Abstract
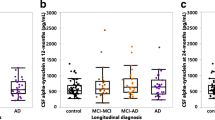
Several studies reported an association between CSF alpha-synuclein (α-syn) and tau in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and demonstrated the significance of α-syn in improving the diagnostic sensitivity/specificity of classical AD CSF biomarkers. In the current study, we measured CSF levels of different α-syn species in a cohort of AD patients (n = 225) who showed a CSF profile typical of AD at baseline as well as in cognitively intact controls (n = 68). CSF total α-syn (t-α-syn) significantly increased in the AD group (p < 0.0001) compared to controls, while oligomeric- and phosphorylated-Ser129-α-syn did not change significantly. ROC analysis showed a sensitivity of 85% and a specificity of 84% (AUC = 0.88) in distinguishing AD from controls. T-α-syn levels correlated positively with tau species in AD group and negatively with baseline MMSE score. Our data support the added value of measurement of CSF α-syn species for further characterization of the CSF AD profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
α-Synuclein (α-syn) is a pre-synaptic neuronal protein that has been linked to a number of neurodegenerative disorders named as “synucleinopathies”1. However, the role of α-syn in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been increasingly recognized since Uéda et al. reported the presence of a non-Aβ component in the extracellular plaques found in the brains of AD patients, which was shown to be a fragment of α-syn2. In fact, the role of α-syn became of particular interest when the co-existence of α-syn and tau pathology was observed in the brains of patients with AD, Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)27. The study was approved by the local Ethical Committee (Comitato Etico delle Aziende Sanitarie della Regione Umbria - CEAS Umbria) and informed written consent was signed by all patients enrolled or by their legal representatives. The work was carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Immunoassays to quantify α-syn species in the CSF
CSF t-, o- and p-S129-α-syn levels were measured using our recently published ELISA assays28. Briefly, for measuring t-α-syn, a 384-well ELISA microplate was coated by overnight incubation at 4 °C with 0.1 μg/ml Syn-140 (sheep anti-α-syn polyclonal antibody) in 200 mM NaHCO3, pH 9.6 (50 μl/well). Similarly, Syn-140 was used for measuring p-S129-α-syn, while the conformation-specific monoclonal antibody (Syn-O2)29, which is specific for α-syn oligomers (0.2 μg/ml), was used as the primary antibody to capture o-α-syn. The plate was then washed with phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween-20 (PBST) and incubated with 100 μl/well of blocking buffer (PBST containing 2.5% gelatin) for 2 hours at 37 °C. After washing, 50 μl of the CSF samples (thawed on ice and Tween-20 added to a final concentration of 0.05%) were added to each well, and the plate was incubated at 37 °C for another 2.5 hours. Antibodies included 11D12 (mouse anti-α-syn monoclonal antibody) for measuring t-α-syn, PS129 (mouse anti-pS129-α-syn monoclonal antibody) for measuring pS129-α-syn and FL-140 (rabbit polyclonal antibody, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for measuring o-α-syn were diluted to the desired concentration (1:5000, 1:1,000 and 1:1,000, respectively) in the blocking buffer before being added to the corresponding wells and incubated at 37 °C for 2 hours. Next, the plate was washed and then incubated for 2 hours at 37 °C with 50 μl/well of species-appropriate secondary antibodies: donkey anti-mouse IgG HRP or goat anti-rabbit IgG HRP (Jackson ImmunoResearch, US), diluted in blocking buffer (1:20,000). After washing, the plate was incubated with 50 μl/well of an enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (SuperSignal ELISA Femto, Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL). Then, the chemiluminescence (relative light units) was immediately measured using a VICTOR™ X3 multilabel plate reader (PerkinElmer). The standard curve for the ELISA assays was carried out using 50 μl/well of serial dilutions of recombinant human α-syn, p-S129-α-syn or o-α-syn in artificial CSF. The samples were screened in a blinded fashion and tested randomly. All the results were confirmed with at least two independent experiments. A series of internal controls was also run to check for run-to-run variations.
Measurement of AD biomarkers
CSF Aβ42, total tau, and p-tau were measured using an ELISA technique (INNOTEST ß amyloid 1–42, hTAU-Ag, p-TAU 181 Ag, Fujirebio Europe, Gent, Belgium) as previously described30.
Data analysis and statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using R software v. 2.15. Continuous variables were described by the median and interquartile range because data distributions were skewed. Correlations were calculated using Spearman’s Rho (rs). The Mann-Whitney test was used for initial comparisons between the two diagnostic groups (p < 0.05). The accuracy of the diagnostic value of the biomarkers31 was assessed by calculating the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve32. Cut-off values were calculated using sensitivity and specificity values that maximized Youden’s index. Because there was a significant difference in age (p < 0.0001) and in the distribution of gender (p < 0.01) between the groups, we corrected for these using a logistic regression approach to adjust for covariates. All CSF samples with an erythrocyte count >500 cells/μl were excluded from further analysis, as traces of blood may influence CSF α-syn levels33,34.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Majbour, N. K. et al. Increased levels of CSF total but not oligomeric or phosphorylated forms of alpha-synuclein in patients diagnosed with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 7, 40263; doi: 10.1038/srep40263 (2017).
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Spillantini, M. G. & Goedert, M. The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920, 16–27 (2000).
Uéda, K. et al. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90, 11282–11286 (1993).
Vekrellis, K., **louri, M., Emmanouilidou, E., Rideout, H. J. & Stefanis, L. Pathological roles of α-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 10, 1015–1025, doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70213-7 (2011).
Parnetti, L. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid Tau/α-synuclein ratio in Parkinson’s disease and degenerative dementias. Mov Disord 26, 1428–1435, doi: 10.1002/mds.23670 (2011).
Toledo, J. B., Korff, A., Shaw, L. M., Trojanowski, J. Q. & Zhang, J. CSF α-synuclein improves diagnostic and prognostic performance of CSF tau and Aβ in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 126, 683–697, doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1148-z (2013).
Kasuga, K. et al. Differential levels of alpha-synuclein, beta-amyloid42 and tau in CSF between patients with dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81, 608–610, doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2009.197483 (2010).
Kapaki, E., Paraskevas, G. P., Emmanouilidou, E. & Vekrellis, K. The diagnostic value of CSF α-synuclein in the differential diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies vs. normal subjects and patients with Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8, e81654, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081654 (2013).
Slaets, S. et al. Increased CSF α-synuclein levels in Alzheimer’s disease: Correlation with tau levels. Alzheimers Dement, doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.10.004 (2014).
Reesink, F. E. et al. CSF alpha-synuclein does not discriminate dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 22, 87–95, doi: 10.3233/jad-2010-100186 (2010).
Ohrfelt, A. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative disorders-a marker of synapse loss? Neurosci Lett 450, 332–335, doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.11.015 (2009).
Korff, A. et al. α-Synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 36, 679–688, doi: 10.3233/JAD-130458 (2013).
Larson, M. E. et al. Soluble α-synuclein is a novel modulator of Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. J Neurosci 32, 10253–10266, doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0581-12.2012 (2012).
Skillbäck, T. et al. Diagnostic performance of cerebrospinal fluid total tau and phosphorylated tau in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: results from the Swedish Mortality Registry. JAMA Neurol 71, 476–483, doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.6455 (2014).
Magnoni, S. et al. Tau elevations in the brain extracellular space correlate with reduced amyloid-β levels and predict adverse clinical outcomes after severe traumatic brain injury. Brain 135, 1268–1280, doi: 10.1093/brain/awr286 (2012).
Blennow, K., Hampel, H., Weiner, M. & Zetterberg, H. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6, 131–144, doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2010.4 (2010).
Wang, H. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein levels are elevated in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica patients during replase. J Neurochem 122, 19–23, doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07749.x (2012).
Kasai, T. et al. Increased α-synuclein levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 261, 1203–1209, doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7334-7 (2014).
Larson, M. E. et al. In J Neurosci Vol. 32 10253–10266 (2012).
Winner, B. et al. In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 4194–4199, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100976108 (2011).
Tokuda, T. et al. Detection of elevated levels of α-synuclein oligomers in CSF from patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology 75, 1766–1772, doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181fd613b (2010).
Hansson, O. et al. Levels of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein oligomers are increased in Parkinson’s disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies compared to Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 6, 25, doi: 10.1186/alzrt255 (2014).
Paleologou, K. E. et al. Detection of elevated levels of soluble alpha-synuclein oligomers in post-mortem brain extracts from patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 132, 1093–1101, doi: 10.1093/brain/awn349 (2009).
Anderson, J. P. et al. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281, 29739–29752, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600933200 (2006).
Fujiwara, H. et al. alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4, 160–164, doi: 10.1038/ncb748 (2002).
Wang, Y. et al. Phosphorylated α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 4, 121ra120, doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002566 (2012).
Dubois, B. et al. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol 6, 734–746, doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70178-3 (2007).
Teunissen, C. E. et al. A consensus protocol for the standardization of cerebrospinal fluid collection and biobanking. Neurology 73, 1914–1922, doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c47cc2 (2009).
Majbour, N. K. et al. Oligomeric and phosphorylated alpha-synuclein as potential CSF biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 11, 7, doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0072-9 (2016).
Vaikath, N. N. et al. Generation and characterization of novel conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies for α-synuclein pathology. Neurobiol Dis 79, 81–99, doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.04.009 (2015).
Parnetti, L. et al. Performance of aβ1-40, aβ1-42, total tau, and phosphorylated tau as predictors of dementia in a cohort of patients with mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 29, 229–238, doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-111349 (2012).
Eusebi, P. Diagnostic accuracy measures. Cerebrovasc Dis 36, 267–272, doi: 10.1159/000353863 (2013).
Robin, X. et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 77, doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-77 (2011).
Hong, Z. et al. DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133, 713–726, doi: 10.1093/brain/awq008 (2010).
Barbour, R. et al. Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis 5, 55–59, doi: 10.1159/000112832 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Mr. Cristiano Spaccatini for his technical support (di Medicina, sezione di Neurologia, Università degli Studi di Perugia, Perugia, Italy). The laboratory of Omar M. El-Agnaf is supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (NY). This work was also supported by grants from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research PRIN 2010–2011 (Grant No. 2010PWNJXK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: O.E., L.P. Executing the experiments N.M., N.V. Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data: N.M., D.C., P.E., N.V., L.P., T.T., P.C., O.E. Drafting of the manuscript: N.M., D.C. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: O.E., L.P., P.C. Statistical analysis: P.E. Obtaining funding: O.E., L.P., P.C. Study supervision: O.E. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Majbour, N., Chiasserini, D., Vaikath, N. et al. Increased levels of CSF total but not oligomeric or phosphorylated forms of alpha-synuclein in patients diagnosed with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 7, 40263 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40263
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40263
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Cerebrospinal fluid reference proteins increase accuracy and interpretability of biomarkers for brain diseases
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Fluid and Biopsy Based Biomarkers in Parkinson's Disease
Neurotherapeutics (2023)
-
Alpha-synuclein: a pathological factor with Aβ and tau and biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Cerebrospinal fluid α synuclein concentrations in patients with positive AD biomarkers and extrapyramidal symptoms
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)
-
A multicentre validation study of the diagnostic value of plasma neurofilament light
Nature Communications (2021)