation are also necessary to survive prolonged desiccation, J. Bacteriol., 1996, 178, 633–637.
M. X. Ruiz-González, G. Á. Czirják, P. Genevaux, A. P. Moller, T. A. Mousseau and P. Heeb, Resistance of Feather-Associated Bacteria to Intermediate Levels of Ionizing Radiation near Chernobyl, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 22969.
M. Wassmann, R. Moeller, G. Reitz and P. Rettberg, Adaptation of Bacillus subtilis cells to Archean-like UV climate: relevant hints of microbial evolution to remarkably increased radiation resistance, Astrobiology, 2010, 10, 605–615.
K. Harada, M. Moriwaki and S. Oda, Arrhenius plot ana- lysis of the mechanism of the thermotolerance induction in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans, J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 1988, 34, 209–212.
Y. Liu, J. Zhou, M. V. Omelchenko, A. S. Beliaev, A. Venkateswaran, J. Stair, L. Wu, D. K. Thompson, D. Xu, I. B. Rogozin, E. K. Gaidamakova, M. Zhai, K. S. Makarova, E. V. Koonin and M. J. Daly, Transcriptome dynamics of Deinococcus radiodurans recovering from ionizing radiation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2003, 100, 4191–4196.
A. Airo, S. L. Chan, Z. Martinez, M. O. Platt and J. D. Trent, Heat shock and cold shock in Deinococcus radiodurans, Cell Biochem. Biophys., 2004, 40, 277–288.
D. Asker, T. Beppu and K. Ueda, Unique diversity of caro- tenoid-producing bacteria isolated from Misasa, a radio- active site in Japan, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2007, 77, 383–392.
J. R. Battista, Against all odds: the survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1997, 51, 203.
M. M. Mathews and N. I. Krisky, The relationship between carotenoid pigments and resistance to radiation in non- photosynthetic bacteria, Photochem. Photobiol., 1965, 4, 813–817.
W. Stahl and H. Sies, Carotenoids and protection against solar UV radiation, Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol., 2002, 15, 291–296.
H. Sies and W. Stahl, Carotenoids and UV protection, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2004, 3, 749–752.
W. Stahl and H. Sies, β-Carotene and other carotenoids in protection from sunlight, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2012, 96, 1179S–1184S.
B. Tian and Y. Hua, Carotenoid biosynthesis in extremophi- lic Deinococcus-Thermus bacteria, Trends Microbiol., 2010, 18, 512–520.
A. Krisko and M. Radman, Biology of extreme radiation re- sistance: they way of Deinococcus radiodurans, Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol., 2013, 5, a012765.
F. Peng, L. Zhang, X. Luo, J. Dai, H. An, Y. Tang and C. Fang, Deinococcus xinjiangensis sp. nov., isolated from desert soil, Int.J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2009, 59, 709–713.
Y. Yang, T. Itoh, S. Yokobori, S. Itahashi, H. Shimada, K. Satoh, H. Ohba, I. Narumi and A. Yamagishi, Deinococcus aerius sp. nov., isolated from the high atmo- sphere, Int.J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2009, 59, 1862–1866.
H. Bouraoui, M. B. Aissa, F. Abbassi, J. P. Touzel, M. O’donohue and M. Manai, Characterization of Deinococcus sahariens sp. nov., a radiation-resistant bacter- ium isolated from a Saharan hot spring, Arch. Microbiol., 2012, 194, 315–322.
R. G. E. Murray, The family Deinococcaceae. The Prokaryotes, Springer, New York, 1992, pp. 3732–3744.
D. Farci, M. W. Bowler, J. Kirkpatrick, S. McSweeney, E. Tramontano and D. Piano, New features of the cell wall of the radio-resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2014, 1838, 1978–1984.
N. Poklar and G. Vesnaver, Thermal denaturation of proteins studied by UV spectroscopy, J. Chem. Educ., 2000, 77, 380.
A. Micsonai, F. Wien, L. Kernya, Y. H. Lee, Y. Goto, M. Réfrégiers and J. Kardos, Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2015, 112, E3095–103.
R. Apweiler, A. Bairoch and C. H. Wu, Protein sequence databases, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2004, 8, 76–80.
E. Gasteiger, C. Hoogland, A. Gattiker, S. Duvaud, M. R. Wilkins, R. D. Appel and A. Bairoch, Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server, in The Proteomics Protocols Handbook, ed. J. M. Walker, Humana Press, 2005, pp. 571–607.
H. Rothfuss, J. C. Lara, A. K. Schmid and M. E. Lidstrom, Involvement of the S-layer proteins HPI and SlpA in the maintenance of cell envelope integrity in Deinococcus radio- durans, R1, Microbiology, 2006, 152, 2779–2787.
B. Folch, Y. Dehouck and M. Rooman, Thermo- and mesostabilizing protein interactions identified by tempera- ture-dependent statistical potentials, Biophys. J., 2010, 98, 667–677.
L. Lemee, E. Peuchant, M. Clerc, M. Brunner and H. Pfander, Deinoxanthin: A new carotenoid isolated from Deinococcus radiodurans, Tetrahedron, 1997, 53, 919–926.
N. E. Gentner and R. E. Mitchel, Ionizing radiation- induced release of a cell surface nuclease from Micrococcus radiodurans, Radiat. Res., 1975, 61, 204–215.
S. Karlin and J. Mrazek, Predicted highly expressed and putative alien genes of Deinococcus radiodurans and impli- cations for resistance to ionizing radiation damage, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2001, 98, 5240–5245.
L. Zhang, Q. Yang, X. Luo, C. Fang, Q. Zhang and Y. Tang, Knockout of crtB or crtI gene blocks the carotenoid biosyn- thetic pathway in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 and influ- ences its resistance to oxidative DNA-damaging agents due to change of free radicals scavenging ability, Arch. Microbiol., 2007, 188, 411–419.
C. S. Cockell, The ultra-violate radiation environment of Earth and Mars: past and present, in Astrobiology: The Quest for the Conditions of Life, ed. G. Horneck and C. Baumstark-Khan, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2002, pp. 219–232.
C. E. Blank, Evolutionary timing of the origins of meso- philis sulphate reduction and oxygenic photosynthesis: a phylogenomic dating approach, Geobiology, 2004, 2, 1–20.
C. E. Blank, Not so old Archaea - the antiquity of biogeo- chemical processes in the archael domain of life, Geobiology, 2009, 7, 495–514.
E. G. Nisbet and N. H. Sleep, The habitat and nature of early life, Nature, 2001, 409, 1083–1091.
J. H. Cleaves and S. L. Miller, Oceanic protection of prebio- tic organic compounds from UV radiation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1998, 95, 7260–7263.
E. D. Brodie and B. J. Ridenhour, Reciprocal selection at the phenotypic interface of coevolution, Integr. Comp. Biol., 2003, 43, 408–418.
T. Held, A. Nourmohammad and M. Lässig, Adaptive evol- ution of molecular phenotypes, J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp., 2014, P09029.
A. Anderson, H. Nordon, R. Cain, G. Parrish and D. Duggan, Studies on a radio-resistant Micrococcus. I. (1956). Isolation, morphology, cultural characteristics, and resistance to gamma radiation, Food Technol., 1956, 10, 575.
D. E. Duggan, A. W. Anderson, P. R. Elliker and R. F. Cain, Ultraviolet exposure studies on a gamma radiation-resistant micrococcus isolated from food, Food Res., 1959, 24, 376–382.
J. R. Battista, A. M. Earl and M. J. Park, Why is Deinococcus radiodurans so resistant to ionizing radiation?, Trends Microbiol., 1999, 7, 362–365.
M. M. Cox and J. R. Battista, Deinococcus radiodurans - the consummate survivor, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2005, 3, 882–892.
J. K. Fredrickson, S. M. Li, E. K. Gaidamakova, V. Y. Matrosova, M. Zhai, H. M. Sulloway, J. C. Scholten, M. G. Brown, D. L. Balkwill and M. J. Daly, Protein oxi- dation: key to bacterial desiccation resistance?, ISME J., 2008, 2, 393–403.
D. Slade and M. Radman, Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2011, 75, 133–191.
A. D. Das and H. Misra, Hypothetical proteins present during recovery phase of radiation resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans are under purifying selection, J. Mol. Evol., 2013, 77, 31–42.
A. Szilágyi and P. Závodszky, Structural differences between mesophilic, moderately thermophilic and extremely thermophilic protein subunits: results of a comprehensive survey, Structure, 2000, 8, 493–504.
S. Ngarize, H. Herman, A. Adams and N. Howell, Comparison of changes in the secondary structure of unheated, heated, and high-pressure-treated beta-lacto- globulin and ovalbumin using fourier transform raman spectroscopy and self-deconvolution, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2004, 52, 6470–6477.
U. Opitz, R. Rudolph, R. Jaenicke, L. Ericsson and H. Neurath, Proteolytic Dimers of Porcine Muscle Lactate Dehydrogenase: Characterization, Folding, and Reconstitution of the Truncated and Nicked Polypeptide Chain, Biochem, 1987, 26, 1399–1406.
M. Kohlhoff, A. Dahm and R. Hensel, Tetrameric triose- phosphate isomerase from hyperthermophilic Archaea, FEBS Lett., 1996, 383, 245–250.
V. Villeret, B. Clantin, C. Tricot, C. Legrain, M. Roovers, V. Stalon, N. Glansdorff and J. van Beeumen, The crystal structure of Pyrococcus furiosus ornithine carbamoyltrans- ferase reveals a key role for oligomerization in enzyme stability at extremely high temperatures, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1998, 95, 2801–2806.
X. C. Abrevaya, I. G. Paulino-Lima, D. Galante, F. Rodrigues, P. J. Mauas, E. Cortón and A. Lage Cde, Comparative survival analysis of Deinococcus radiodurans and the haloarchaea Natrialba magadii and Haloferax volca- nii exposed to vacuum ultraviolet irradiation, Astrobiology, 2011, 11, 1034–1040.
K. Zerulla and J. Soppa, Polyploidy in haloarchaea: advantages for growth and survival, Front. Microbiol., 2014, 5, 274.
J. Soppa, Polyploidy in archaea and bacteria: about desicca- tion resistance, giant cell size, long-term survival, enforce- ment by eukaryotic host and additional aspects, J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, 24, 409–419.
Acknowledgments
DP is grateful to the European Synchrotron Research Facility and the Partnership for Structural Biology (Grenoble, France) for preliminary studies. The ΔDR_2577 strain was kindly provided by Professor Mary E. Lidstrom (University of Washington, Seattle, USA). DF gratefully acknowledges the support from the L’Oréal-UNESCO Fellowship for Women in Science 2017, Italy (L’Oréal Italia Per le Donne e la Scienza). The authors acknowledge the reviewers for the helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farci, D., Slavov, C. & Piano, D. Coexisting properties of thermostability and ultraviolet radiation resistance in the main S-layer complex of Deinococcus radiodurans. Photochem Photobiol Sci 17, 81–88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00240h
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00240h