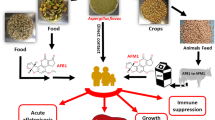
Abstract
Aflatoxin is a group of strongly toxic and carcinogenic mycotoxins produced by Aspergillus flavus and other Aspergillus species, which caused food contamination and food loss problems widely across the world especially in develo** countries, thus threatening human health and sustainable development. So, it is important to develop new, green, and broad-spectrum biocontrol technology for the prevention of aflatoxin contamination sources. Previously, we found that the PO8 protein from aflatoxigenic A. flavus could be used as a biomarker to predict aflatoxin production in peanuts (so the PO8 is named as an early warning molecule), which infers that the PO8 is relative to aflatoxin production. Therefore, in the study, based on inhibiting the PO8, a new and quick strategy for screening aflatoxin biocontrol strains for develo** control agents was presented. With the PO8 inhibition method, four biocontrol strains (2 strains were isolated from peanut kernels with sterilized surface and another 2 strains from peanut rhizosphere soil) were selected and combined to increase prevention wide-spectrum. As a result, the combination showed over 90% inhibition to all tested aflatoxigenic A. flavus isolated from three different peanut production areas (north, middle, and south areas of China), and better than any single strain. The field experiments located in five provinces of China showed that the practice prevention effects (inhibition of aflatoxigenic fungi on the surface of the peanuts) were from 50% to over 80%. The results indicated that the strategy of inhibiting the early warning molecule PO8 can be used to develop aflatoxin control agents well.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Aflatoxins, derivatives of polyketide, secondary metabolites primarily produced by fungal species from the Aspergillus genus, especially, Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus, are a group of structurally related toxic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic mycotoxins1,2, The aflatoxigenic A. flavus strains LNZW-1, SX-1-1, SDJY-95-1, ANHBB-14, AnhHSZ-53, Hubzhx-33, JXZS-118-8, XZCY-21-5, HNDX-8, and GDZJ-15 were isolated from the peanut soils in Liaoning, Shanxi, Shandong, Anhui, Hubei, Jiangxi, **zang, Hunan and Guangdong peanut-planting provinces of China, which is depicted in Fig. 6. The A. flavus strains were grown on DG-18 agar medium (protein 5 g, glucose 10 g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0 g, magnesium sulfate 0.5 g, zinc sulfate 0.01 g, copper sulfate 0.005 g, ammonium chlortronitol 0.002 g, gildamycin hydrochloride 0.05 g, agar 15 g, and 1 L water, pH adjusted to 5.6 ± 0. 2, 121 °C sterilized for 20 min). The conidia were harvested with a 0.01% Tween-80 solution after 5–6 days of culture at 28 °C in darkness. The biocontrol bacteria including 2BQN19 (Stenotrophomonas sp.), 54 (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens), HS10 (Bacillus licheniformis), 1JN2 (Bacillus subtilis), 5BS2 (Bacillus subtilis), B6 (Bacillus sp.), Y2 (Bacillus cereus), DY (Bacillus licheniformis), AAC (Enterobacter ludwigii), CB (Brevibacillus laterosporus), JDF (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens), JZ (Bacillus mucilaginosus), selected from the biocontrol strain library in our laboratory, were isolated from peanut or their rhizosphere soil, which were previously reported by Yang35, Li et al. (2019)29, and Zhang et al. (2021)36. The biocontrol bacteria strains were cultured at 28 °C for 18–24 h in an LB liquid medium, which contained 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of peptone, and 10 g of NaCl per liter. A. flavus and the bacterial antagonists, respectively, were prepared by quantifying the conidia and bacterial cells using a hemocytometer. Briefly, ten A. flavus strains were grown in conical flasks containing 50 ml Sabouraud’s Dextrose Broth (peptone 10 g, glucose 40 g, 121 °C sterilized for 20 min) with 5 × 105 conidia/mL and shaken (180 rpm) at 28 ± 1 °C for 8 days. The mycelium was collected by filtration at different incubation times every 24 h under sterile conditions with sterile water and gauze, and then quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and freeze-dried for further use. The culture medium was also collected into the sterile tubes and then stored at −20 °C for use. Three biological replicates were set up for all control and experimental groups. Briefly, the A. flavus strain JXZS-118-8 was grown in conical flasks containing 50 ml Sabouraud’s Dextrose Broth with 5 × 105 conidia/mL and shaken (180 rpm) at 28 °C for 12 h. And then, 12 biocontrol bacteria strains were added to the above conical flasks to reach a final concentration of 107CFU/mL and continued to culture for 36 h. At different incubation times (24 h, 30 h, and 36 h), the mycelia were collected into the sterile tubes and then stored at −20 °C. Three biological replicates were set up for all experimental and control groups. Briefly, the A. flavus strains LNZW-1, JXZS-118-8, and GDZJ-15 were grown in conical flasks containing 50 ml Sabouraud’s Dextrose Broth with 5 × 105 conidia/mL and shaken (180 rpm) at 28 ± 1 °C for 12 h. And then, the suspension of four biocontrol bacteria strains (AAC, CB, JDF, JZ,) and their mixture (AAC + CB + JDF + JZ) was added to the above conical flasks to reach a final concentration of 107 CFU/mL and continued to culture for 36 h. At different incubation times (24 h, 30 h, and 36 h), the mycelia that were collected for the detection of PO8 by being filtered out of the liquid medium with sterile gauze and washed three times with sterilization water to separate mycelia from bacterial cells, and Sabouraud’s Dextrose Broth were collected into the sterile tubes and then stored at −20 °C for the detection of AFB1. Three biological replicates were set up for all experimental and control groups. Healthy postharvest mature peanut seeds were selected for the experiments to investigate the phenotypic data of the peanut matrices. All seeds were surface-sterilized by immersion in 70% ethanol for 1 min and rinsed with sterile distilled water three times for 1 min each, and then the moisture on the peanut surface was absorbed by sterilization filter paper. Two hundred microliters of the conidial suspension (5.0 × 105 CFU/mL) were added to the experimental and control plates, respectively. In the experimental group, 3 mL of bacterial suspension of the AAC, CB, JDF, JZ, and their mixture were added to the 10.0 g peanut seeds in a sterile Petri plate (ensure that the peanut surface is completely covered). In the control group, 3 mL of ultrapure water was added to the peanut seeds in sterile Petri plates. Then, the experimental and control group samples were placed in an incubator and cultured at 28 °C in darkness for 7 days. Three biological replicates were set up for all experimental and control groups. The four biocontrol bacteria strains screened out were mixed to produce biocontrol agents BBBE for use in field trials in 2021. Field trials were conducted at five sites, including Junan County (JN, Shandong Province), Zhengyang County (ZY, Henan Province), Siyang County (SY, Jiangsu Province), **angyang County (XY, Hubei Province), Fuzhou City (FZ, Fujian Province) in 2021. In experimental plots, biological bacteria fertilizer of 30 kg hm−2 was added with fertilizer material, the peanut variety was the main local variety, and the local conventional sowing method, as well as management measures, were adopted for weeding pest, and boom control. At the same time, the control plots were set. The method to isolate and identify A. flavus was conducted according to the method proposed by Zhang et al.37. In detail, using the five-point sampling method, 5 peanut plants were randomly selected within the range of 2 m2, and the peanut rhizosphere soil samples were collected, and they were mixed into one sample. A total of 10 samples including five control samples and five treatment samples were collected from each demonstration base. To prepare soil suspensions, 10.0 g soil samples were added to conical flasks containing 90 mL of sterile water on the ultra-clean workbench, and mixed them thoroughly by shaking at 28 °C (200 rpm/min, 2 h). After that, 50 μL of soil suspension was transferred to the sterile plates with DG-18 solid medium and spread evenly using a glass spreader. And these plates were placed in an incubator at 28 °C in darkness. The colonies were observed and counted regularly, and the hyphae were identified by morphological and molecular biology methods. The plates that were contaminated were cleaned up in time to avoid cross-contamination. The number of aflatoxin-producing A. flavus colonies per gram of soil was calculated by the following formula: Where N is the colony count of the plates, V1 is the volume of injection, m is the mass of the sample, and V is the volume of the soil suspension. The method of PO8 extraction differs in different samples. The extraction of PO8 in mycelia was as follows: 10 mg mycelium was added into 2 ml tubes, 500 μL of 1 × PBS (0.01 mol/L) buffer, and four steel balls (3 mm in diameter) were added, grounded at 60 Hz for 30 s in beveller, 12,000 rpm, centrifuged for 10 min, and then the supernatant was filtered with a membrane of 0.22 μm (pore size), and stored at −20 °C for further use. In the peanut inoculation experiment, the PO8 was extracted according to the following protocol: 2.5 g peanut was added into 50 ml tubes, 10 mL of 1 × PBS buffer, and four steel balls (65 mm in diameter) were added, grounded at 2500 rpm for 10 min, 4500 rpm, centrifuged for 10 min, and then the supernatant was filtered with a membrane of 0.22 μm (pore size), and stored at −20 °C for further use. PO8 quantification was conducted by the method proposed by Wang et al. (2017) with modifications20. Sandwich ELISA was developed to quantify PO8 according to the following protocol: 96-well microtiter plates (Corning, NY, USA) were coated with 200 μL/well of capture antibody (PO8-VHH Nano-antibody) in 1 × PBS buffer at a concentration of 3 μg/mL and incubated at 4 °C overnight. Plates were rinsed six times with 350 μL/well of 1 × PBST (1 × PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20), subsequently blocked with 300 μL/well of 3% skimmed milk in 1 × PBST buffer at 37 °C for 2 h. After nine items of washings with 1 × PBST, 200 μL of serially diluted mycelia were added at 37 °C for 1 h; washing cycles were repeated and 200 μL of rabbit polyclonal antibody at a concentration of 2 μg/mL in 1 × PBS was added and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h; after washing, 200 μL HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (Solarbio, Bei**g, China, 1:5000 dilution) was incubated at 37 °C for 1 h; after nine times washing, 100 μL of TMB solution were incubated at 37 °C for 10 min; the reaction was then terminated by adding 50 μL of 2 M H2SO4 and the absorbance values were detected at 450 nm using the CMax Plus microplate reader (Molecular Devices, CA, USA). The relative reduction of PO8 was calculated by the following formula: Where CPO8 is the concentration of PO8 in control groups, EPO8 is the concentration of PO8 in experimental groups. AFB1 extraction was conducted as follows: Briefly, aflatoxins B1 in mycelium or peanuts were extracted using 80% Methanol: water = 80:20, the supernatant was purified using a vacuum filtration system with a 25 mm membrane filter (0.22 μm pore size). Quantitative analysis of aflatoxins was performed by Agilent 1100 HPLC, equipped with a fluorescence detector (FLD), and Romer Derivatisation Unit was used in the system. The HPLC conditions were as follows: chromatographic column: Waters Symmetry C18 5 μm, 4.6 mm × 250 mm, (C18-A analytical column (15 cm × 4.6 mm × 5 μm); injection volume: 10 μl; column temperature: 30 °C; flow rate: 1.0 ml/min; mobile phase: methanol: water = 45:55 (volume ratio); and fluorescence detection wavelength: excitation wavelength 360 nm and emission wavelength 440 nm. One-way ANOVA was carried out to evaluate any significant difference in the control effect of biocontrol bacteria, using SPSS 26.0. The different letter means different significance levels (p < 0.05).Methods
Strains and culture conditions
The observation of the secretion regularity of PO8 at different times in high virulence-producing A. flavus strains
Screening of biocontrol bacterial strain based on PO8 inhibition
Peanut Inoculation experiment
Field trials
Determination of A. flavus abundance in peanut rhizosphere soil
Detection of PO8 by Sandwich-ELISA
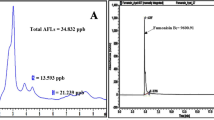
Detection of AFB1 by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Statistical analysis
Data availability
The raw data reported in this article were deposited in a public repository. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.23354255.
References
Huang, M. N. et al. Genome-scale mutational signatures of aflatoxin in cells, mice, and human tumors. Genome Res. 27, 1475–1486 (2017).
Chawanthayatham, S. et al. Mutational spectra of aflatoxin b1 in vivo establish biomarkers of exposure for human hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, E3101–E3109 (2017).
Jallow, A., **e, H., Tang, X., Zhang, Q. & Li, P. Worldwide aflatoxin contamination of agricultural products and foods: from occurrence to control. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 20, 2332–2381 (2021).
**e, H. et al. Fungi population metabolomics and molecular network study reveal novel biomarkers for early detection of aflatoxigenic Aspergillus Species. J. Hazard Mater. 15, 127173 (2022).
Gao, X. et al. Aflatoxin contamination of corn samples collected from six regions of China. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 40, 46–49 (2011).
Moretti, A., Pascale, M. & Logrieco, A. F. Mycotoxin risks under a climate change scenario in Europe. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 84, 38–40 (2019).
Lee, H. J. & Ryu, D. Worldwide occurrence of mycotoxins in cereals and cereal-derived food products: public health perspectives of their co-occurrence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65, 7034–7051 (2017).
Hell, K. & Mutegi, C. Aflatoxin control and prevention strategies in key crops of sub-saharan africa. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 5, 459–466 (2011).
Ren, X., Zhang, Q., Zhang, W., Mao, J. & Li, P. Control of aflatoxigenic molds by antagonistic microorganisms: inhibitory behaviors, bioactive compounds, related mechanisms, and influencing factors. Toxins 12, 24 (2020).
Hassan, Z. U., Thani, R. A., Alnaimi, H., Migheli, Q. & Jaoua, S. Investigation and application of bacillus licheniformis volatile compounds for the biological control of toxigenic aspergillus and Penicillium spp. ACS Omega 4, 17186–17193 (2019).
Afsharmanesh, H., Perez-Garcia, A., Zeriouh, H., Ahmadzadeh, M. & Romero, D. Aflatoxin degradation by bacillus subtilis utb1 is based on production of an oxidoreductase involved in bacilysin biosynthesis. Food Control 94, 48–55 (2018).
Higazy, N. S. et al. Investigation and application of bacillus pumilus qbp344-3 in the control of aspergillus carbonarius and ochratoxin a contamination. Food Control 119, 107464 (2021).
Liu, K. et al. Antimicrobial Bacillus velezensis HC6: production of three kinds of lipopeptides and biocontrol potential in maize. J. Appl. Microbiol. 128, 242–254 (2019).
Raksha Rao, K., Vipin, A. V., Hariprasad, P., Anu Appaiah, K. A. & Venkateswaran, G. Biological detoxifcation of aflatoxin b1 by Bacillus Licheniformis CFR1. Food Control 71, 234–241 (2017).
Shang, L. et al. Isolation and identification of a bacillus megaterium strain with ochratoxin a removal ability and antifungal activity. Food Control 106, 106743 (2019).
Siahmoshteh, F. et al. Efficacy of Bacillus Subtilis and Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens in the control of aspergillus parasiticus growth and aflatoxins production on pistachio. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 254, 47–53 (2017).
Atehnkeng, J., Ojiambo, P. S., Cotty, P. J. & Bandyopadhyay, R. Field efficacy of a mixture of a toxigenic Aspergillus flavus link: fr vegetative compatibility groups in preventing aflatoxin contamination in maize (Zea mays L.). Biol. Control. 72, 62–70 (2014).
Liang, M. et al. A versatile nano zyme integrated colorimetric and photothermal lateral flow immunoassay for highly sensitive and reliable Aspergillus flavus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 213, 114435 (2022).
Yan, H. et al. Sensitivity enhancement of paper-based sandwich immunosensor via nanobody immobilization instead of IgG antibody, taking aflatoxigenic fungi as an analyte example. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 373, 132760 (2022).
Wang, T. et al. Determination of Aspergillus pathogens in agricultural products by a specific nanobody-polyclonal antibody sandwich ELISA. Sci. Rep. 7, 4348 (2017).
Gomaa, E. Z. Chitinase production by bacillus thuringiensis and bacillus licheniformis: their potential in antifungal biocontrol. J. Microbiol. 50, 103–111 (2012).
Idris, H. A., Labuschagne, N. & Korsten, L. Suppression of pythium ultimum root rot of sorghum by rhizobacterial isolates from Ethiopia and South Africa. Biol. Contr. 45, 72–84 (2008).
Ghazanchyan, N. L., Kinosyan, M. H., Tadevosyan, P. E., Khachaturyan, N. S. & Afrikian, E. G. Brevibacillus Laterosporus as perspective source of new bioinsecticides. Ann. Agrarian Sci. 16, 413–415 (2018).
Li, C. et al. Biocontrol of potato common scab by brevibacillus laterosporus bl12 is related to the reduction of pathogen and changes in soil bacterial community. Biol. Control 153, 104496 (2021).
Zhang, Y., Cai, Y., Wang, C., Zeng, Q. & Pan, X. Effect of Bacillus Mucilaginosus fertilizer on growth and nutrients absorption of two tobacco seedlings in seedbed. Chinese J. Soil Ence. 48, 100–110 (2015).
Li, X. et al. Growth promoting effect of a transgenic Bacillus mucilaginosus on tobacco planting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74, 1120–112 (2007).
Dai, J., Yang, Y., Dong, Y. & **u, Z. Solid-state co-cultivation of bacillus subtilis, bacillus mucilaginosus, and paecilomyces lilacinus using tobacco waste residue. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 190, 1092–1105 (2020).
Einloft, T. C., Oliveira, P., Radunz, L. L. & Dionello, R. G. Biocontrol capabilities of three bacillus isolates towards aflatoxin b1 producer aspergillus flavus in vitro and on maize grains. Food Control 125, 107978 (2021).
Li, P., Yao Y., Ding, X., Zhang, Q. & Zhang, W. Enterobacter Ludwig BG10-1 and its application in the biological control of Aspergillus Flavus. CN201610155898.9.
Ongena, M. & Jacques, P. Bacillus Lipopeptides: Versatile Weapons for Plant Disease Biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 16, 115–125 (2008).
Penha, R. O., Vandenberghe, L. P. S., Faulds, C., Soccol, V. T. & Soccol, C. R. Bacillus Lipopeptides as powerful pest control agents for a more sustainable and healthy agriculture: recent studies and innovations. Planta 251, 70 (2020).
P´erez-García, A., Romero, D. & Vicente, A. Plant protection and growth stimulation by microorganisms: biotechnological applications of bacilli in agriculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 22, 187–193 (2011).
Bluma, R. V. & Etcheverry, M. G. Influence of bacillus spp. isolated from maize agroecosystem on growth and aflatoxin b1 production by Aspergillus Section Flavi. Pest Manag. Sci. 62, 242–251 (2006).
Etcheverry, M. G. et al. Biological interactions to select biocontrol agents against toxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus and fusarium verticillioides from maize. Mycopathologia 167, 287–295 (2009).
Yang, X. Screening the Biocontrol Bacterium against Aspergillus Flavus and identification the antibacterial lipopeptide of biocontrol strain. Master Dissertation, Nan**g Agriculture University, Nan**g, JS (2016).
Zhang, Q., Yue, X., Bai, Y. & Li, P. One-Step and efficient screening method for aflatoxin prevention and control bacteria. CN20211065377.4
Zhang, X. et al. Distribution and aflatoxin contamination by Aspergillus Flavus in peanut from the southwest China. Oil Crop Sci. 41, 773–780 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the key project of the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (32030085), a Major project of Hubei Hongshan Laboratory (2021hszd015), the Key Research and Development Projects in Hubei Province (2021BBA227), and the Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan-Shuguang Project (3570).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea was initiated and designed experiments by Q.Z., M.G., who conducted experiments and analyzed the data, and prepared the initial draft and final version. J.F. and H.Y. guided the data analysis, and X.Y. contributed materials. S.Z. guided field experiments. Q.Z. and P.L. proofread and edited the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M., Fu, J., Yan, H. et al. Approach for quick exploration of highly effective broad-spectrum biocontrol strains based on PO8 protein inhibition. npj Sci Food 7, 45 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-023-00210-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-023-00210-5
- Springer Nature Limited